Contact: +91 99725 24322 |
Menu
Menu
Quick summary: Delve into the world of circular agriculture with our knowledgeable expert. Discover the strategies and benefits of resource efficiency, waste reduction, increased resilience, and sustainable farming practices. Join us on the path to a greener future.

Imagine a world where every resource is used thoughtfully, every bit of waste finds a purpose, and farming not only feeds us but also nurtures the planet. Sounds ideal, right? This vision is at the heart of circular agriculture, a model that’s gaining global traction.
Now, think about conventional agriculture: it often takes more than it gives back. Overuse of water, excessive reliance on chemical inputs, and massive amounts of waste harm our environment and threaten food security. Add the looming challenges of climate change, and it’s clear that our current systems are unsustainable.
So, what’s the solution? Circular agriculture. By mimicking natural systems, it reduces waste, regenerates ecosystems, and creates a closed-loop system where resources are continually reused. In this blog, we’ll explore the five principles that can help agribusinesses adopt circular agriculture and take a step toward sustainable food production.
Key Takeaways
Circular agriculture is a sustainable farming system designed to minimize waste, maximize resource efficiency, and create a regenerative cycle of production. By mimicking natural ecosystems, it ensures that resources like water, nutrients, and energy are continually reused within the agricultural system. The goal is to transition from the traditional linear model of “take, make, dispose” to a circular model that closes the loop, reducing environmental impact while maintaining productivity and profitability. This approach aligns with the principles of the circular economy, which seeks to decouple economic growth from resource consumption by prioritizing reuse, recycling, and regeneration across industries.
Reducing resource input is at the heart of circular agriculture. It’s about doing more with less by using advanced methods to conserve resources like water, energy, and nutrients. This doesn’t just protect the environment—it also cuts costs for farmers and agribusinesses.
For instance, precision agriculture uses technologies like GPS and sensors to apply water and fertilizers exactly where and when they’re needed. Instead of blanketing an entire field, resources are delivered in precise amounts to targeted areas. This reduces wastage, improves crop yields, and protects nearby ecosystems from runoff.
Another example is adopting renewable energy solutions such as solar panels or biogas plants on farms. These solutions reduce reliance on fossil fuels, lower greenhouse gas emissions, and even generate extra income when excess energy is sold back to the grid.
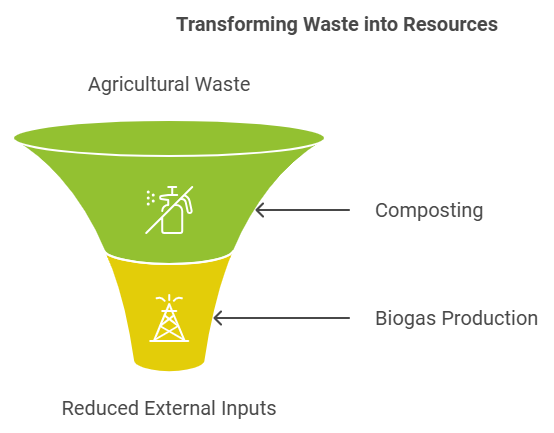
In traditional agriculture, nutrients from the soil are often depleted without being replenished, leading to declining soil fertility. At the same time, organic waste from farms and food processing goes unused, adding to environmental pollution. Circular agriculture offers a solution by recycling nutrients back into the system, mimicking natural ecosystems where nothing goes to waste.
Key Practices:
Example:
Imagine a vegetable farm using compost made from leftover produce and crop residues. By doing this, the farm reduces its dependency on chemical fertilizers, enhances soil health, and minimizes the amount of organic waste sent to landfills. For example, many coffee plantations use the pulp of coffee cherries, once considered waste, as compost to enrich the soil.
In conventional farming systems, waste is often treated as just that—something to discard. However, circular agriculture encourages a mindset shift, transforming agricultural by-products and food waste into valuable resources. This approach reduces the amount of waste sent to landfills while creating opportunities to generate new revenue streams and enhance farm profitability. Effective waste management in circular agriculture transforms by-products and residues into valuable resources, reducing landfill impact while supporting sustainability and economic growth.
Key Practices:
Example:
Consider a wheat farm where straw from harvested crops is used to create biogas, which powers the farm’s machinery. Meanwhile, some of the straw is also processed into animal feed for nearby livestock farms, reducing waste and improving the farm’s sustainability.
One of the key principles of circular agriculture is to actively work on regenerating natural ecosystems. Instead of depleting the environment, circular agriculture focuses on restoring the health of the soil, improving water quality, and increasing biodiversity to create more resilient and sustainable farming systems. The idea is to make farming not just sustainable, but regenerative—helping to restore the earth for future generations.
Key Practices:
Example:
In a coffee farm, farmers may implement agroforestry by planting shade trees alongside coffee plants, which improves soil quality and biodiversity. Meanwhile, they could use cover crops like legumes to naturally enhance soil fertility, reducing the need for chemical fertilizers. Additionally, the farm could adopt IPM practices, introducing beneficial insects that control pest populations, keeping the ecosystem in balance.
A core principle of circular agriculture is to foster collaboration across the entire supply chain. This involves building strong partnerships among farmers, food processors, retailers, and even consumers to collectively implement circular strategies. Rather than working in silos, these stakeholders can share knowledge, resources, and innovations to reduce waste, improve resource use, and create a sustainable food system. It’s about understanding that every link in the supply chain has a role to play in sustainability, and by working together, the benefits multiply.
Key Practices:
Example:
An example of successful collaboration could be seen in a farm-to-table initiative where farmers, local food processors, and retailers collaborate to reduce waste. Farmers could sell their surplus directly to processors who can use the leftover parts (e.g., skin, pulp) for different food products. Retailers then help promote these items to consumers with messaging around waste reduction, creating a more sustainable consumption cycle.
Technology solutions like blockchain traceability systems can address many of the challenges in circular agriculture by providing transparency, efficiency, and accountability across the supply chain.
Blockchain enables real-time tracking of resources like water, energy, and fertilizers used in agriculture. It ensures that these inputs are monitored and optimized, addressing the challenge of reducing resource inputs. By capturing data on how and where resources are used, agribusinesses can make informed decisions about reducing waste and minimizing resource consumption. Precision agriculture technologies powered by blockchain can help farmers understand exactly how much water or energy they are using and adjust their practices accordingly.
Example: With blockchain, a farmer can track the precise water usage for each crop, making it easier to adopt water-saving strategies, such as drip irrigation or rainwater harvesting.
A climate consultancy partnered with TraceX to assess and quantify the water and energy benefits of adopting natural farming practices. By leveraging TraceX’s blockchain-based platform, the consultancy gathered accurate, real-time data to validate the environmental advantages of sustainable agricultural methods. This collaboration not only supported evidence-based decision-making but also provided the consultancy with robust insights to advocate for the transition to more sustainable farming systems.
Blockchain can help manage the flow of organic waste and by-products within the agricultural system by tracking the journey of compost, manure, and waste-to-fertilizer products. This helps create a circular loop by ensuring that nutrients are recycled efficiently and not lost in the waste stream. With transparent tracking, companies can ensure that fertilizers are sourced from sustainable methods, such as composting or converting agricultural waste into bio-based fertilizers.
Example: A compost supplier can use blockchain to certify that their products are made from food waste, and consumers can trace these products back to the source, ensuring that waste is being repurposed sustainably.
Blockchain enables the efficient repurposing of waste by tracking agricultural by-products and ensuring they are directed to the appropriate uses, such as bioenergy or animal feed. The system provides a secure and transparent way to monitor where waste materials are going, ensuring that they are not ending up in landfills and are being used to generate value.
Example: Crop residues can be tracked via blockchain from the farm to the biogas plant where they are converted into energy. Blockchain ensures accountability, making the process transparent and efficient.
Blockchain can facilitate the monitoring of sustainable practices such as agroforestry, cover cropping, and integrated pest management. By recording the adoption of these practices in a transparent and immutable ledger, it helps agribusinesses demonstrate their commitment to regenerating ecosystems and improving biodiversity. Additionally, stakeholders across the supply chain—like food processors and retailers—can verify that sustainability practices are being adhered to.
Example: If a farm is implementing cover cropping to regenerate soil health, blockchain can track the practice and provide certification to downstream partners like retailers, ensuring that they meet sustainability criteria.
One of the major barriers to circular agriculture is the fragmentation of the supply chain. Blockchain bridges this gap by creating a shared, decentralized platform where every stakeholder—from farmers to food processors to retailers—can access the same data. This fosters trust and collaboration across the supply chain, making it easier to implement circular agriculture strategies collectively.
Example: A food processor working with multiple farms can use blockchain to verify that the farms are adhering to circular principles, such as reducing waste or using organic inputs. By collaborating on a shared platform, both parties can work together to optimize the supply chain.
Blockchain systems offer transparent and tamper-proof records that can help agribusinesses comply with evolving regulations around sustainability. For instance, the European Union’s EU Deforestation Regulation (EUDR) requires companies to prove that their supply chains are free of deforestation-linked commodities. Blockchain can track the journey of commodities like palm oil, soy, and cocoa, from farm to fork, ensuring compliance and reducing the risk of regulatory violations.
Example: A cocoa supplier using blockchain can provide proof that their product has not contributed to deforestation, fulfilling compliance requirements for EUDR or other regulations like FSMA FTL.
A Nigerian firm partnered with TraceX to achieve full cocoa supply chain traceability, enhancing data accuracy and ensuring compliance with the EU Deforestation Regulation (EUDR). This initiative improved operational efficiency and reinforced the firm’s commitment to quality and sustainable sourcing, aligning its practices with global standards.
Consumers increasingly demand transparency regarding the environmental and ethical practices behind the products they buy. Blockchain technology can verify and showcase how agricultural products are grown, processed, and distributed sustainably. This helps businesses justify their efforts in adopting circular practices, which can enhance their market appeal and customer loyalty.
Example: A consumer buying a sustainable coffee product can scan a QR code that links to a blockchain record showing how the coffee was grown, processed, and transported sustainably, providing proof of the brand’s commitment to circular agriculture.
Blockchain’s efficiency and automation can help agribusinesses scale circular agriculture practices across large operations. By automating the tracking of inputs, waste, and outputs in real time, blockchain systems can ensure that even large supply chains are transparent, accountable, and efficient.
Example: A multinational agribusiness can use blockchain to track the sustainability efforts of its operations across multiple countries, ensuring consistency in circular agriculture practices and scaling up initiatives effectively.
The TraceX traceability and sustainability platform empowers circular agriculture by enabling real-time tracking and data-driven insights across the agricultural value chain. Its blockchain-powered system ensures transparency and accountability, allowing businesses to trace products from farm to fork while minimizing waste and inefficiencies. By integrating solutions for nutrient recycling, waste repurposing, and resource optimization, the platform helps agribusinesses align with circular principles. Additionally, its sustainability features monitor key indicators like soil health, biodiversity, and carbon footprint, fostering regenerative practices and closed-loop systems. This comprehensive approach supports a transition toward sustainable food systems, improving resilience and creating shared value.
Circular agriculture is more than a concept—it’s a roadmap to sustainable agribusiness. By adopting its principles—reducing resource input, closing nutrient loops, repurposing waste, regenerating ecosystems, and fostering collaboration—businesses can unlock long-term resilience and profitability while mitigating environmental impact. Transitioning may come with challenges, but the integration of technology and a shared vision for sustainability can turn circular agriculture into a thriving reality for all stakeholders.
Circular agriculture emphasizes resource efficiency, waste reduction, and regenerative practices, unlike traditional farming, which often relies on linear models that deplete resources and generate waste.
Technology solutions like blockchain-based traceability systems help monitor resources, enhance transparency, and enable nutrient recycling and waste repurposing within agricultural systems.
Yes, circular agriculture is scalable. Practices like composting, agroforestry, and collaborative networks can be implemented by smallholders, with technology making it easier to integrate sustainable methods affordably.
