Contact: +91 99725 24322 |
Menu
Menu
Quick summary: People today are looking beyond the food on their plates.. Where are they sourced, who are the producers? In what way is the food processed? And how safe it is for consumption? Consumers prefer healthier and trustworthy food brands.. End to end visibility in the food supply chains with traceability solutions will bridge the gap between the producer and the consumer..

You’re a consumer standing in the grocery aisle, faced with countless choices. You reach for a product, but before placing it in your cart, you pause to scan the label. Where was this food sourced? Is it sustainably produced? Was it ethically harvested? In today’s world, questions like these are no longer niche concerns—they are at the forefront of consumer decision-making. This shift is where food traceability becomes a game changer.
According to Nielsen,73 percent of consumers are willing to pay more for a product that offers complete transparency
For brands, this presents both an opportunity and a challenge. This guide explores the essential elements of effective food traceability, outlining strategies for brands to enhance their transparency, engage consumers, and ultimately strengthen their market position. By adopting robust traceability practices, companies can differentiate themselves in a competitive landscape and create lasting relationships with conscientious consumers.
Key Takeaways
At its core, food traceability refers to the ability to track and trace the journey of a food product as it moves through the supply chain—from farm to fork. This includes documenting every stop it makes, who handles it, and what processes it undergoes. Whether it’s a jar of jam or a pack of chicken breasts, food traceability ensures that businesses and consumers know where that item came from, how it was processed, and where it’s going.
Why has food traceability gained so much traction? The food industry is under enormous pressure to meet growing consumer expectations, ensure safety, and comply with increasingly strict regulations.
Imagine there’s a food recall due to contamination—perhaps an outbreak of salmonella in lettuce or a listeria incident involving dairy products. Without a proper traceability system, tracing the origin of the issue can be time-consuming and inefficient, leading to larger recalls and potentially more harm to consumers. Traceability systems help identify exactly where in the supply chain a problem occurred, allowing businesses to act quickly and minimize the impact.
Consumers today don’t just care about whether food is safe—they care about quality and freshness too. Traceability allows businesses to monitor factors like storage conditions, handling processes, and transportation timelines, ensuring that the product that reaches the consumer is of the highest quality possible. It also allows companies to check compliance with sustainability claims, such as organic or fair-trade certification, which have become increasingly important for conscious consumers.
With regulations like the EU Deforestation Regulation (EUDR) and other global standards coming into play, companies are now required to demonstrate where their products come from, especially if they involve commodities linked to deforestation or other environmental concerns (like soy or palm oil). Having a traceability system in place ensures that companies can easily provide this information and meet compliance requirements, avoiding hefty penalties or import bans.
One of the primary purposes of food traceability is to ensure food safety. By tracking the product through its entire journey, businesses can pinpoint where issues like contamination or tampering occurred and respond swiftly. A robust traceability system minimizes the risk to consumers and mitigates the damage to a brand’s reputation in the event of a food safety crisis.
Traceability isn’t just about avoiding disasters—it’s also about maintaining consistency in product quality. Companies can use traceability systems to track key quality indicators, such as the temperature at which products were stored, or the time it took to transport them. This level of oversight can significantly reduce spoilage and ensure that customers receive fresh, high-quality products.
Global food regulations are becoming increasingly strict, and compliance is now a major focus for companies in the food industry. Regulations like the EUDR, the Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) in the U.S., and ISO 22005 require companies to maintain accurate records of their product origins. A robust traceability system allows businesses to seamlessly meet these regulatory demands and avoid the severe penalties that can result from non-compliance.
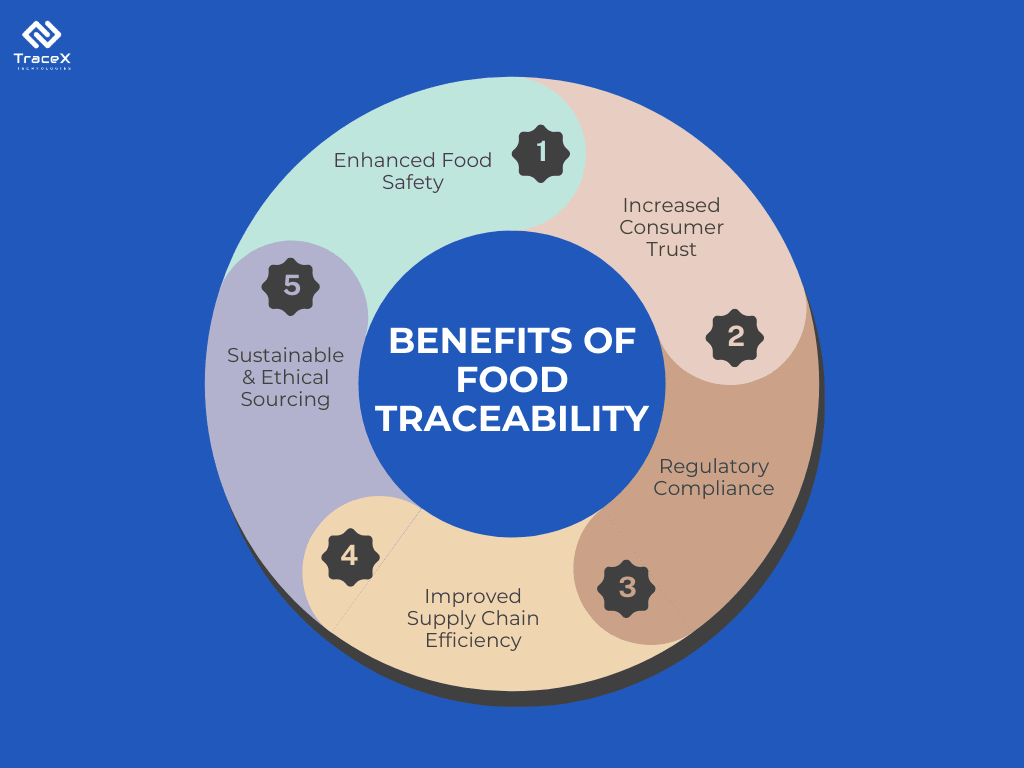
In an era where consumers are more informed than ever, transparency is no longer a luxury; it’s an expectation. Conscious consumers today want to know where their food comes from, how it was produced, and the journey it took to reach their plates. They are actively seeking brands that provide clear, accurate, and accessible information about their products. This surge in demand is fuelled by concerns over food safety, ethical sourcing, and environmental sustainability.
For brands in the food industry, trust is a key currency. Trust drives loyalty, repeat purchases, and brand advocacy. But building that trust requires more than just high-quality products—it requires transparency across the entire supply chain. Traceability is the tool that allows businesses to offer that transparency. By implementing food traceability systems, companies can track and verify the origin, movement, and handling of their products at every stage of the supply chain. This level of insight can help brands ensure food safety, meet quality standards, and maintain compliance with evolving regulations like the EU Deforestation Regulation (EUDR).
Regulations like the EUDR are reshaping the way businesses operate, demanding stricter controls on the sourcing of agricultural commodities to prevent deforestation and ensure sustainable practices. Without robust traceability, businesses risk non-compliance, which can lead to hefty fines, import restrictions, and a tarnished brand image.
But here’s the challenge—many businesses still struggle to implement an effective traceability system. Manual processes, fragmented supply chains, and lack of integration between systems make it difficult for brands to track their products from farm to fork. Add to that the complexity of ensuring compliance with new regulations, and the task can feel overwhelming.
So, how can brands overcome these hurdles? By investing in digital traceability solutions and leveraging technologies like blockchain to create transparent, secure, and reliable records. Brands that embrace this shift will not only meet consumer expectations but also future-proof their operations against evolving regulatory demands.
This sets the stage for understanding why traceability matters more than ever for building consumer-centric brands and how it directly ties into their long-term success.
Implementing an effective food traceability system involves a structured approach that ensures transparency and accountability throughout the supply chain. Here’s a concise breakdown of the five key steps to achieve robust food traceability:
1. Types of Traceability
Food traceability can be categorized into internal and external types:
Both internal and external traceability systems are vital for food safety, product recalls, and meeting regulatory requirements
2. Effectiveness of a Food Traceability System
An effective food traceability system provides transparency, accountability, and real-time monitoring across the supply chain. To be effective, it should:
3. Traceability Requirements and Implementation
Implementing a traceability system requires identifying key requirements and carefully mapping out each step of the supply chain.
Critical Tracking Events (CTEs) and Key Data Elements (KDEs) are essential components of an effective traceability system. CTEs are specific points in the supply chain where significant actions occur, such as receiving, processing, shipping, and recalling products. These events are crucial for understanding a product’s journey. KDEs, on the other hand, are the detailed pieces of information collected at each CTE, including lot numbers, timestamps, product origin, and storage conditions. Together, CTEs and KDEs provide a comprehensive framework for tracking and verifying the integrity of products, ensuring food safety, compliance, and consumer trust throughout the supply chain.
4. Drivers of Traceability
5. Private Standards for Traceability
In addition to government regulations, many private standards exist to promote food safety, quality, and sustainability through traceability. These standards are often set by industry groups, certification bodies, or even retailers and manufacturers. Examples include: These private standards not only help companies improve their operations but also serve as proof of quality and safety to consumers and retailers. GS1 is a global organization dedicated to improving supply chain efficiency and visibility through standardized identification and communication systems. Best known for its barcode standards, GS1 enables businesses to uniquely identify products, locations, and more, facilitating accurate data exchange across diverse industries.
To ensure a robust food traceability system, businesses should prioritize adopting best practices with digital traceability solutions, moving away from manual processes to more accurate, real-time tracking systems. These solutions enhance efficiency and reduce errors, creating a seamless flow of information. Leveraging cloud-based platforms is key for improving data accessibility and sharing across the supply chain, enabling better visibility from production to consumer. Collaboration with suppliers at all levels is critical—without full participation from everyone, traceability can fall short. Providing transparency to consumers, such as through labeling or digital apps, not only fosters trust but also meets the growing demand for product origin and safety information. Finally, conducting regular audits and continuously updating the traceability system ensures compliance with ever-evolving regulations and helps address any gaps or inefficiencies in the process. These steps collectively create a traceability system that enhances brand reputation and ensures food safety.
Traceability use cases in food and agriculture value chains play a critical role in enhancing safety, quality, and sustainability. In the fresh produce sector, systems are implemented to track the journey of fruits and vegetables from farm to table, allowing for swift responses to contamination outbreaks and ensuring that consumers can access information about origin and farming practices. In the meat industry, traceability solutions enable the monitoring of animal welfare and feed sources, fostering transparency that meets consumer demands for ethically sourced products. Additionally, in the dairy sector, traceability tools are used to verify milk quality and safety, providing insights into processing and handling practices. These use cases not only help mitigate risks and improve compliance with regulations but also empower consumers with information, ultimately supporting more sustainable practices across the food and agriculture ecosystem.
Blockchain technology plays a transformative role in food traceability by providing an immutable, transparent ledger that records every transaction throughout the supply chain. This decentralized approach ensures that all stakeholders—farmers, processors, distributors, and consumers—can access real-time data about a product’s journey from farm to table. By enabling secure and verifiable tracking of food items, blockchain enhances food safety, as any contamination can be quickly traced back to its source, facilitating swift recalls and minimizing public health risks. Additionally, it promotes trust among consumers, who can verify claims about sustainability and ethical sourcing through easily accessible information. As a result, blockchain not only strengthens food security but also supports compliance with regulatory standards and fosters a more sustainable food system.
The TraceX food traceability platform is designed to enhance transparency and accountability throughout the food supply chain. Utilizing blockchain technology, it provides an immutable record of each product’s journey, from farm to consumer. This platform enables stakeholders—such as farmers, processors, retailers, and consumers—to access real-time data about food origins, processing methods, and handling practices.
1. Real-Time Tracking: Users can monitor the movement of products at every stage, ensuring quick identification of any issues, such as contamination or spoilage.
2. Data Integrity: The blockchain framework guarantees that once data is recorded, it cannot be altered, which enhances trust and reliability among participants.
3. Consumer Engagement: The platform allows consumers to access detailed information about the food they purchase, including origin, production methods, and certifications, fostering informed choices.
4. Regulatory Compliance: By maintaining detailed records, TraceX helps businesses comply with food safety regulations and standards, simplifying audits and inspections.
5. Sustainability Insights: The platform can track sustainability practices, allowing businesses to demonstrate their commitment to ethical sourcing and environmental stewardship.
Overall, the TraceX food traceability platform empowers stakeholders to make informed decisions, enhances food safety, and promotes sustainable practices within the food supply chain.
Incorporating food traceability into your brand strategy is no longer optional—it’s essential for meeting consumer expectations and maintaining a competitive edge. By leveraging technology and creating a culture of transparency, brands can foster trust, improve product safety, and demonstrate a commitment to sustainability. As consumers become more discerning, the brands that prioritize traceability will not only survive but thrive in the evolving food landscape.
Food traceability refers to the ability to track the journey of food products from their origin to the consumer. This involves documenting every stage of the supply chain, including production, processing, distribution, and retail.
Food traceability enhances consumer trust by providing transparency about sourcing and production practices. It can also improve compliance with food safety regulations, facilitate quicker responses to food recalls, and promote sustainable practices.
Common technologies include blockchain for secure data sharing, QR codes for consumer access to product information, and IoT devices for real-time monitoring of conditions during transportation and storage.
