Contact: +91 99725 24322 |
Menu
Menu
Quick summary: Explore the symbiotic relationship between agroforestry and cocoa supply chains in our latest blog. Uncover how innovative solutions, like TraceX's blockchain-powered traceability, are reshaping the cocoa industry by promoting sustainability, transparency, and ethical practices. Dive into the complexities of agroforestry integration and discover the transformative impact on cocoa cultivation and supply chain dynamics.

Chocolate, the world’s beloved treat, may be hiding a bittersweet secret. Yes, it melts on your tongue like a blissful dream, but the journey of the cocoa bean might come at a cost to nature’s vibrant diversity. Agroforestry in Cocoa referring here to planting or managing the regeneration of companion trees with cocoa, can make important contributions to strengthening and sustaining cocoa productivity.
Traditionally, cocoa thrives under the lush canopies of diverse rainforests, supporting a thriving tapestry of plants and animals. However, the industry relies heavily on small-scale farms, facing constant threats from pests, diseases, and the ever-growing demand for more chocolate. This pressure to boost yields quickly often leads to unsustainable practices.
According to Nature, in Côte d’Ivoire. the majority of farmers (86%) use agroforestry practices in their farming systems, with pruning techniques being used by 82% and fertilizers applied by 27%. Additionally, 54% of farmers are adopting improved agroforestry practices or planting more trees in their cocoa plantations.
Cocoa holds immense significance in global industries, especially the confectionery sector. As a key ingredient in chocolate production, cocoa contributes significantly to the global economy and supports livelihoods in cocoa-producing regions. Agroforestry, a sustainable land-use practice, integrates trees into cocoa cultivation. This concept not only enhances environmental sustainability by preserving biodiversity but also transforms cocoa value chains. Agroforestry improves soil health, reduces environmental impact, and fosters long-term resilience in cocoa farming. By combining agricultural and forestry practices, agroforestry presents a promising approach to address both economic and ecological challenges in the cocoa industry, ensuring a more sustainable and resilient future.
Discover how this innovative approach not only enriches cocoa yields but also nurtures biodiversity, promotes soil health, and uplifts the livelihoods of farmers. Join us on a journey where the delicate dance between agriculture and nature creates a sustainable, resilient, and mutually beneficial future for cocoa cultivation.
Cacao monoculture, the practice of cultivating only cacao trees, offers short-term yield advantages but leads to soil degradation, loss of nutrients, and deforestation.
This unsustainable method contributes to environmental degradation, soil erosion, and biodiversity loss, making cacao vulnerable to climate change and pests. The slash-and-burn technique exacerbates deforestation, creating a cycle of land degradation and social deprivation. Low cocoa prices further intensify this cycle, as farmers struggle to afford essential inputs, forcing them to clear more land. Agroforestry emerges as a sustainable solution, breaking the deforestation cycle and promoting environmental and social resilience.
Agroforestry, in the context of cocoa cultivation, refers to a land-use system that strategically combines trees with cocoa crops, promoting ecological balance and sustainable farming. This integrated approach enhances biodiversity, improves soil health, and mitigates environmental impact. Trees, such as shade-providing species, are intentionally planted alongside cocoa plants, offering a symbiotic relationship. The shade benefits cocoa quality, while the diversified environment supports wildlife and preserves ecosystem health. Agroforestry in cocoa cultivation not only fosters resilience against pests and diseases but also provides additional income sources through diverse products like fruits or timber. This harmonious integration of trees and crops exemplifies a holistic and sustainable approach, ensuring the long-term viability of cocoa farming practices.
The cocoa value chain comprises several stages, beginning with cultivation. Farmers plant and maintain cocoa trees, nurturing the pods containing cocoa beans. Harvested pods undergo extraction and fermentation, crucial for flavor development. After drying, the beans are transported to processing facilities, where they undergo roasting, grinding, and refining to produce cocoa products. Challenges in traditional cocoa production include susceptibility to pests, diseases, and environmental factors, often leading to yield fluctuations. Labor-intensive farming practices and outdated processing methods contribute to inefficiencies. However, opportunities lie in adopting sustainable agricultural practices, embracing modern processing technologies, and promoting fair trade initiatives. Addressing these challenges can enhance the overall cocoa value chain, ensuring economic viability for farmers and sustainable cocoa production for the global market.
Shade-grown cocoa, cultivated under the canopy of diverse tree species, brings a myriad of benefits. Firstly, this approach mimics cocoa’s natural habitat, fostering biodiversity by providing habitat for various flora and fauna. The shade protects cocoa plants from direct sunlight, preventing stress and enhancing the gradual ripening of pods, ultimately improving the flavor profile of the beans. Additionally, the symbiotic relationship between cocoa and shade trees encourages natural pest control and reduces the reliance on chemical interventions, contributing to environmentally sustainable farming practices.
Companion planting, an integral aspect of agroforestry, involves strategically pairing cocoa trees with compatible companion plants for mutual benefits. These plants may deter pests, fix nitrogen in the soil, or provide additional income through diverse agricultural products. This practice not only enhances soil fertility but also promotes efficient land use, optimizing the overall productivity of cocoa farms.
Agroforestry practices effectively address erosion control and water management. The root systems of trees and companion plants help bind the soil, preventing erosion and maintaining its structure. Moreover, the presence of vegetation contributes to water retention, reducing runoff and enhancing the overall water-holding capacity of the soil. This not only safeguards against soil degradation but also ensures sustainable water use in cocoa cultivation, vital for the longevity and resilience of cocoa farms.
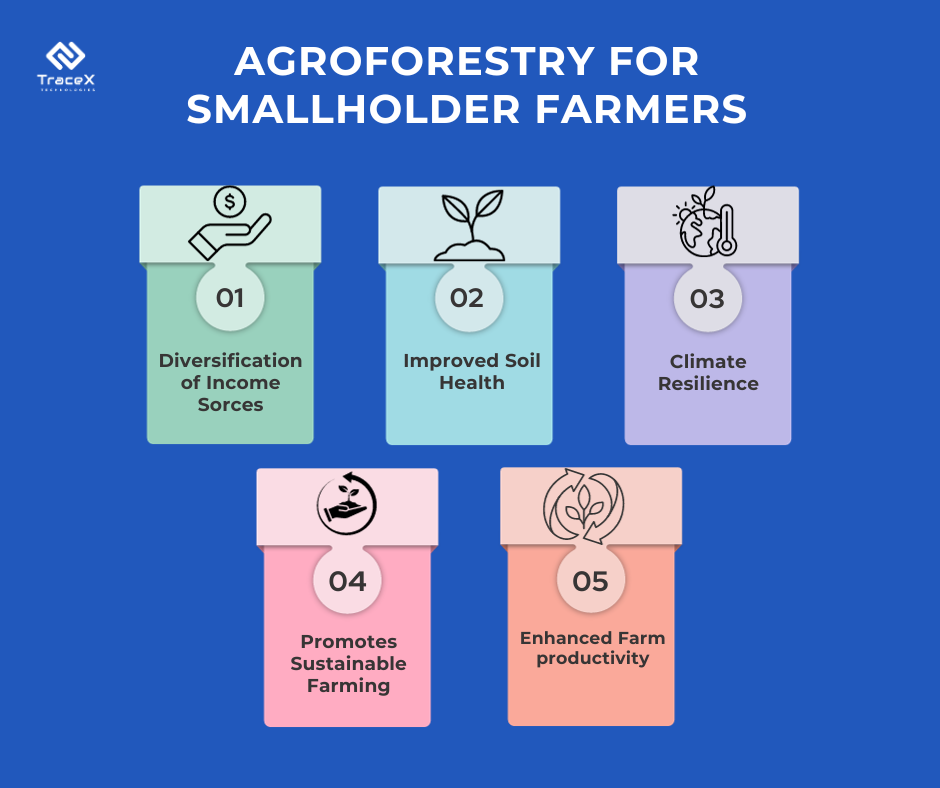
Cocoa farmers adopting agroforestry practices experience notable economic benefits. Agroforestry enhances overall cocoa yield and quality, leading to increased income. Diversification through companion planting introduces additional revenue streams from companion crops. Moreover, improved resilience to pests and diseases reduces production risks, securing farmers’ livelihoods.
Socially, agroforestry fosters community engagement by encouraging knowledge-sharing among farmers and promoting cooperative efforts. The integration of diverse crops enhances food security, providing both sustenance and surplus for local communities. Additionally, the environmentally sustainable practices associated with agroforestry contribute to improved living conditions by preserving natural resources and creating a more stable, resilient agricultural ecosystem.
TraceX, with its blockchain-powered traceability solutions, plays a transformative role in addressing challenges in cocoa agroforestry. By providing a transparent and immutable ledger, TraceX ensures the traceability of cocoa products throughout the supply chain. This not only helps in verifying the authenticity and quality of cocoa but also contributes to sustainable agroforestry practices.
With real-time monitoring, TraceX enhances transparency by recording every step in the cocoa value chain. This transparency aids in identifying inefficiencies, reducing waste, and ensuring fair practices. TraceX facilitates adherence to sustainability standards by tracking agroforestry practices. It helps in monitoring environmental impact, promoting biodiversity, and ensuring compliance with ethical farming methods. The data collected by TraceX enables stakeholders to make informed decisions, optimize processes, and implement improvements for a more sustainable and resilient cocoa agroforestry system.
In conclusion, agroforestry emerges as a transformative approach in cocoa cultivation, presenting a sustainable solution to the challenges faced in traditional farming. By integrating diverse tree species, agroforestry not only promotes biodiversity and improves soil health but also contributes to economic prosperity and social well-being. Though challenges exist, strategic investments, collaborative efforts, and education can pave the way for widespread adoption. The long-term benefits, including increased cocoa quality, diversified income sources, and climate resilience, underscore the significance of embracing agroforestry in cocoa value chains. This holistic approach not only secures the livelihoods of cocoa farmers but also ensures a more sustainable and resilient future for the global cocoa industry.
