Contact: +91 99725 24322 |
Menu
Menu
Quick summary: This blog delves into the European Union's ambitious goal of achieving carbon neutrality by 2050. We explore the cutting-edge technologies and sustainable practices paving the way for a greener future. However, the road ahead is not without its hurdles.

The clock is ticking on climate change. The urgency for action is undeniable, and the European Union (EU) has emerged as a global leader in the fight for a sustainable future. At the heart of this fight lies the ambitious goal of carbon neutrality by 2050. But what exactly does carbon neutrality in Europe mean, and what roadmap is being followed to achieve this monumental transformation? Join us as we unpack Europe’s ambitious journey towards a carbon-neutral future, a journey that holds immense significance not just for the continent itself, but for the entire planet.
According to Statista, the European Union has set its sights on an ambitious goal: becoming the world’s first carbon-neutral continent by 2050. To achieve this, they’ve charted a course that includes a significant reduction in greenhouse gas emissions – a 55% cut by 2030 compared to 1990 levels.
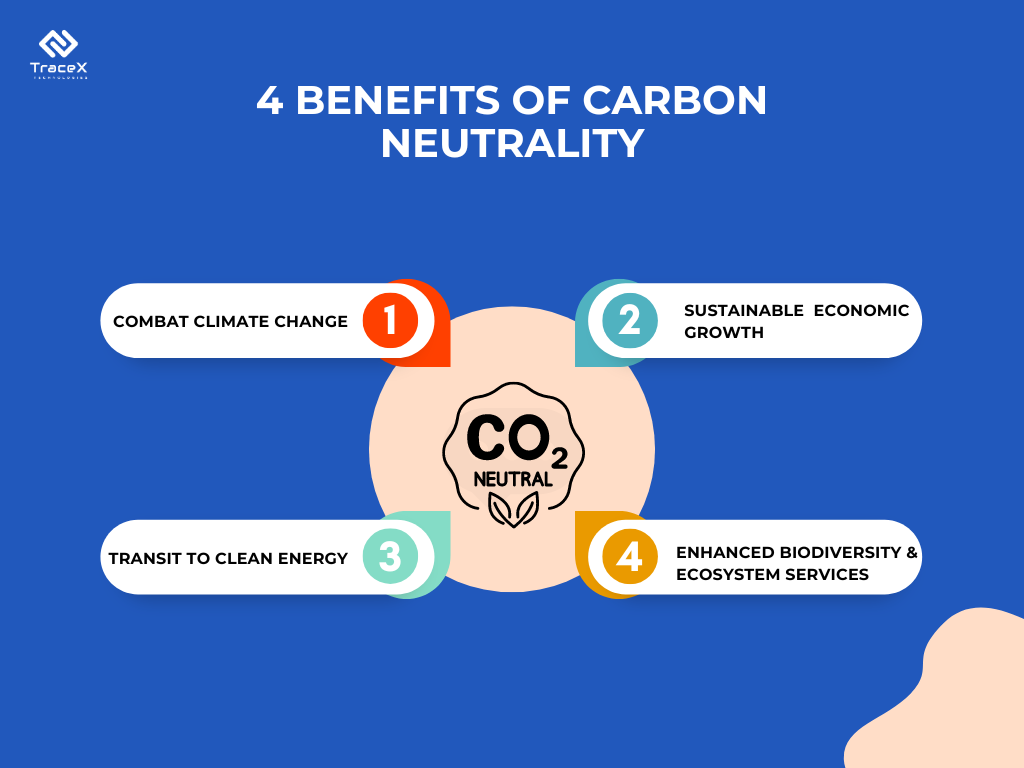
Carbon neutrality, often referred to as “net zero carbon,” is the state of achieving a balance between the carbon dioxide emitted into the atmosphere and the carbon dioxide removed from it. This balance can be achieved by:
Carbon neutrality is crucial in the fight against climate change. The accumulation of greenhouse gases, particularly carbon dioxide, in the atmosphere is the primary driver of global warming. By achieving carbon neutrality, we can stabilize and eventually reduce the concentration of these gases, mitigating the adverse effects of climate change such as rising global temperatures, extreme weather events, and sea level rise.
The European Union (EU) has set ambitious climate goals to become the first climate-neutral continent by 2050, as part of the European Green Deal. The EU aims to reduce its greenhouse gas emissions by at least 55% by 2030 compared to 1990 levels. Enhancing the share of renewable energy in the EU’s energy mix. Promoting energy-efficient technologies and practices to reduce overall energy consumption. These targets are part of the EU’s broader strategy to transition to a sustainable and competitive economy while addressing the urgent challenge of climate change. By committing to carbon neutrality, the EU positions itself as a global leader in climate action. This leadership role not only enhances the EU’s international standing but also encourages other countries to adopt similar ambitious targets, fostering global cooperation in tackling climate change.
The EU’s vision of a carbon-neutral future by 2050 is a complex and multifaceted endeavour.
1. Ambitious Goals and Timelines:
The EU has established clear and measurable goals for achieving carbon neutrality. The cornerstone of this strategy is the European Climate Law, a landmark legislation adopted in 2021. This law enshrines the 2050 carbon neutrality target in EU legislation, making it a legally binding obligation for member states. The law also sets an ambitious interim target: a 55% reduction in net greenhouse gas emissions by 2030 compared to 1990 levels. These targets serve as a roadmap, outlining the significant progress needed over the next decades.
2. A Robust Legislative Framework: The Fit for 55 Package
To translate these goals into concrete action, the EU has introduced the Fit for 55 package. This comprehensive legislative package consists of several proposals aimed at revising and strengthening existing legislation to align with the 2030 and 2050 targets. Some key elements of the Fit for 55 package include:
3. A Holistic Approach: Targeting All Sectors
The EU’s carbon neutrality strategy recognizes that achieving this goal requires a comprehensive approach encompassing all sectors of the economy. Here’s a look at the key focus areas:
By tackling these diverse sectors simultaneously, the EU aims to create a truly systemic transformation towards a low-carbon economy.
The fight against climate change demands a multi-pronged approach, and the European Union’s ambitious carbon neutrality goal recognizes the vital role that healthy ecosystems can play. Two key strategies in this regard are sustainable land management (SLM) and afforestation.
Traditional agricultural practices can contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions, particularly deforestation for agricultural land and the use of fertilizers that release nitrous oxide. Sustainable land management (SLM) offers a path to transform these practices into allies in the fight against climate change.
Here’s how SLM can help Europe achieve carbon neutrality:
By implementing SLM practices across Europe’s vast agricultural landscape, the EU can unlock a significant potential for carbon sequestration and emission reductions.
2. Afforestation
Forests play a crucial role in capturing and storing carbon dioxide. In the context of achieving carbon neutrality, afforestation, the establishment of new forests on previously non-forested land, becomes a valuable strategy. Here’s how afforestation can contribute to the EU’s goals:
However, it’s crucial to ensure that afforestation initiatives are well-planned and implemented with a focus on native species and ecosystem restoration. Furthermore, afforestation should not come at the expense of existing, biodiverse ecosystems.
Traceability solutions and digital Measurement, Reporting, and Verification (dMRV) systems offer powerful tools to address several key challenges in sustainable land management (SLM).
Overall, traceability solutions and dMRV systems are valuable tools for promoting sustainable land management. By increasing transparency, monitoring progress, facilitating knowledge sharing, and demonstrating impact, these technologies can empower farmers, inform consumers, and incentivize investment in a more sustainable future.
TraceX DMRV platform is designed to transform sustainable land management practices
The Traceability platform tracks the origin of agricultural products and the land management practices used throughout the supply chain, creating transparency for consumers and producers alike.
The Digital MRV platform utilizes digital tools to collect and verify data on land management practices. This ensures accountability and prevents greenwashing by providing verifiable proof of sustainability efforts.
The road to carbon neutrality in Europe is ambitious, but the journey has begun. By harnessing innovation, mobilizing investments, fostering social justice, and strengthening international cooperation, the EU can overcome the challenges and emerge as a global leader in building a sustainable future. As individuals, we can all play a part by making informed choices, supporting sustainable businesses, and holding our leaders accountable. Together, we can turn Europe’s bold vision of a carbon-neutral future into a reality.
