Contact: +91 99725 24322 |
Menu
Menu
Quick summary: Explore the vital role of traceability in waste management. Learn how digitized solutions revolutionize waste tracking, enhance efficiency, and promote sustainability.
Today waste management and environmental sustainability has become very important, and traceability emerges as a powerful ally in our efforts towards achieving greater circularity. The ability to trace and record the movement and disposal of waste items over the course of their lifecycle is referred to as traceability in waste management.
According to World Bank, without urgent action, global waste will increase by 70% on current levels by 2050. Each human being creates an average of 500kg of waste per year and only 20% of global plastic waste is recycled.
In this blog, we delve into the realm of waste traceability and its pivotal role in enhancing circular economy practices, all while reducing waste’s negative consequences on our planet. This blog will discuss why capturing waste data is critical to circularity and sustainability.
The ability to systematically record and follow a product’s or material’s movement, origin, and change over the course of its lifecycle is referred to as traceability. It entails gathering information and data at numerous stages, including production, distribution, and disposal. The capacity to track items or materials back to their source promotes responsibility and trust across a variety of industries. Traceability is crucial for quality control, safety, regulatory compliance, and transparency in supply chains.
Traceability in waste management is keeping track of information on waste production, collection, transportation, treatment, and disposal. To ensure compliance with rules and track environmental impact, each step is documented. In the end, this information encourages ethical and sustainable waste management practises by assisting in the identification of inefficiencies, tracking hazardous trash, and improving transparency.
To ensure the precise tracking of products or materials throughout their lifecycle, a traceability system typically includes essential elements like data collection and recording methods, unique item identification or labelling, tracking technology (such as barcodes, RFID), a centralised database or software, and a standardised documentation and reporting process.
Common garbage collection, sorting, and disposal techniques like landfilling, burning, and recycling are part of current waste management practises. Advanced practises provide a strong emphasis on waste reduction, source separation, and advancing the circular economy through material reuse and recycling. Depending on local infrastructure, laws, and environmental considerations, these techniques differ globally.
Challenges to conventional garbage disposal include inadequate landfill area, greenhouse gas emissions from incineration and landfills, and incorrect disposal techniques. These techniques frequently don’t effectively use resources, promote waste reduction, or safeguard ecosystems, which adds to sustainability and health problems.
Due to the expanding global population, depleting natural resources, and environmental crises of pollution and climate change, there is an urgent need for more sustainable solutions. In order to ensure a healthier, more resilient environment for both the present and future generations, sustainable solutions attempt to lessen resource depletion and minimise environmental damage.
Traceability in waste management allows for tracking and documentation of the movement and disposal of waste materials. In order to ensure compliance with rules and encourage transparency, it requires tracking information about origin, transit, treatment, and final disposal. This data supports responsible waste management practises, identifies inefficiencies, and aids in monitoring environmental effect.
By facilitating the identification and tracking of materials within a closed-loop system, traceability plays a critical role in encouraging circularity.
It guarantees that resources may be successfully recovered, repurposed, or recycled, minimising waste and the demand for new raw materials. Traceability promotes sustainability, transparency, and advances the goals of the circular economy.
Due to its capacity to minimise greenhouse gas emissions, avoid pollution, and conserve resources, effective waste management is essential for environmental sustainability. Recycling and proper disposal help preserve water quality, reduce damage to ecosystems, and save energy. Sustainable waste management techniques also support a healthy environment for both the present and the next generation.
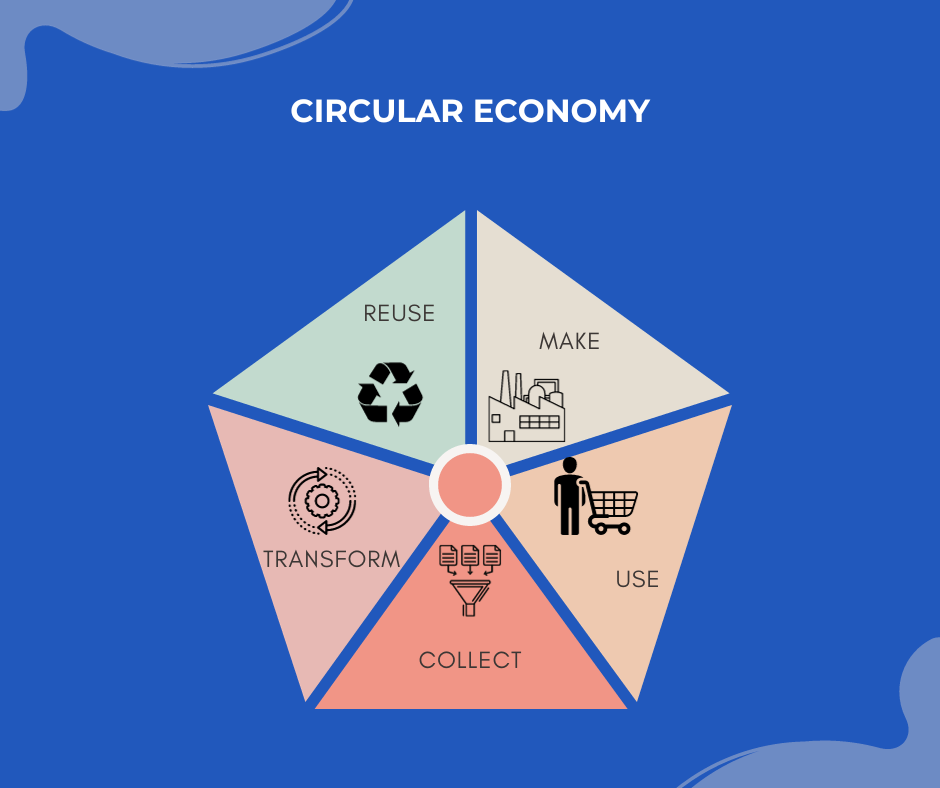
The concepts of the circular economy encourage the efficient use of resources while reducing waste. They include reusing materials, recycling things at the end of their useful lives, and engineering products to be durable and recyclable. These guidelines seek to lessen the negative effects on the environment, save resources, and establish a closed-loop system for a more sustainable economy.
By making it possible to track and manage materials throughout their lifecycles, traceability aids circularity. It aids in finding chances for materials and goods to be recycled, reused, or renovated, therefore minimising waste. In a circular economy, traceability is an essential tool for boosting resource efficiency and sustainability since it guarantees responsible disposal.
Circular waste management initiatives include:
1. Extended producer responsibility (EPR) programs, where manufacturers take responsibility for the end-of-life of their products.
2. Recycling and upcycling initiatives that turn waste materials into new products.
3. Composting organic waste into nutrient-rich soil.
4. Community swap events to exchange goods.
5. Repair and refurbishment programs to extend product lifespans. These efforts promote resource conservation and waste reduction.
Radio waves are used by the RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification) technology to wirelessly identify and track items. It is made up of data-transmitting RFID readers and tags with distinctive identification. RFID is utilised in a variety of industries to manage inventories, track assets, regulate access, and improve the efficiency and accuracy of the supply chain.
Using satellite signals, GPS (Global Positioning System) tracking identifies a person or an object’s exact location. Information pertaining to geographic features and locations is referred to as geospatial data. It is advantageous for industries like navigation, logistics, urban planning, and environmental monitoring to combine GPS tracking with GIS data since this enables real-time location monitoring, route planning, and spatial analysis.
Through the provision of transparent and unchangeable records of garbage transactions and disposal, blockchain technology can improve waste management. This can make it easier to track out the source of waste, guarantee legal compliance, and promote ethical behaviour. Blockchain-based smart contracts can automate payment and verification procedures, enhancing the ecosystem for waste management’s effectiveness and confidence.
The Internet of Things (IoT) involves attaching commonplace items to the web for remote monitoring and control. IoT applications include everything from industrial sensors that track the functioning of machinery to smart household gadgets like thermostats and security cameras. In a variety of industries, including healthcare, agriculture, and transportation, these technologies enhance efficiency, convenience, and data-driven decision-making.
Waste comes in various forms from solid to hazardous and they require separate handling processes which complicates the traceability process.
There is a lack of standardized systems and protocols for traceability in waste management which makes it difficult to adopt a universal approach.
Maintaining accurate data at every stage of waste management from collection to disposal is crucial and data entry errors or inaccuracies can undermine traceability efforts.
Since traceability involves tracking waste back to its source, it can raise privacy concerns for businesses.
Implementing traceability requires appropriate technology infrastructure.
Traceability systems can prove to be costly for smaller waste management systems.
Meeting the varying regulations and compliance standards related to waste management can be challenging.
Integrating traceability systems with existing waste management processes can be complex and time consuming.
Manufacturing companies can reap enormous advantages from implementing a digitized traceability solution. This technology offers automation and streamlining of material and product tracking and documentation, leading to enhanced efficiency, accuracy and data driven decision making.
Traceability software automates monitoring and documentation of materials and products, reducing the reliance on manual data entry and mitigating risk of errors.
Digital solutions also facilitate real-time tracking across the supply chain, providing visibility and enabling swift response to any issues. It also eases the collection, storage and analysis of large data sets related to materials, products and waste. This empowers informed decision making. The generation of reports ensures compliance with regulations governing the handling, storage and disposal of materials and products.
TraceX’s blockchain traceability solutions enhance transparency, accuracy and efficiency in waste management and circularity. They empower companies to make informed decisions, comply with regulations and contribute to a more sustainable and circular economy.
In conclusion, waste management is crucial to environmental sustainability and ethical resource management. It involves more than merely disposing of our waste. By embracing traceability, circular economy ideas, and cutting-edge technologies, we may reevaluate how we handle trash. We can minimise environmental effect, save resources, and build a more sustainable world for future generations by reducing, reusing, recycling, and appropriately managing garbage. To turn garbage into a useful resource, it takes a team effort on the part of people, companies, and governments.
