Contact: +91 99725 24322 |
Menu
Menu

As climate change, sustainability, and market demand challenges grow, agribusinesses are under immense pressure to optimize their farm management practices. Farm management guide offers actionable strategies to streamline farm operations and overcome the challenges that most agribusinesses face, such as fragmented data, inefficient resource use, and unpredictable yields.
Many agribusinesses still rely on outdated, manual processes, leading to inefficiencies and lost revenue. But how do you keep track of everything from crop planning to resource allocation and regulatory compliance? This guide shows how to modernize these processes with technology-driven solutions like farm management software, giving agribusinesses the tools they need to stay competitive in an evolving industry.
Key Takeaways
Farm Management is a branch of Agriculture Economics that deals with the principles and practices of farming, with an objective to get maximum profitability from the farms. Farming today is more than just producing crops. It needs to address the productivity, profitability and sustenance and conservation of farms. All farmland are not equal, hence their management to realize return on investment is crucial. It is a decision-making process, in which resources are allocated to operate the farm business in a way to achieve some objectives. These resources include land, labor, capital and knowledge
A farm is normally an area of land under the single ownership of a farmer used to raise crops or for pasture. The management refers to the production planning and the necessary activities undertaken to get maximum returns from the cultivated yield. Agriculture encompasses growing of crops, raising livestock for milk, eggs and meat, providing raw materials to industries and marketing of products for use. The farm practices have improved over a time to realize quality yields to feed the growing population. The natural inputs are today replaced with purchased inputs and the production is nowadays being oriented towards the market rather than use by the family. Agriculture is getting business oriented.
There are more than 570 million farms around the world, most of which are small and family operated.
Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs) play a vital role in supporting smallholder farmers. They enable collective bargaining, improve market access, and provide farmers with better pricing. FPOs are increasingly leveraging technology to optimize their operations and empower farmers with digital tools.
Farm management has become indispensable for agribusinesses facing modern challenges like climate unpredictability, resource scarcity, and growing demand for sustainability. With fluctuating markets and strict compliance regulations, agribusinesses need to optimize every aspect of their operations, from crop rotation to labor management. However, managing these complexities manually often leads to inefficiencies and missed opportunities.
This is where a farm management guide comes in, offering a roadmap for streamlining processes, enhancing productivity, and reducing costs. Agribusinesses can benefit from integrating farm management software, which provides real-time insights, better planning, and data-driven decisions—making it easier to adapt to evolving market and environmental conditions.
Farm management encompasses strategic decision-making across various operational areas, from crop planning to marketing. It involves overseeing inputs, managing resources, coordinating labor, and ensuring sustainability. The scope of farm management covers:
Farm management software plays a crucial role in enabling agribusinesses to manage this vast scope effectively, providing data-driven insights and real-time monitoring capabilities.
The principles of Farm Management are the fundamental laws on which the farming practices are built. They provide a foundation for effective practices and guide the farmer or farm manager to take the right decisions.
The 6 principles of Farm Management are
This helps in deciding the optimum usage of input that needs to be applied for crop cultivation.
For example, while considering the use of weedicides, the farmer needs to balance the cost involved as against the value of the expected yield.
The farmer has limited capital and he has to use that for cultivation of crops. He has to decide the type of crops and the area and maximize the net revenue as a whole.
In agriculture varying inputs can be substituted in varying degrees for producing a given output. A farmer can choose a combination of sources like farm manure, vermicompost, other inorganic fertilizers for meeting the nutrient requirements of crops. For example, the farmer can use mechanical equipment, manual labor or chemicals to control weeds. He needs to decide which method is cost and performance effective. It has to be ensured that the substituted method ensures greater saving than the cost of technique used.
This principle describes the product-to-product relationship. Instead of considering inputs, a product mix is considered. Joint products, complementary products and supplementary products. It guides in determining optimum combination of products.
This is also called alternative cost. It is the earning from the next best alternative. For example if a farmer can earn a profit of $1000 from a farm growing apples and $3000 by growing avocados, then the opportunity cost of growing apples is $3000, by continuing to grow apples, he is earning $2000 less profit than he could have earned.
This is related to resource productivity and cost of production.
Cost of production is given importance while taking production decisions. There could be short run and long run accounting periods. This explains details of regional specialization in the production of commodities.
The main objectives of farm management are to optimize the use of resources, maximize profits, and ensure sustainability. It’s all about making the best decisions for both short-term gains and long-term growth. This includes efficient planning of crop cycles, labor management, and cost-effective use of inputs like seeds, water, and fertilizers. At the same time, a focus on sustainability ensures that natural resources are preserved for future generations. By balancing profitability with environmental stewardship, farm management helps agribusinesses thrive in an increasingly competitive and regulated market. It’s about smart choices that lead to better yields and stronger resilience in the face of challenges like climate change and fluctuating market prices.
Farm management focuses on achieving the following objectives:
Several best practices are essential for achieving efficient farm management. These include:
By integrating these practices, agribusinesses can enhance productivity while ensuring sustainability. Farm management software assists in the execution of these practices by offering monitoring tools, resource tracking, and automation features.
Farm management aims to achieve two primary goals:
Technology solutions provide the framework to align with these goals by enabling data-driven planning and monitoring, reducing operational inefficiencies, and improving decision-making.
These goals align directly with the principles of Integrated Farm Management (IFM), which emphasizes a holistic approach to farming that balances productivity with sustainability.
Integrated Farm management systems must adhere to certain principles to be effective:
Farm management software helps agribusinesses streamline and optimize their operations by providing real-time insights and data-driven decision-making capabilities.
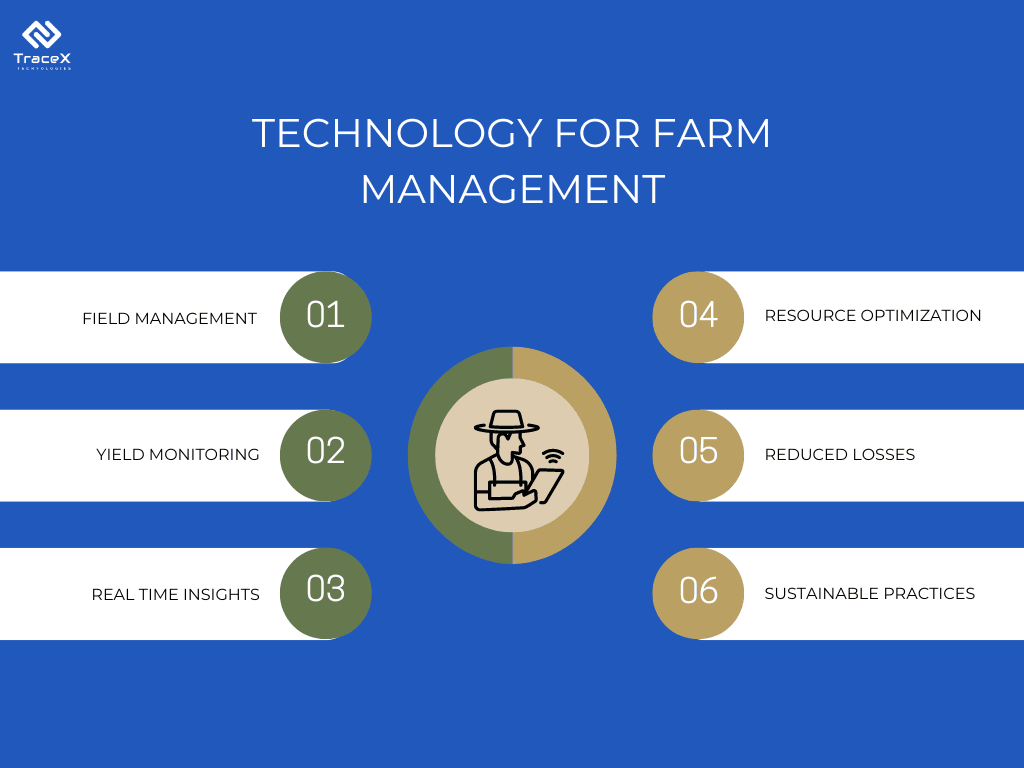
These platforms offer tools for tracking crop performance, managing resources such as water and fertilizers, monitoring labor, and forecasting yields. With centralized data, agribusinesses can efficiently plan planting and harvesting schedules, reduce wastage, and enhance overall productivity. Additionally, farm management software facilitates compliance with regulations, ensuring traceability across the supply chain, and aids in integrating sustainable farming practices, ultimately leading to better resource utilization, improved yields, and enhanced profitability for farmers and agribusinesses alike.
he TraceX Farm Management Platform is a comprehensive technology solution designed to enhance farm productivity, sustainability, and traceability for agribusinesses. By leveraging blockchain technology, it enables real-time tracking of farm operations, including crop management, resource allocation, and harvest forecasting, all while ensuring data integrity and transparency throughout the supply chain.
Key features include:
The platform integrates seamlessly with agribusiness operations, helping companies achieve greater efficiency, transparency, and sustainability across the agricultural supply chain.
In collaboration with C-SAFE, the Sri Amaranarayana Farmer Producer Organization (FPO) has tackled inefficiencies in the tomato value chain using TraceX’s Farm Management platform. This innovative solution enhances visibility and transparency throughout the supply chain, from farm to market. By addressing critical issues such as manual record-keeping and the lack of digitization, TraceX empowers farmers to track agronomy practices effectively. This transformation not only streamlines operations but also enables better decision-making, ultimately leading to increased productivity and profitability for the FPO members.
In conclusion, a comprehensive farm management guide serves as an essential roadmap for agribusinesses looking to enhance productivity, optimize resources, and improve overall sustainability. By adopting best practices and leveraging advanced technology solutions, such as farm management software, businesses can navigate the complexities of modern agriculture. The right strategies not only improve operational efficiency but also empower farmers to achieve their goals while positively impacting their communities and the environment. As we face ongoing challenges in the agricultural sector, investing in effective farm management practices will be crucial for success and resilience in the years to come.
Effective farm management encompasses resource optimization, financial management, risk assessment, and adherence to sustainability practices. It involves planning, organizing, and executing operations to achieve optimal productivity and profitability.
Technology, particularly farm management software, helps agribusinesses streamline operations, enhance decision-making, and improve data management. It enables real-time monitoring of resources, financial analytics, and efficient communication among stakeholders.
Sustainability is vital in farm management as it ensures the long-term viability of farming practices. By focusing on sustainable techniques, agribusinesses can minimize their environmental impact, improve soil health, and promote ethical practices, ultimately leading to enhanced consumer trust and market competitiveness.



We use cookies on our website to give you the most relevant experience by remembering your preferences and repeat visits. By clicking “Accept All”, you consent to the use of ALL the cookies. However, you may visit "Cookie Settings" to provide a controlled consent.
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
WhatsApp us
Your Blueprint for Traceable & Sustainable Supply Chain
The countdown has started. Less than 100 days remain to be compliant. Don’t miss out on your chance to grab access to our early bird offer!
Your essential compliance guide