Contact: +91 99725 24322 |
Menu
Menu
Quick summary: Discover the world of sustainability frameworks and standards in our latest blog. Learn how these guidelines provide a strategic approach to addressing environmental, social, and economic challenges. Explore how TraceX's sustainability and carbon management solutions can help your business excel in this dynamic landscape.

Companies across industries are under increasing pressure to meet sustainability goals, but navigating the various frameworks and standards can feel like wading through a sea of jargon and regulations. Sustainability frameworks and standards are set rules and specifications that offer a planned strategy for tackling environmental, social, and economic problems sustainably. They act as a point of reference for businesses looking to evaluate and enhance their sustainability performance
According to a KPMG survey of corporate responsibility reporting, more than 90% of the world’s largest companies report on their sustainability performance through various frameworks and standards.
From climate action to ethical labor practices, the path to sustainability is multifaceted and can be overwhelming. But by aligning with the right frameworks, you can not only meet compliance requirements but also drive long-term value and credibility for your business. Let’s dive in!
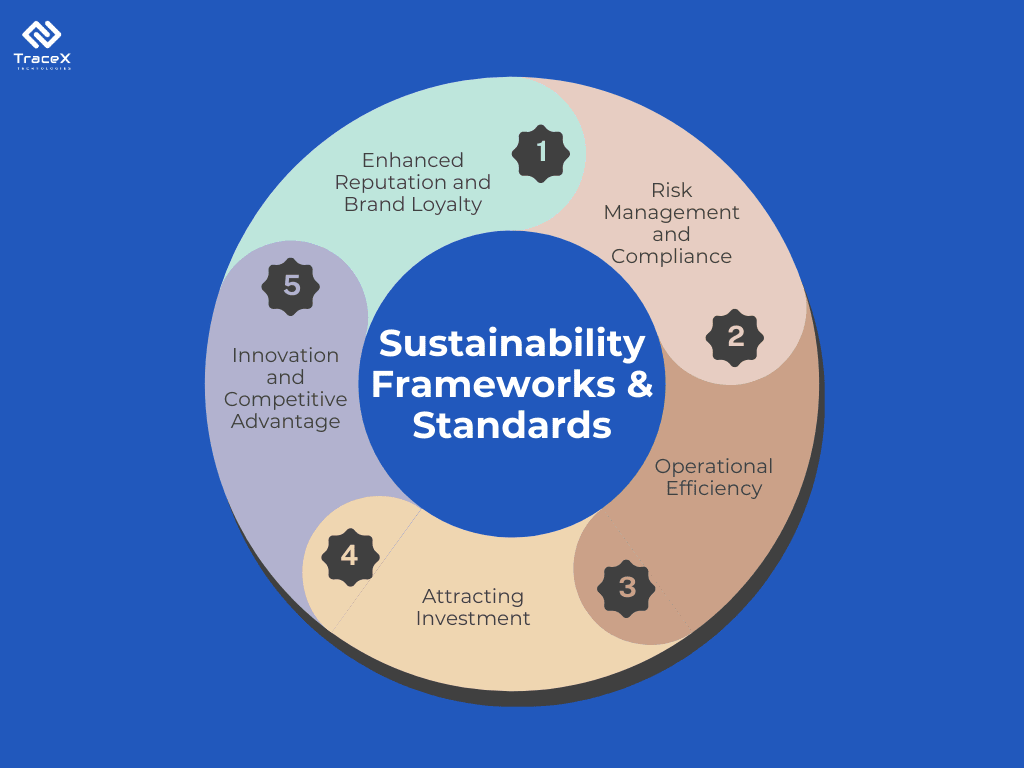
Key Takeaways
Frameworks and benchmarks for sustainability have been created to evaluate and advance sustainable practices across a range of industries. To assess and enhance environmental, social, and economic performance and ensure long-term viability and responsible resource management, they offer a common set of principles, criteria, and measurements.
Key considerations in assessing sustainability frameworks are as follows:
For reporting on sustainability, the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) is a commonly used framework. Organizations can use these rules and standards to reveal their consequences on the economy, environment, and society. The importance of GRI can be attributed to its thorough and broadly embraced methodology, which encourages reporting that is transparent and accountable. Organizations can use it to efficiently manage, evaluate, and share their sustainability performance with stakeholders. GRI reporting improves credibility, makes benchmarking easier, and aids in decision-making, ultimately promoting sustainable development and ethical business practices throughout the world.
The Global Reporting Initiative’s sustainability reporting system is supported by a set of principles known as the GRI reporting principles. Stakeholder inclusivity, materiality, sustainable context, completeness, accuracy, and comparability are some of these concepts. On the other hand, GRI indicators are particular measurements and data points that are used to assess and report on an organization’s performance in terms of sustainability, including economic, environmental, and social factors. With the aid of indicators, reporting may be standardized and streamlined, allowing for useful analysis and comparison of sustainability initiatives.

A group of 17 international goals known as the Sustainable Development Goals
(SDGs) were adopted by the United Nations to address social, economic, and environmental issues. The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) serve as a guide for sustainable development, with goals to end poverty, lessen inequality, safeguard the environment, and advance peace and prosperity for all. The SDGs serve as a comprehensive framework that directs governments, organizations, and people in aligning their actions and policies to create a future that is both more sustainable and equitable for people and the environment.
Here’s an overview of the 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and their relevance to different sectors:
Here are some examples of companies aligning their strategies with specific Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs):
To promote corporate environmental transparency, CDP (previously known as the Carbon Disclosure Project) focuses on monitoring and disclosing carbon emissions. It nudges businesses to disclose their greenhouse gas emissions, threats, and mitigation plans. By doing this, CDP hopes to promote sustainable practices across industries and raise awareness, accountability, and action about climate change.
By pressing businesses to publish their environmental data, including carbon emissions, CDP plays a critical role in promoting climate action and transparency. This information promotes accountability for a more sustainable future, encourages emission reductions, and helps investors, stakeholders, and governments make well-informed decisions.
There are many advantages to joining CDP and using their reporting platform. By showcasing a dedication to environmental transparency and sustainability, it improves a company’s reputation. It makes useful information, comparisons, and analyses of climate-related risks and possibilities available. It makes it easier to interact with stakeholders, customers, and investors who value environmental performance. Additionally, it enables businesses to enhance their total environmental performance and link their strategy with international climate goals.
The Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) is designed to enhance the transparency of corporate environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance across the EU. This directive mandates that companies disclose detailed information on their sustainability practices, encompassing everything from climate change impacts to human rights and governance. By expanding reporting requirements beyond financials, the CSRD aims to push businesses toward responsible and sustainable operations that align with the EU’s broader climate and sustainability goals.
Similar to other sustainability reporting standards, the CSRD encourages businesses to be more accountable for their environmental and social impacts. The directive is not just about meeting legal obligations—it helps businesses better manage ESG risks, attract investors, and improve stakeholder relationships. By providing consistent and comparable ESG data, companies can align their sustainability strategies with global goals like the Paris Agreement and the European Green Deal.
There are clear benefits to adhering to the CSRD. It helps businesses improve transparency, address climate-related risks, and create value for shareholders and customers. It also ensures companies remain competitive in the EU market, as non-compliance could lead to reputational risks and financial penalties. Moreover, by proactively disclosing sustainability data, businesses can demonstrate leadership in ESG and strengthen their relationships with investors focused on sustainable growth.
This shift to more robust sustainability reporting helps create a more level playing field, ensuring businesses are accountable for their long-term impact on the environment and society.
The Science-Based Targets Initiative (SBTi) is a globally recognized framework that empowers companies to set greenhouse gas emissions reduction targets aligned with climate science. It provides guidelines and resources to help businesses establish targets that are in line with the goal of limiting global warming to well below 2°C, as set by the Paris Agreement.
1. Credibility and Accountability: By committing to science-based targets, companies demonstrate transparency and accountability in their climate actions. This enhances their reputation among consumers, investors, and stakeholders who are increasingly prioritizing sustainability.
2. Strategic Planning: The SBTi framework helps businesses integrate sustainability into their core strategy. Setting science-based targets encourages companies to evaluate their operations, identify emissions hotspots, and implement effective mitigation measures.
3. Competitive Advantage: As consumers and investors increasingly demand sustainability, aligning with SBTi standards can differentiate companies in the marketplace. It provides a structured approach to sustainability that can enhance brand loyalty and open up new market opportunities.
4. Collaboration and Support: SBTi offers support for companies at various stages of their sustainability journey. From tools for target setting to a community of like-minded organizations, SBTi fosters collaboration and knowledge sharing to drive climate action collectively.
Incorporating the SBTi standard into your business strategy not only demonstrates a commitment to combating climate change but also helps create a resilient and sustainable future for your organization
Voluntary Sustainability Standards (VSS) are independent certifications that companies choose to adopt to ensure their products and processes meet sustainability and ethical sourcing criteria. Common VSS include certifications like Fairtrade, Rainforest Alliance, and the Roundtable on Sustainable Palm Oil (RSPO). These standards go beyond regulatory requirements, allowing businesses to showcase their commitment to sustainability and responsible sourcing, often appealing to conscious consumers.
Incorporating VSS into your business not only enhances environmental and social responsibility but also boosts brand credibility and opens doors to global markets, where sustainability is increasingly valued.
In short, while sustainability frameworks require meticulous tracking and reporting, a well-designed SaaS platform can take the heavy lifting off your shoulders, saving time, reducing errors, and ensuring you’re always in compliance.
A technology platform like TraceX can significantly simplify the adoption of sustainability frameworks by automating and optimizing complex processes.
1. Data Collection Automation: TraceX integrates with multiple data sources across the supply chain, automatically capturing key sustainability metrics such as carbon emissions, water usage, and energy consumption. This eliminates manual data entry, reduces errors, and provides real-time, accurate data that aligns with frameworks like CDP and GRI.
2. End-to-End Traceability: For businesses trying to track sustainability across global supply chains, TraceX ensures full traceability of raw materials from source to final product. This visibility is crucial for compliance with sustainability standards and helps verify the authenticity of deforestation-free or low-carbon claims, aligning with frameworks like the EU Deforestation Regulation (EUDR).
3. Simplified Reporting: Different frameworks require different reports, but TraceX’s platform simplifies this by providing built-in templates, automated calculations, and analytics tools. Whether it’s CDP disclosures or GRI reports, TraceX helps streamline the reporting process, ensuring businesses can comply without the complexity.
4. Stakeholder Engagement: Transparency is key for engaging customers, investors, and regulators. TraceX allows businesses to share verified data and sustainability credentials with stakeholders, building trust and ensuring clear communication of environmental performance.
The promotion of sustainable practices and openness across industries is made possible by sustainability frameworks and standards like the GRI and SASB. To help organizations measure, manage, and report on their impacts on the environment, society, and governance, they offer guidelines, principles, and indicators. Organizations can contribute to the global sustainable development goals by coordinating their strategy with the SDGs. Furthermore, accreditations like ISO 14001 support businesses in managing their environmental impacts and enhancing environmental performance. These frameworks and standards promote decision-making, accountability, and a more fair and sustainable future for all.
The most widely used sustainability frameworks include the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI), Carbon Disclosure Project (CDP), Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB), Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD), and the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
These frameworks guide businesses in measuring, managing, and reporting their environmental and social impact, improving transparency, and helping them meet regulatory and stakeholder expectations.
Choosing the right sustainability framework depends on factors such as industry, company size, regulatory requirements, and specific environmental or social goals the business aims to address.
