Contact: +91 99725 24322 |
Menu
Menu
Quick summary: Discover how carbon offset projects in Africa, contribute to emissions reduction while uplifting local communities. Explore the impact on job creation, healthcare, and education through the utilization of carbon revenue.

Did you know that, despite its relatively low carbon footprint, Africa is one of the continent most vulnerable to the effects of climate change? According to recent studies, Africa suffers disproportionate risks from climate change, including extreme weather events, droughts, and food poverty. By focusing on carbon offset projects in Africa, we can not only solve the environmental difficulties faced by climate change, but also open up huge economic prospects for local communities.
Carbon offset projects help to mitigate climate change by compensating for greenhouse gas emissions through activities that reduce or sequester carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. These programmes include reforestation, renewable energy initiatives, and sustainable agricultural techniques.
The World Bank Group backs several projects across Africa aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions and earning carbon credits. Many of these initiatives are situated in the least developed nations, benefiting impoverished communities by generating employment and enhancing health and education through the utilization of carbon revenue.
Carbon offset projects address climate change by removing greenhouse gases, particularly carbon dioxide, from the atmosphere. They often involve activities that restore or protect natural ecosystems like forests, which absorb carbon as they grow. Alternatively, projects might focus on reducing emissions at their source, such as capturing methane from landfills or developing renewable energy sources. When individuals or businesses invest in these projects, they essentially “offset” their own carbon footprint by supporting initiatives that remove the equivalent amount of carbon they emit. This approach allows them to achieve carbon neutrality while supporting sustainable development and environmental benefits in the project location.
Deforestation, caused by agricultural expansion, logging, and infrastructure development, adds significantly to Africa’s carbon footprint by releasing vast amounts of stored carbon into the sky. Land degradation exacerbates the problem since deteriorated soils emit carbon dioxide and reduce their ability to retain carbon. Furthermore, using traditional fuels such as wood and charcoal for cooking and heating increases emissions.
Despite Africa’s lower emissions, it bears a disproportionate weight of climate change consequences. Rising sea levels endanger coastal communities, while unpredictable weather disrupts agricultural systems, resulting in food insecurity and economic instability.
Relying solely on emission reduction plans ignores the critical need to address existing emissions and adapt to current repercussions. Thus, comprehensive policies incorporating both reduction and adaptation measures are required to properly address Africa’s climate issues.
1. Reforestation: Initiatives aimed at planting trees in deforested or degraded areas to restore ecosystems, enhance carbon sequestration, and preserve biodiversity.
2. REDD+ (Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Forest Degradation): Programs designed to incentivize developing countries to reduce emissions from deforestation and forest degradation, as well as promote conservation and sustainable management of forests.
3. Sustainable Forest Management: Practices that ensure the long-term health and productivity of forests while balancing environmental, social, and economic benefits.
Forests are Earth’s powerhouses, absorbing vast amounts of carbon dioxide and mitigating climate change. But are you curious about the specific impact forest carbon projects have?
1. Solar Power: Harnessing sunlight to generate electricity through photovoltaic panels or concentrated solar power systems.
2. Wind Energy: Utilizing wind turbines to convert kinetic energy from wind into electricity.
3. Biogas Digesters: Anaerobic digestion of organic waste to produce biogas, a renewable energy source primarily composed of methane.
1. Soil Carbon Sequestration: Techniques such as agroforestry, cover cropping, and no-till farming that enhance soil organic carbon storage, contributing to climate change mitigation.
2. Sustainable Land Management Practices: Strategies to minimize soil erosion, conserve water, and maintain soil fertility through methods like terracing, contour farming, and crop rotation.
3. Reducing Methane Emissions from Livestock: Implementing dietary adjustments, waste management systems, and improved breeding practices to mitigate methane emissions from enteric fermentation and manure management in livestock farming.
Carbon offset initiatives in Africa provide a wide range of environmental, economic, and social benefits.
Overall, these programmes provide a comprehensive approach to tackling environmental issues while also promoting inclusive and sustainable development throughout Africa.
Africa presents a unique landscape for carbon offset projects due to its vast natural resources and rapidly developing economies. Here are some technology solutions that can be adopted to enhance these projects:
1. Remote Sensing and Satellite Imagery:
2. Blockchain Technology:
3. Internet of Things (IoT) Sensors:
4. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning:
5. Mobile Applications:
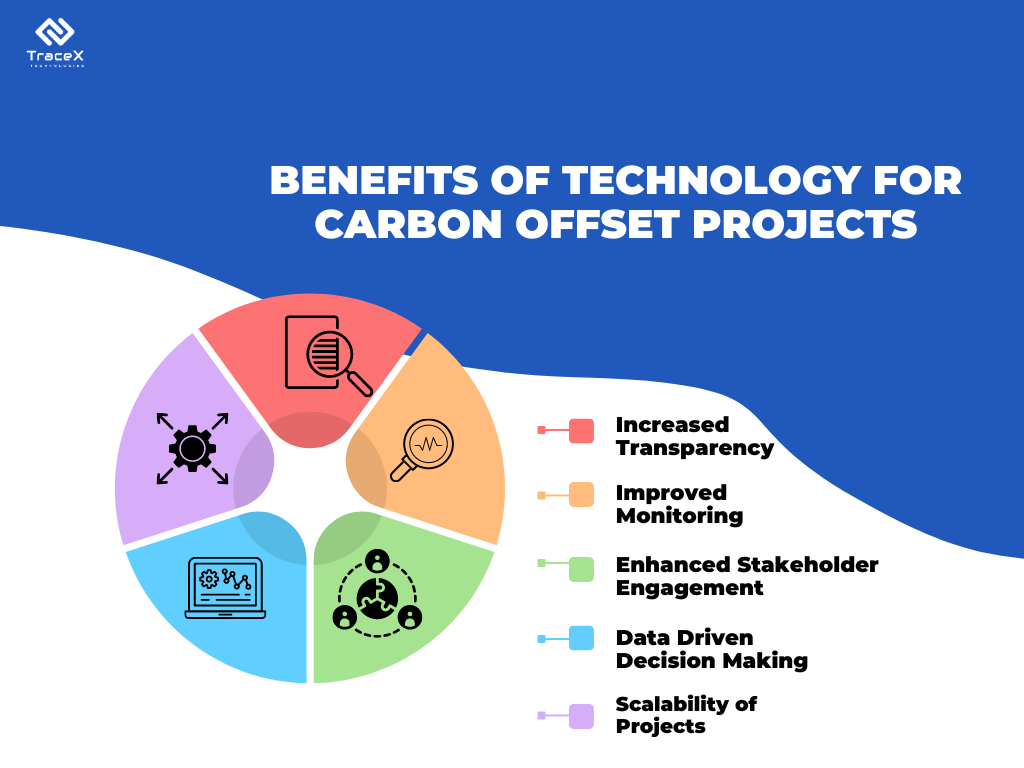
The combination of these technologies can significantly improve the effectiveness and impact of carbon offset projects in Africa. By leveraging these innovative solutions, Africa can become a leader in the fight against climate change while fostering sustainable development on the continent.
TraceX’s Digital MRV (Monitoring, Reporting, and Verification) solutions can be a game-changer for African carbon markets. Here’s how:
TraceX leverages cutting-edge technologies like remote sensing, mobile apps, and data analytics to streamline the entire MRV process. This translates to:
By streamlining MRV, TraceX empowers African nations to unlock the full potential of their carbon offset projects, contributing to climate change mitigation and sustainable development on the continent.
Carbon offset projects are increasingly being incorporated into Africa’s climate action plans, indicating a growing acknowledgment of their potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions while promoting sustainable development. Advances in technology and monitoring have improved project evaluation, allowing for more accurate measurement and verification of carbon sequestration and emission reductions. Remote sensing, satellite photography, and blockchain technology all give increased transparency and accountability, ensuring that offset initiatives are credible.
As individuals and corporations look for meaningful methods to combat climate change, funding credible carbon offset initiatives in Africa presents an appealing possibility. Investing in these initiatives allows stakeholders to support environmental protection, economic growth, and social development in the region while also offsetting their own carbon footprint. It’s time to take action and make a positive impact on Africa’s climate resilience and sustainability.
Carbon offset initiatives in Africa provide a significant tool for combating climate change and fostering sustainable development. These programmes reduce greenhouse gas emissions by investing in forestry, renewable energy, and better agricultural methods, all while creating green jobs and empowering local people. Readers can learn more about and support reputable carbon offset initiatives in Africa by visiting project directories such as the Gold Standard and the Verified Carbon Standard, connecting with NGOs like the World Wildlife Fund and the United Nations Development Programme, or seeking certification bodies such as the Climate, Community, and Biodiversity Alliance. Together, we can improve Africa’s climate resilience and environmental sustainability.
