Contact: +91 99725 24322 |
Menu
Menu
Quick summary: Learn about the importance of crop monitoring in agriculture. Discover how modern technologies, like satellite monitoring and digital tools, can enhance yield, ensure soil health, and promote sustainable farming practices.

Crop monitoring in agriculture is transforming how farmers manage their fields, offering real-time insights into crop health and growth. With tools like satellite imagery, sensors, and data analytics, farmers can detect issues early and take timely action. But here’s the challenge: without proper monitoring, unexpected problems like pests, diseases, or drought can go unnoticed, leading to reduced yields and financial setbacks.
According to World Economic Forum, IoT technologies often used for crop monitoring can lead to a 20 to 30% reduction in water usage and 15 to 20% reduction in pesticide use.
Embracing modern crop monitoring not only helps in overcoming these hurdles but also supports sustainable practices, making farming more efficient and profitable.
Key Takeaways
Agriculture places a high priority on crop monitoring since it enables early detection of pests and diseases, optimises resource use, and promotes sustainable practices. Monitoring supports farmers in making informed decisions, increasing productivity, and minimising environmental impact, which results in improved economic outcomes and long-term agricultural sustainability. Monitoring provides essential information about crop health, growth, and environmental conditions.
Modern crop monitoring relies heavily on agriculture technology since it offers cutting-edge tools and methods for data gathering, analysis, and decision-making. Real-time monitoring of crop health, soil conditions, and weather patterns is now possible because of innovations like satellite imaging, drones, IoT sensors, and AI-powered analytics. Smart farming helps farmers practise precision agriculture, make the most use of their resources, and act quickly in case of emergencies, resulting in more output, lower expenses, and more environmentally friendly agricultural methods.
Powerful tools like remote sensing and satellite photography are used to gather important data about the Earth’s surface at a distance. Images and information about the state of the land, water, and atmosphere are captured by satellites with a variety of sensors. In agriculture, remote sensing and satellite imaging are used to check soil moisture levels, identify soil pests and diseases, and monitor crop health.
Field IoT (Internet of Things) devices are a network of networked things that have internet connectivity and sensors to gather and exchange data in real-time. IoT devices are used in agriculture to track a variety of characteristics, including crop health, soil moisture, temperature, and humidity. These tools give farmers remote access to vital information, the ability to make data-driven decisions, optimise resource use, and implement precision agriculture techniques, all of which contribute to higher production, lower costs, and more environmentally friendly farming methods in the long run.
Tools for data collection and analysis are crucial parts of contemporary agriculture because they make it possible to efficiently collect and interpret agricultural data. These tools cover a wide range of technology, such as drones, satellite imaging, IoT sensors, and AI-driven analytics. They let farmers keep an eye on things like crop health, soil quality, and weather trends. The analysed data is then used to adopt precision farming techniques, increase yields, decrease waste, and promote sustainable agricultural practises. It also helps to optimise resource allocation.
Continuous observation and study of air conditions and long-term climatic patterns are required for weather and climate monitoring. Satellites, weather stations, and other cutting-edge technology are used for this monitoring. Accurate weather and climatic information is essential for agriculture in order to plan planting, irrigation, and crop management. Farmers may boost crop yields and overall farm resilience by better preparing for extreme events, adapting to changing conditions, and maximising agricultural practices by knowing weather patterns and climate trends.
Continuous observation and study of air conditions and long-term climatic patterns are required for weather and climate monitoring. Satellites, weather stations, and other cutting-edge technology are used for this monitoring. Accurate weather and climatic information is essential for agriculture in order to plan planting, irrigation, and crop management. Farmers may boost crop yields and overall farm resilience by better preparing for extreme events, adapting to changing conditions, and maximising agricultural practises by knowing weather patterns and climate trends.
Improved yield prediction and planning in agriculture is achieved through the use of advanced technologies and data analytics.
By combining contemporary technologies and data-driven insights, farmers can make better decisions. Farmers may choose crops, plan planting dates, and use irrigation, fertiliser, and pest control techniques with the use of real-time data from IoT sensors, satellite imaging, and AI analytics. As a result, they are better able to adapt quickly to changing circumstances, allocate resources optimally, reduce risks, and increase overall farm production and profitability, resulting in more effective and sustainable agricultural practices.
The health and density of vegetation are evaluated and tracked using NDVI (Normalised Difference Vegetation Index) analysis, a remote sensing method. The NDVI calculates the difference in vegetation reflectance between near-infrared and visible red light, giving a numerical number that represents vegetative vigour. Low NDVI values signify stressed or sparse vegetation, while high values suggest healthy and thick vegetation.
In order to integrate GPS (Global Positioning System) and GIS – Geographic Information Systems in agriculture, location data from GPS must be combined with spatial data from GIS software. Farmers can produce intricate spatial visualization’s by using GPS technology to precisely track the location of farmed equipment, soil samples, or other data points and integrate them with GIS mapping.
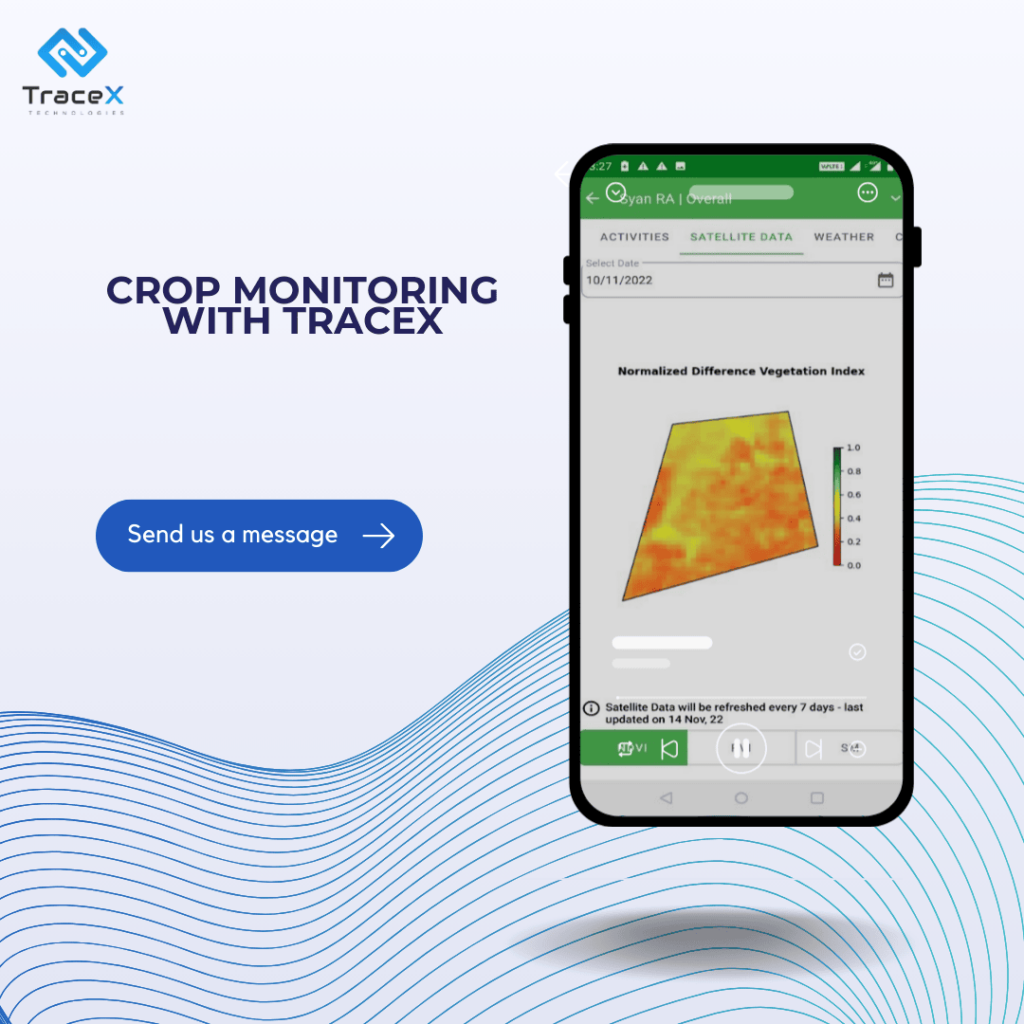
In an agribusiness’s land restoration project, crop monitoring for soil health was implemented using satellite monitoring by geo-mapping the farms. This process involved registering the farms for satellite observation, allowing for continuous assessment of critical soil parameters like NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index), soil moisture levels, and macro-nutrients. Regular satellite imagery and data analysis provided a clear picture of the soil’s health over time, enabling the agribusiness to track changes, address nutrient deficiencies, and optimize land restoration efforts with more precision and efficiency. This approach ensured that the land was restored effectively while supporting sustainable agricultural practices.
Unmanned aircraft systems called drones are used to collect data and high-resolution photos in the air. Drones are used for aerial imaging in agriculture to assess field conditions, monitor crop health, and spot possible problems like pest infestations or nutrient deficits. Farmers may execute targeted interventions, make educated decisions, and optimise agricultural practises for increased crop yields and resource efficiency thanks to the real-time and comprehensive data collected by drones.
Farmers now have the opportunity to remotely monitor and manage their fields through smartphones and tablets thanks to mobile apps made specifically for real-time monitoring in agriculture. These apps combine data from many sources, including satellite imaging, weather stations, and IoT sensors, to provide up-to-date information on crop health, soil moisture, and other factors.
The TraceX Farm Management Platform advocates for efficient crop monitoring by leveraging advanced digital tools that provide real-time insights into crop health and soil conditions. It enables farmers to track various parameters such as soil moisture, nutrient levels, and vegetation health through features like satellite monitoring and geo-mapping. These capabilities ensure that farmers can detect issues like nutrient deficiencies or pest infestations early, make data-driven decisions, and optimize their farming practices. This not only enhances yield but also supports sustainable and precision agriculture practices
In today’s world, effective crop monitoring is essential for sustainable agriculture. By leveraging advanced tools like satellite monitoring and digital platforms, farmers can gain real-time insights, optimize yields, and ensure the long-term health of their crops. Embracing such technology not only boosts productivity but also promotes sustainable practices that are crucial for future food security.
Crop monitoring helps farmers track crop growth, detect early signs of stress or disease, and optimize irrigation and fertilizer use, leading to higher yields and sustainable farming practices.
Satellite monitoring provides real-time data on soil moisture, vegetation health, and other key parameters. This allows farmers to make informed decisions about crop management, saving time and resources.
Yes, platforms like TraceX offer detailed insights into crop conditions through geo-mapping and data analytics, enabling better planning, monitoring, and decision-making for improved farm productivity.
