Contact: +91 99725 24322 |
Menu
Menu
Quick summary: Explore the intricate world of food traceability systems with our comprehensive guide, uncovering the vital role of batch IDs in safeguarding food safety, ensuring quality control, and maintaining regulatory compliance. Discover best practices and innovative technologies that empower businesses to track every step of the food journey, fostering transparency and trust in the global food supply chain.

In an age where consumers are increasingly concerned about the safety and quality of the food they consume, traceability has emerged as a critical component of the food supply chain. At the heart of effective traceability systems lies the concept of batch identification (ID). Batch IDs serve as unique markers that allow food producers, regulators, and consumers to track and trace the journey of food products from farm to table.
Food traceability systems refer to the processes and technologies used to track and trace the movement of food products throughout the supply chain. These systems enable stakeholders to identify the origin, production, processing, distribution, and handling of food items. These systems utilize a combination of technologies, processes, and standards to capture, record, and manage critical information about food products at each stage of production, processing, distribution, and sale.
Food traceability systems are essential tools for safeguarding public health, enhancing food safety and quality, promoting sustainability, and building consumer trust in the food supply chain. They empower stakeholders with the information and capabilities needed to make informed decisions, respond effectively to emergencies, and ensure the integrity of the food products they produce, distribute, and consume.
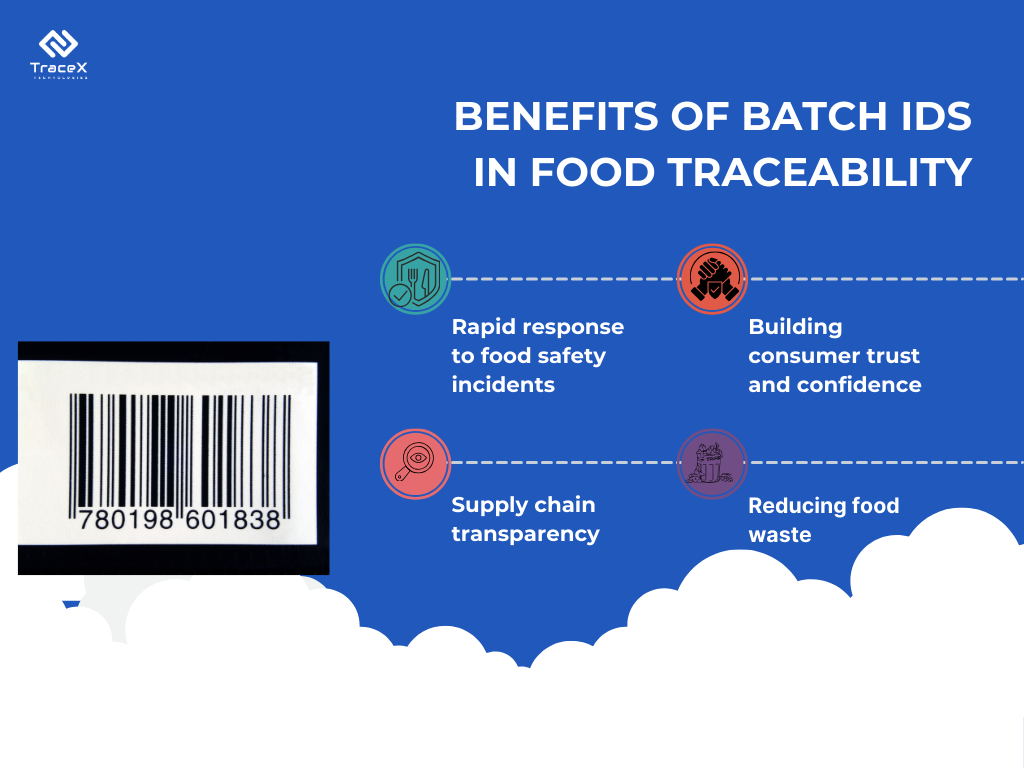
Batch IDs, also known as lot numbers or batch numbers, are unique identifiers assigned to specific batches or lots of food products. These identifiers allow for the differentiation of products based on factors such as production location, time of manufacture, and ingredients used. Batch IDs play a crucial role in traceability systems by providing a means to link individual food items to their respective production batches, enabling comprehensive tracking and tracing capabilities throughout the supply chain. Each batch ID contains key information that can be used to retrieve relevant data about the product, including its production history, expiration date, and any associated quality or safety attributes. Through the use of batch IDs, stakeholders can swiftly identify and respond to potential food safety issues, conduct targeted recalls, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
Food Safety: Traceability is crucial for ensuring food safety. In the event of a foodborne illness outbreak or contamination, traceability systems enable rapid identification and recall of affected products. This helps prevent further distribution of contaminated food and minimizes the risk to public health.
Quality Control: Traceability allows food manufacturers to monitor and maintain the quality of their products throughout the supply chain. By tracking factors such as storage conditions, transportation routes, and handling practices, companies can identify potential sources of quality degradation and take corrective actions.
Supply Chain Management: Traceability systems provide valuable data insights that help optimize supply chain operations. Companies can use this information to streamline inventory management, reduce waste, and improve efficiency in production and distribution processes.
Consumer Confidence: With growing concerns about food safety and sustainability, consumers are increasingly demanding transparency and accountability from food producers. Implementing robust traceability systems demonstrates a commitment to product integrity and consumer safety, thereby enhancing trust and loyalty among customers.
Batch IDs, also known as batch numbers or lot numbers, are unique identifiers assigned to specific groups or batches of food products. These identifiers play a crucial role in food traceability by providing a means to track and trace products throughout the supply chain. The primary functions of batch IDs in food traceability include:
Batch IDs are designed to be unique identifiers that distinguish one batch of food products from another. They typically consist of a combination of letters, numbers, and/or symbols that are sequentially or randomly assigned by the manufacturer. The uniqueness of batch IDs ensures that each batch of products can be accurately tracked and traced throughout the supply chain.
To track food batches effectively, batch IDs are often integrated into barcode or RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) tags affixed to product packaging. These technologies enable automated data capture and retrieval, making it easier to monitor the movement of batches through various stages of production, distribution, and sale.
Expiration Dates: Expiration dates, also known as “use by” or “best before” dates, indicate the recommended shelf life of a food product. These dates are typically printed on the packaging along with a batch ID, allowing consumers and retailers to identify the specific batch of products and determine their freshness.
Lot Numbers: Lot numbers are alphanumeric codes assigned to a specific production run or batch of food products. They are often printed on product packaging or labels and can be used to trace the entire production history of the batch, including raw materials used, production dates, and processing methods.
Barcodes and QR Codes: Barcodes and QR codes contain encoded information, including batch IDs, that can be scanned using handheld or automated scanning devices. These codes are commonly used in retail environments to track inventory and facilitate product recalls.

1. Identification of Contaminated Batches: In the event of a food safety issue or contamination, batch IDs enable rapid identification of affected products. By tracing the batch ID, stakeholders can pinpoint the source of contamination and take immediate action to prevent further distribution of tainted food, thus safeguarding public health.
2. Precise Recall Procedures: Batch IDs facilitate targeted recalls by identifying specific batches of products that may be compromised. This targeted approach minimizes the disruption to unaffected products and reduces the economic impact on food manufacturers and retailers while ensuring that potentially harmful products are removed from the market promptly.
1. Monitoring Production Processes: Batch IDs allow for meticulous monitoring of production processes. By associating each batch with specific production parameters such as ingredients, equipment, and environmental conditions, manufacturers can identify deviations from quality standards and implement corrective measures to maintain product consistency and integrity.
2. Traceability of Raw Materials: Batch IDs enable traceability not only of finished products but also of raw materials and ingredients used in their production. This traceability ensures that suppliers adhere to quality specifications and allows for swift identification of any substandard or adulterated ingredients, thereby upholding product quality and safety standards.
1. Speedy Identification and Retrieval: Batch IDs streamline recall processes by enabling swift identification and retrieval of affected products. With accurate batch-level traceability, manufacturers can quickly locate and remove specific batches from the supply chain, reducing the risk of widespread contamination and minimizing potential harm to consumers.
2. Minimized Recall Costs: Targeted recalls made possible by batch IDs help minimize the financial impact of recalls on food manufacturers and retailers. By isolating affected batches and minimizing the recall scope, companies can reduce costs associated with disposal, reimbursement, and brand damage.
1. Regulatory Requirements: Batch IDs are often mandated by food safety regulations such as the Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) and Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP). These regulations require food manufacturers to implement traceability systems that include batch identification to ensure compliance with safety and quality standards.
2. Documentation and Reporting: Batch IDs facilitate documentation and reporting requirements imposed by food regulations. By maintaining detailed records of batch-related information, manufacturers can demonstrate compliance with regulatory requirements and provide authorities with accurate and timely information in the event of audits or inspections.
Establishing clear and standardized labeling requirements ensures that batch IDs are easily identifiable and comprehensible across the supply chain. Consistency in labeling format, including font size, style, and placement, enhances readability and minimizes errors in data interpretation. Batch IDs should be accompanied by essential information such as production dates, expiration dates, lot numbers, and product descriptions. This additional information provides context and enhances the usefulness of batch IDs for traceability purposes. Adhering to regulatory labeling requirements ensures compliance with food safety and quality standards. Regulatory bodies may specify specific labeling elements or formats to facilitate traceability and ensure consumer safety.
Leveraging barcode and RFID technologies enables automated data capture and retrieval, enhancing the efficiency and accuracy of traceability processes. These technologies allow for real-time tracking of product movements and facilitate rapid identification of specific batches in the event of recalls or quality issues. Blockchain technology offers decentralized and immutable data storage, making it ideal for enhancing transparency and trust in food traceability systems. By recording batch-related information on a blockchain ledger, stakeholders can securely track the entire journey of food products from farm to fork, ensuring data integrity and authenticity. Integrating batch ID systems with enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems enables seamless data exchange and synchronization across different departments within an organization. This integration streamlines inventory management, production planning, and compliance reporting, enhancing operational efficiency and traceability capabilities.

Conducting regular internal audits of traceability procedures helps identify gaps or weaknesses in the system and ensures compliance with internal policies and standards. These audits should include thorough reviews of data accuracy, record-keeping practices, and adherence to standardized procedures. External audits by third-party certification bodies or regulatory agencies provide independent validation of traceability practices and demonstrate commitment to food safety and quality. External audits may also uncover areas for improvement and help benchmark performance against industry best practices.
Collaborating with suppliers and partners fosters transparency and accountability throughout the supply chain. Sharing traceability data and information exchange protocols with upstream and downstream stakeholders enhances visibility into product origins, processing methods, and distribution channels. Collaborative relationships with suppliers enable proactive risk management and mitigation strategies. By sharing insights into potential hazards or quality issues, stakeholders can work together to implement preventive measures and ensure the integrity of products at every stage of the supply chain.
TraceX’s product labeling and printing feature provides organizations with robust tools to manage product identification and traceability throughout the supply chain.
Unique Code IDs and Batch Code IDs:
Effortless Label Management:
In conclusion, implementing batch IDs in food traceability systems is essential for ensuring the safety, quality, and integrity of the food supply chain. By adhering to clear and standardized labeling requirements, adopting digital traceability technologies, conducting regular audits and reviews, and fostering collaboration with suppliers and partners, food businesses can enhance their ability to track and trace products from farm to fork. These best practices not only facilitate compliance with regulatory requirements but also improve operational efficiency, mitigate risks, and enhance consumer trust and confidence in the safety and quality of the food they consume. Ultimately, the effective utilization of batch IDs contributes to a more transparent, resilient, and sustainable food system that prioritizes the well-being of consumers and the integrity of the products they rely on.
