Contact: +91 99725 24322 |
Menu
Menu
Quick summary: Unlock the significance of Forest Carbon Projects in the fight against climate change. Explore our blog to understand why these initiatives matter, how they contribute to carbon sequestration, and the broader impact on climate action. Delve into the vital role of forests and gain insights into the transformative potential of Forest Carbon Projects for a sustainable future.

In the face of escalating climate change concerns, forest carbon projects have emerged as powerful tools in the collective effort to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions and foster environmental sustainability. These projects harness the unique capacity of forests to sequester and store carbon, playing a pivotal role in both climate action and biodiversity conservation. As the world grapples with the urgent need to reduce carbon footprints, the focus on forest carbon projects has intensified, driven by a recognition of the vital role forests play in maintaining the delicate balance of our planet.
According to World Bank, Deforestation and forest degradation contribute about 12% of the world’s greenhouse gas emissions, but nature-based solutions, including forests, can provide up to 37% of the mitigation needed to keep the global temperature rise to below 2°C.
This blog delves into the realm of forest carbon projects, unraveling their significance, mechanisms, and the transformative impact they wield in the fight against climate change. Together, we will delve into the innovative strategies, challenges, and promising trends that characterize the evolving landscape of harnessing the carbon-capturing potential of our planet’s invaluable forests.
Forest carbon projects are initiatives aimed at mitigating climate change by preserving and restoring forests. These projects often involve activities such as afforestation, reforestation, and sustainable forest management to sequester carbon dioxide and enhance overall carbon stocks. The carbon credits generated through these projects contribute to global efforts to offset carbon emissions.
Conserving forests plays a crucial role in addressing carbon emissions, as forests act as carbon sinks, absorbing and storing large amounts of carbon dioxide. By preserving these vital ecosystems, forest carbon projects help mitigate climate change, promote biodiversity, and support sustainable development, underscoring the critical need to prioritize and invest in such initiatives.
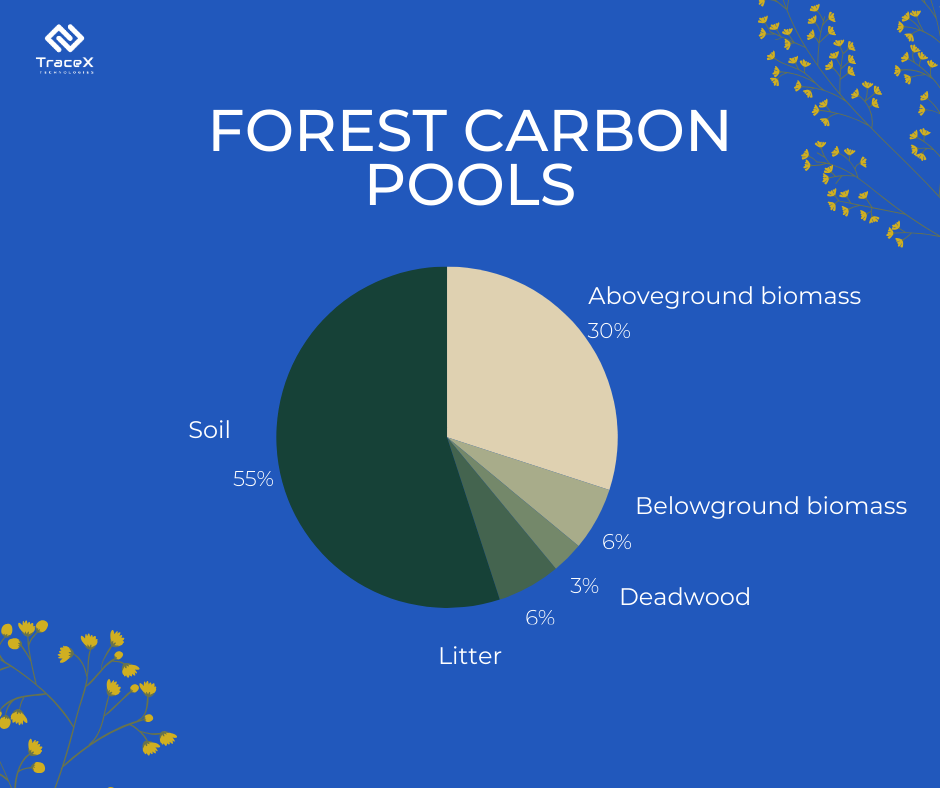
Forests play a pivotal role in the carbon cycle, acting as both sources and sinks of carbon dioxide (CO2). Through photosynthesis, trees absorb CO2, converting it into organic carbon and releasing oxygen. This process, coupled with carbon storage in biomass and soils, constitutes carbon sequestration. Forests, thus, act as essential carbon sinks, helping regulate atmospheric carbon levels and mitigate climate change.
Deforestation disrupts the carbon cycle by releasing stored carbon back into the atmosphere. When trees are cut down or burned, the stored carbon in biomass and soil is rapidly released as CO2, contributing significantly to greenhouse gas emissions. This process exacerbates climate change, emphasizing the critical role of forests in maintaining carbon balance and the urgency of curbing deforestation to mitigate carbon emissions.
Forest carbon projects are initiatives designed to mitigate climate change by enhancing carbon sequestration and reducing emissions within forest ecosystems. These projects often involve activities that either enhance the capacity of existing forests to sequester carbon or establish new forest areas. The primary goal is to generate carbon credits, which can be traded in carbon markets, contributing to global efforts to offset greenhouse gas emissions.
Reforestation: Planting trees in areas that were previously deforested.
Reforestation projects focus on replenishing areas that have suffered from deforestation, aiming to restore the ecological balance by planting trees. This not only enhances carbon sequestration but also contributes to biodiversity conservation and soil health.
Afforestation: Creating new forests in areas that were not previously forested.
Afforestation involves the establishment of entirely new forests in areas that were not previously forested. This proactive approach helps expand forest cover, creating additional carbon sinks, and provides diverse ecosystems that support various plant and animal species.
Avoided Deforestation: Preventing the clearing or degradation of existing forests.
Projects centered on avoided deforestation play a crucial role in preserving existing forests under threat of clearing or degradation. By preventing the loss of these carbon-rich ecosystems, these initiatives maintain their capacity to sequester carbon and uphold the biodiversity they harbor.
Improved Forest Management (IFM): Sustainable practices that enhance carbon storage and promote biodiversity within existing forests.
Improved Forest Management projects focus on optimizing the health and productivity of existing forests. Through sustainable practices, selective logging, and ecosystem restoration, IFM aims to strike a balance between human utilization of forest resources and the preservation of their vital ecological functions, including carbon sequestration.
Each project type addresses carbon sequestration and emission reduction in distinct ways, offering diverse approaches to combat climate change through responsible forest management.
By integrating environmental conservation with social development, forest carbon projects contribute to holistic and sustainable solutions that address climate change while supporting the well-being of local populations.
Certification programs such as REDD+ (Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Forest Degradation) and VCS (Verified Carbon Standard are frameworks that establish criteria for measuring, reporting, and verifying emissions reductions from forest carbon projects. REDD+ focuses on avoiding deforestation and degradation, while VCS provides a rigorous standard for ensuring the credibility of carbon credits generated by such projects. Adhering to these programs helps validate the environmental integrity and sustainability of forest carbon initiatives.
Adhering to international standards is crucial for ensuring transparency, accountability, and effectiveness in carbon sequestration efforts. Standardization provides a common language and set of criteria, allowing for consistent evaluation of projects globally. Compliance with recognized standards enhances the credibility of carbon credits, instills confidence in investors, and facilitates participation in international carbon markets. It ensures that forest carbon projects deliver meaningful environmental benefits, contribute to global climate goals, and adhere to best practices for sustainable forest management.
Addressing these challenges is critical for fostering trust in forest carbon projects and achieving their intended environmental and social benefits.
Corporations increasingly invest in forest carbon projects as part of their sustainability strategies. Motivations include mitigating climate risks, meeting carbon neutrality goals, and addressing stakeholder expectations. Participation in these projects allows companies to demonstrate environmental responsibility, enhance brand image, and contribute to global climate action. Additionally, access to verified carbon credits offers a tangible way for corporations to offset their carbon footprint.
Forest conservation aligns with broader sustainability goals by addressing environmental, social, and economic dimensions. Preserving forests supports biodiversity, mitigates climate change, and safeguards ecosystem services. Socially, it fosters community engagement, protects indigenous rights, and promotes sustainable development. Economically, it creates green employment opportunities and contributes to long-term ecological resilience. Integrating forest conservation into corporate sustainability goals exemplifies a holistic approach that recognizes the interconnectedness of environmental and social well-being, contributing to a more comprehensive and responsible business model.
Technology plays a pivotal role in monitoring and reporting the outcomes of forest carbon projects. MRV tools enable real-time monitoring of key parameters within forest ecosystems. This includes tracking changes in forest cover, assessing biodiversity levels, and measuring carbon sequestration rates. Accurate reporting is crucial for transparency and accountability. MRV tools help generate comprehensive reports on the progress and impact of forest carbon projects. Verification is an essential step to confirm that the reported data is accurate and reliable. MRV tools facilitate the verification process by providing detailed and verifiable data on carbon sequestration, changes in land use, and the overall health of the forest.
Advanced tools, such as satellite imagery, remote sensing, and data analytics, enable real-time tracking of project activities. These technologies enhance accuracy in measuring carbon sequestration, verifying emissions reductions, and ensuring transparency in project reporting. The data-driven insights provided by technology contribute to the credibility of forest carbon initiatives and support informed decision-making for project stakeholders.
Digital solutions like TraceX represent a groundbreaking innovation in forest carbon project monitoring. Leveraging blockchain and other digital technologies, TraceX provides a secure and transparent platform for tracking project activities, carbon credits, and the impact on deforestation. This digital solution enhances traceability, accountability, and stakeholder confidence by offering a verifiable record of the project’s environmental contributions, contributing to a more reliable and efficient monitoring system in the realm of sustainable forest management.
Emerging trends in forest carbon projects include the integration of blockchain for enhanced transparency, artificial intelligence for advanced monitoring and data analysis, and a growing emphasis on nature-based solutions. The recognition of indigenous knowledge and practices, along with the rise of corporate biodiversity initiatives, is shaping the evolving landscape of sustainable forest management.
Opportunities for scaling up forest carbon projects lie in increased collaboration between governments, private sectors, and local communities. Leveraging innovative financing models, engaging in strategic partnerships, and incorporating nature-based solutions into climate policies can amplify the impact of these projects. The growing demand for high-quality carbon credits presents an opportunity for increased market participation, encouraging more significant investments in forest conservation and carbon sequestration initiatives.
In conclusion, the future of forest carbon projects holds great promise amidst the global imperative to combat climate change and promote sustainability. Emerging trends, such as blockchain integration and advanced technologies, reflect a commitment to transparency and efficiency in monitoring. The acknowledgment of indigenous knowledge and the rise of corporate biodiversity initiatives underscore a holistic approach to sustainable forest management. Opportunities for scaling up and increasing impact are abundant through collaborative efforts, innovative financing, and the integration of nature-based solutions. As forest carbon projects continue to evolve, their role in mitigating climate change, preserving biodiversity, and fostering sustainable development stands as a beacon of hope in our collective journey towards a more resilient and harmonious planet.
