Contact: +91 99725 24322 |
Menu
Menu
Quick summary: Discover the essential insights into navigating the complex world of the Voluntary Carbon Market through a detailed exploration of Carbon Offset Standards. Uncover how these standards shape the future of carbon offsetting and their significance in achieving sustainability goals

In the quest to combat climate change and reduce carbon emissions, carbon offsetting has emerged as a valuable tool and carbon offset standards are the guiding principles and criteria that ensure the legitimacy and effectiveness of these offsets. They establish guidelines for the processes of project development, measuring emission reductions, and verification. Leading standards like the Verified Carbon Standard (VCS) and the Clean Development Mechanism (CDM) make sure that carbon offsets represent actual emissions reductions and assist to slow down climate change. By upholding accountability and openness in the offset market, these norms help stakeholders build credibility.
Understanding these standards is crucial for anyone looking to navigate the complex world of carbon offsetting and contribute to a more sustainable future. In this blog we delve into the realm of carbon offset standards, exploring what they are, why they matter and how they shape our collective efforts to address the climate crisis.
Through investments in initiatives that lower or capture an equivalent volume of carbon dioxide or other greenhouse gases from the atmosphere, carbon offsets allow one to make up for greenhouse gas emissions. These initiatives may involve planting new trees, producing green energy, or capturing landfill methane. By balancing their carbon footprints, carbon offsets enable people, organizations, and governments to take accountability for their emissions and support international efforts to mitigate climate change.
To lessen the consequences of climate change, carbon offsets are required. There are still some greenhouse gas emissions despite efforts to limit them. By funding initiatives that eliminate or reduce emissions in an equivalent amount elsewhere, carbon offsets offer a way to make up for these emissions. In the end, they assist in meeting global emissions reduction targets by assisting people and organizations in taking immediate action to prevent climate change while attempting to transition to a low-carbon future.
By allowing for a global reduction in greenhouse gas emissions, carbon offsets are essential for mitigating climate change. They make it easier to reduce emissions in industries like aviation and other industrial processes that are difficult to instantly decarbonize. A transition to a low-carbon economy and long-term climate resilience are further benefits of the sustainable practices that carbon offset programs frequently support, such as reforestation and renewable energy.
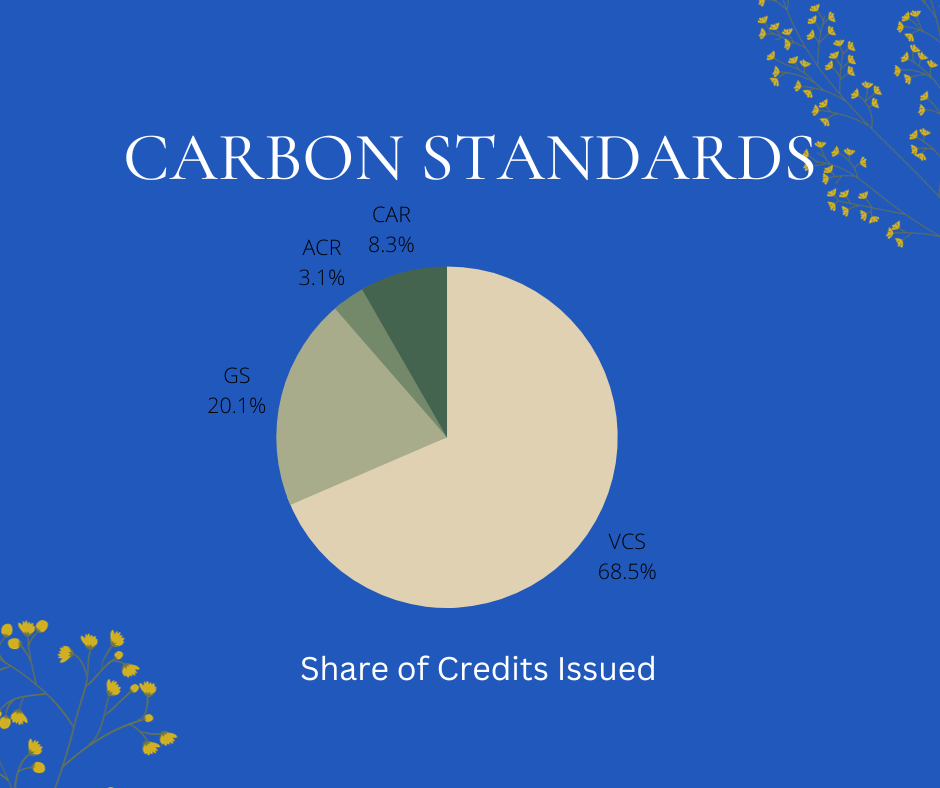
Credible emissions reduction projects can follow recommendations from reputable carbon offset standards such as the Verified Carbon Standard (VCS), Clean Development Mechanism (CDM), Gold Standard, and Puro.earth. The emphasis of VCS and CDM is on exact measurement and verification. Along with carbon reductions, the Gold Standard emphasizes sustainable development. The marketplace on Puro.earth, which connects consumers and sellers of carbon removal, is well-known. These guidelines are crucial in preserving the openness and reliability of the carbon offset markets and in advancing environmentally friendly actions.
Clear project procedures, rigorous emission reduction measurement and verification, additionality assessment, and sustainable development criteria are important characteristics and needs of carbon offset standards. Along with transparency in project documentation, registration, and issuance procedures, these requirements also call for the avoidance of duplicate counting of emissions reductions. To ensure continuous compliance and effectiveness in reaching emissions reduction goals, guidelines frequently call for third-party audits and yearly reviews.
The Verified Carbon Standard (VCS) stands as one of the most respected and widely recognized carbon offset standards globally. Established to ensure the quality and transparency of carbon offset projects, VCS meticulously evaluates and verifies projects that reduce or remove greenhouse gas emissions. By adhering to rigorous methodologies and criteria, VCS- certified projects guarantee that their emission reductions are real, additional, measurable and sustainable.
The Gold Standard stands as a widely esteemed carbon standard within the industry inaugurated in 2003 with the collaboration of WWF and other global NGOs, its core mission is to uphold the utmost environmental integrity and foster sustainable development through emission reduction projects. Rooted in the belief that addressing climate change necessitates a multifaceted approach, the God standard emphasizes that climate projects should extend beyond emission reductions. Alongside validating the tangible and quantifiable emissions reductions achieved by offset projects, Gold standard certification also demands verified contributions to various Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
American Carbon Registry standard lays out comprehensive guidelines and specifications governing the quantification, surveillance, reporting, validation, registration and issuance of project-based carbon credits derived from GHG emission reductions and removals.
This standard sets the benchmark for the requisite environmental and social integrity, as well as scientific precision, essential to establish ACR- registered as exemplars of the highest quality. These reductions are real, supplementary, enduring, free from leakage, conservatively assessed, independently verified by competent third parties, devoid of double counting and actively contributing to sustainable development.
The Climate Action Reserve operates as a nationwide offsets program with a primary objective of upholding the environmental soundness of greenhouse gas emissions reduction projects within the United States Carbon market. This mission encompasses the establishment of stringent and high caliber standards for quantification and validation of such projects, along with the supervision of independent third-party verification entities. These exacting standards not onle safeguard environmental integrity of offset utilization but also bring about trustworthiness and operational efficiencies within carbon markets.
There are various procedures involved in certifying carbon offset programs.
Depending on the standard used, there are different requirements and eligibility for carbon offset projects. Projects often need to show additionality, which means they reduce emissions beyond what would be expected from business as usual. They should comply with the specific requirements of the chosen standard, which may include sustainable development, environmental integrity, and transparency, and employ recognized methodology for measuring and verifying emissions reductions. Reforestation, renewable energy, methane capture, among other projects, might be considered eligible as long as it complies with the requirements of the selected standard.
The monitoring and verification of carbon offset initiatives is essential. Data is gathered continuously to track emission reductions and verify adherence to established requirements. Then, independent third-party auditors validate this information to ensure that the claimed emissions reductions are accurate, measurable, and realized. Through this procedure, carbon offset markets are kept transparent, credible, and honest, giving buyers the assurance that their purchases are actually helping to reduce emissions.
Standards for carbon offsets confront a number of difficulties.
For the sector, finding the ideal balance between strict standards and encouraging global carbon reductions is a constant issue.
TraceX’s DMRV solutions empower companies to align with carbon offset standards in the voluntary carbon market.
To sum up, carbon offset rules are essential to our efforts as a society to mitigate climate change. They offer the framework required to guarantee that carbon offset programs are reliable, open, and successful in lowering greenhouse gas emissions. The continuing development and adherence to these standards are crucial for fostering trust in the carbon offset markets and making significant strides towards a more sustainable and resilient future, despite the fact that problems still exist in this constantly changing industry. One of the most important issues of our day may be addressed by people, corporations, and governments working together to support initiatives that really decrease emissions and advance sustainability.
