Contact: +91 99725 24322 |
Menu
Menu
Quick summary: Explore the benefits of biochar in agriculture, including its role in carbon sequestration, soil health improvement, and sustainable farming practices. Discover how this innovative solution can transform agricultural ecosystems and contribute to climate resilience.

In the face of rising soil degradation, water scarcity, and climate change, farmers are under pressure to find sustainable solutions that enhance soil health and boost crop yields. This challenge is pushing the agricultural sector to rethink traditional practices and adopt innovative approaches Biochar in agriculture promises to improve soil fertility and sequester carbon.
According to research conducted at IIT Delhi, biochar could sequester an average of 376.11 megatonnes of carbon dioxide equivalent carbon in the soil and could help India reduce 41 to 63% of emissions from agriculture and its allied activities.
Biochar a carbon-rich material derived from organic waste that holds the potential to revolutionize farming. Can biochar truly be the answer to sustainable agriculture’s toughest challenges? Let’s explore its potential and how it could transform the future of farming.
Biochar is a porous, carbon-rich material made by pyrolyzing organic material in a low-oxygen environment, such as agricultural waste or wood. Although hydrogen, oxygen, and other minor amounts of various mineral elements are present, carbon makes up the majority of it.
Early in the twenty-first century, this indigenous knowledge was rediscovered, rekindling interest in biochar as a long-term remedy for soil development and carbon sequestration, making it a crucial part of modern environmental and agricultural practices. Biochar can be produced from almost as many types of feedstocks as there are types of biomass including: agricultural wastes, rice husks, bagasse, paper products, animal manures, and even urban green waste
Because of its numerous advantages, biochar is crucial for sustainable agriculture. It promotes healthier plant development, improves nutrient and water retention in the soil, and lessens the need for chemical fertilizers. Additionally, biochar may clean up contaminated soils and sequester carbon, reducing climate change.
Heating organic material, such as biomass, without oxygen, is a process known as pyrolysis. It commonly happens between 300°C and 800°C (572°F and 1472°F) in temperature. Depending on variables like temperature and heating rate, the organic material undergoes decomposition during pyrolysis, producing products including biochar, bio-oil, and syngas.
Feedstock selection for pyrolysis can include various organic materials such as wood, agricultural waste, crop residues, and even municipal solid waste. The choice depends on factors like availability, desired end products, and local conditions.
Biochar production begins with the collection of biomass, which can encompass materials such as crop residues, wood chips, saw dust and even animal manure. These biomass sources are selected based on their suitability and availability for the pyrolysis process. Once gathered the biomass is subjected to drying to reduce moisture content and subsequently processed into smaller fragments.
The pyrolysis phase occurs in a specialized reactor or kiln. The biomass is subjected to a elevated temperature typically ranging from 400 to 700˚C within an oxygen deprived environment that initiates a complex chemical breakdown of organic matter. Initially, volatile compounds are released as gases which can be harnessed as a renewable energy source. As the temperature continues to rise, the residual solid material further decomposes and carbonizes, ultimately yielding biochar.
Enhancing soil fertility is making the soil better able to support strong plant development and maintain agricultural productivity. It entails a number of procedures, including the addition of organic matter (such as compost or biochar), nutrient level adjustments, pH optimisation, and soil erosion control.
The ability of soil to hold onto important nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium and make them available to plants is referred to as nutrient retention and availability in soil. By boosting cation exchange capacity and lowering nutrient leaching, organic amendments like biochar and compost improve nutrient retention.
(CEC) improvement refers to enhancing a soil’s ability to hold and exchange essential nutrients (cations) with plant roots. Practices like adding organic amendments such as biochar and compost increase CEC, making more nutrients available to plants for better growth and nutrient utilization.
It plays a vital role in mitigating climate change by reducing the concentration of CO2, a greenhouse gas responsible for global warming. Practices like reforestation
, afforestation, and the use of carbon-storing materials like biochar help sequester carbon, thus contributing to climate change mitigation.
By increasing soil’s porosity and aggregation, biochar enhances soil structure, which promotes water infiltration and retention. Controlling soil moisture lowers the possibility of drought stress on plants and enhances the general health of the soil.
Biochar can reduce soil-borne diseases by altering the soil’s microbial composition and structure, making it less hospitable to pathogens. This helps protect plants from infections and enhances overall soil health.
By boosting soil structure, increasing nutrient availability, and improving water retention, biochar increases crop output and quality. Increased yields and improved quality, including improved flavor, nutrition, and disease resistance, lead to healthier, more productive plants.
Utilizing mechanical methods like tilling or ploughs, incorporation entails incorporating biochar or other organic amendments into the top layer of the soil. By ensuring equitable dispersion, this method maximizes the advantages of increased soil structure, nutrient retention, and moisture control.
Plows, rototillers, or specialized incorporation machines are just a few examples of the tools and techniques that can be used to incorporate biochar into the soil. The benefits of biochar for soil health and plant growth are effectively integrated into the soil thanks to these techniques for blending it in evenly.
Considerations for biochar dosage in soil vary depending on the kind of soil, the type of crop, and the objectives. In general, lighter soils may only need a small amount of biochar—1–5% by weight—while heavier soils may benefit from higher doses of biochar—5–10%.
This enhances the compost’s capacity to hold onto nutrients, microbial activity, and general quality. When the composting process is finished, biochar can provide a beneficial soil amendment rich in organic matter by improving the compost’s capacity to retain nutrients and lowering nutrient loss.
Adding biochar to the composting process results in biochar-amended compost. This is commonly accomplished by combining decomposing organic resources like manure, yard trash, and kitchen scraps with charcoal.
Composting with biochar has various advantages for the health of the soil and plants. Compost’s overall quality is improved by the addition of biochar, which increases its capacity to store water and retain nutrients. This mixture improves nutrient availability, moisture control, and microbial activity when added to soil, which results in healthier plants and better soil structure.
Spreading biochar or other materials topically means doing so without first incorporating them into the soil. The soil can be covered with a layer of biochar as a mulch to retain moisture, manage weeds, and control soil temperature.
By creating a habitat for advantageous bacteria, biochar has the ability to affect the microbial populations in soil. Its porous design can operate as a haven for good bacteria and fungi. Biochar can also change the pH and chemical composition of the soil, which can impact the activity of microbial communities.
Due to its porous structure and enhanced habitat conditions, biochar encourages the growth of beneficial bacteria and mycorrhizal fungi in soil. This promotes their development and activity, which in turn improves nutrient uptake and leads to higher agricultural yields.
Particularly in acidic soils, biochar can affect soil pH by slightly raising it. It serves as a buffer, lowering the acidity of the soil to assist in maintaining a stable pH. However, the type of biochar and the initial pH of the solution affect how much of this action occurs.
A life cycle analysis (LCA) of the production of biochar evaluates the environmental impact of the product over the course of its full lifecycle, from the extraction of raw materials to disposal. The examination looks at things like emissions, resource utilization, and energy consumption. LCAs of biochar production frequently discover that it has benefits for carbon sequestration.
Local communities may benefit socially and economically from the production and usage of biochar. It can assist the local economy by generating jobs in manufacturing, distribution, and application. Additionally, increasing agricultural productivity and soil fertility can result in greater food security and farmer income, lowering poverty and promoting community well-being.
Ethical considerations regarding land use and biomass sourcing for biochar production include ensuring sustainable practices that don’t deplete natural resources, harm ecosystems, or displace local communities. Responsible land management, protection of biodiversity, and respect for indigenous rights are essential.
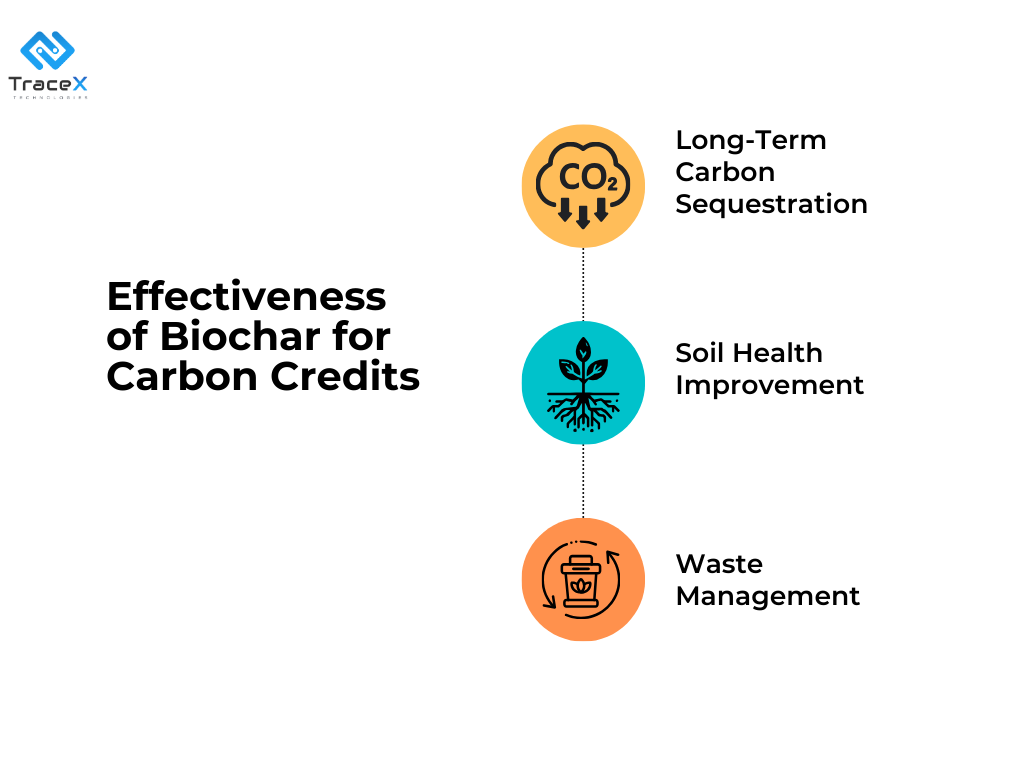
Biochar is increasingly recognized as a powerful carbon credit solution in the fight against climate change. Made by pyrolyzing organic waste at high temperatures in a low-oxygen environment, biochar serves as a stable form of carbon sequestration, locking carbon into the soil for hundreds to thousands of years. This characteristic makes biochar a valuable tool for offsetting carbon emissions and generating carbon credits.
Biochar projects can be verified and certified under carbon credit standards like the Verified Carbon Standard (VCS) or Gold Standard, which assess the amount of carbon dioxide sequestered during the pyrolysis process and over the biochar’s lifespan.
To generate carbon credits, biochar producers must track their production processes, quantify the carbon sequestered, and undergo third-party verification. These credits can then be sold to companies seeking to offset their emissions.
As companies and governments seek to meet net-zero targets and comply with regulations like the CSRD (Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive), the demand for high-quality carbon credits is growing. Biochar offers a tangible, measurable way to address this need.
By converting organic waste into a carbon-negative resource, biochar not only contributes to climate resilience but also supports regenerative agriculture practices. This makes it a crucial tool for businesses looking to reduce their carbon footprint, meet sustainability goals, and earn carbon credits in a competitive market.
Digital MRV Solutions are instrumental in streamlining the carbon credit verification process.
1. Real-Time Data Collection: DMRV solutions utilize advanced technologies such as IoT sensors, satellite imagery, and blockchain to collect data on carbon sequestration activities in real time. This continuous data flow enhances accuracy and transparency.
2. Automated Reporting: These solutions automate the reporting process, reducing the time and effort needed to compile verification reports. Automated systems can generate detailed, compliant reports that meet regulatory standards, ensuring that all necessary information is captured efficiently.
3. Increased Transparency: By utilizing blockchain technology, DMRV solutions provide an immutable record of all data related to carbon credit generation. This transparency builds trust among stakeholders, as it enables easy access to verified information.
4. Enhanced Accuracy: With precise data analytics and algorithms, DMRV solutions improve the accuracy of carbon estimates, reducing the risk of errors or fraud in carbon credit claims.
5. Scalability: These solutions can be scaled to monitor various projects simultaneously, making it easier for organizations to manage multiple carbon credit initiatives without increasing administrative burdens.
6. Cost-Effectiveness: By automating processes and improving efficiency, DMRV solutions can lower the overall costs associated with carbon credit verification, making it more accessible for companies and organizations.
TraceX’s Digital MRV (Monitoring, Reporting, and Verification) platform leverages advanced technologies like blockchain and satellite monitoring to enhance carbon credit verification and sustainability practices. By providing real-time data collection and automated reporting, TraceX ensures accurate tracking of carbon sequestration activities. This transparency not only builds trust among stakeholders but also streamlines compliance with regulatory standards. With a focus on scalability and cost-effectiveness, TraceX’s DMRV solution empowers organizations to efficiently manage their carbon projects and contribute to meaningful climate action.
Biochar represents a transformative opportunity in agriculture, merging carbon sequestration with soil health enhancement. As a sustainable solution, it not only addresses climate change by capturing carbon for the long term but also improves soil fertility and agricultural productivity. By adopting biochar practices, farmers can create resilient ecosystems, contribute to global sustainability efforts, and take significant steps toward a carbon-neutral future. Embracing biochar is not just a step forward for individual farms; it is a crucial part of the collective effort to combat climate change and promote responsible land management.
Biochar is a stable form of carbon produced through the pyrolysis of organic materials, such as agricultural waste, in a low-oxygen environment. This process converts biomass into a charcoal-like substance that can be used as a soil amendment.
Biochar enhances soil fertility by increasing nutrient retention, improving soil structure, and promoting beneficial microbial activity. It also aids in water retention, making crops more resilient to drought conditions.
Yes, biochar can be used as a carbon credit solution. By sequestering carbon for hundreds to thousands of years, biochar projects can generate verified carbon credits under various standards, helping businesses offset their emissions and achieve sustainability goals.
