Contact: +91 99725 24322 |
Menu
Menu
Quick summary: Explore the exciting opportunities and pressing challenges surrounding Kenya's carbon market. Learn how Kenyan agribusinesses can leverage this market to generate revenue, gain access to premium markets, and become sustainability leaders. Discover the role of technology in overcoming hurdles and propelling Kenya towards a future of climate-smart agriculture.

Food security and environmental responsibility are on a collision course in Kenya’s agribusiness sector. While the nation strives to feed a growing population, traditional agricultural practices often contribute to rising greenhouse gas emissions. However, a glimmer of hope emerges with the recent developments of carbon markets in Kenya.
Kenya’s voluntary carbon market is taking off, attracting big names like tech giants and oil companies. As Africa’s vast carbon credit potential becomes a reality, Kenya is at the forefront, leveraging this market to fight climate change and promote sustainable development.
Kenya’s burgeoning carbon market presents exciting opportunities for agribusinesses to not only contribute to environmental sustainability but also unlock new avenues for growth and profitability.
Carbon markets create a system where companies that reduce their emissions below a set target can earn tradable carbon credits. These credits represent a verified unit of carbon dioxide (CO2) removed or prevented from entering the atmosphere. Agribusinesses can participate in carbon credit programs by implementing sustainable practices that demonstrably reduce their carbon footprint. Examples include practices like:
Independent third-party verification bodies assess the effectiveness of these practices to quantify the carbon emissions reduced. The resulting carbon credits can then be sold on the carbon market to companies looking to offset their emissions.
Agribusinesses that successfully earn carbon credits can generate a new revenue stream by selling them to companies or individuals seeking to offset their carbon footprint. This creates a financial incentive for adopting sustainable practices, promoting a shift towards a more environmentally friendly agricultural sector.
Consumers worldwide are increasingly prioritizing products grown with sustainable practices and a lower environmental impact. This trend is particularly strong in developed countries, where eco-conscious purchasing decisions are driving market demand. Participation in carbon markets allows agribusinesses to obtain certifications that verify their carbon-neutral status. This provides a valuable marketing tool, differentiating their products from competitors in the global marketplace. Sustainability-conscious consumers are often willing to pay a premium for products that boast a lower carbon footprint. This price advantage can generate increased profits for agribusinesses participating in carbon markets. Carbon-neutral certification can open doors to new and lucrative markets that specifically cater to environmentally conscious consumers. This expands the reach of Kenyan agribusinesses and fosters export opportunities.
Customers are increasingly seeking brands that demonstrate a genuine commitment to environmental responsibility. By actively participating in carbon markets, agribusinesses send a clear message about their commitment to sustainability. This resonates with environmentally conscious consumers and strengthens brand image.
Transparency and accountability are key components of successful carbon markets. Kenyan agribusinesses that participate in these initiatives demonstrate their dedication to ethical and sustainable practices. This builds trust with consumers and fosters long-term brand loyalty.
The carbon market lacks complete standardization across different regions and programs. This inconsistency can make it difficult for businesses to compare carbon credits and navigate the market complexities. The price of carbon credits can fluctuate significantly depending on supply and demand. This can make it challenging for businesses to accurately predict their potential revenue or the cost of offsetting emissions.
Ensuring the legitimacy and accuracy of carbon credits is crucial. Weak verification systems can lead to the circulation of dubious credits, undermining the market’s integrity. Quantifying and verifying emission reductions, especially in the complex agricultural sector, can be challenging. This requires robust data collection and monitoring systems, which can be expensive to implement and maintain.
Smallholder farmers, who form the backbone of Kenyan agriculture, may face challenges in accessing carbon markets due to factors like limited resources, information gaps, and complex bureaucratic procedures. Ensuring equitable distribution of benefits from carbon trading activities is crucial. Without proper safeguards, larger agribusinesses may disproportionately benefit, leaving smallholder farmers behind.
The carbon market landscape is still evolving, with regulations and policies constantly being developed and refined. This uncertainty can make it difficult for businesses to plan long-term strategies for participation. Effective enforcement of regulations is essential to prevent fraud and ensure market integrity. Weak enforcement can create loopholes, undermining the credibility of the entire system.
Managing the vast amount of data generated in carbon credit transactions requires a robust data management infrastructure. Lack of such infrastructure can hinder efficient market operations and transparency. Accurately measuring and monitoring emission reductions, particularly in agriculture, may require specialized technologies that might not be readily available or affordable for all participants.
Addressing these challenges is crucial for ensuring the long-term success and sustainability of Kenya’s carbon market. By fostering transparency, establishing robust verification systems, promoting equitable access, and fostering a stable regulatory environment, Kenya can unlock the full potential of this market for both environmental and economic benefit.
Technology solutions like DMRV (Measurement, Reporting, and Verification) and satellite integrations can play a crucial role in addressing several challenges faced by the carbon market, particularly in the agricultural sector:
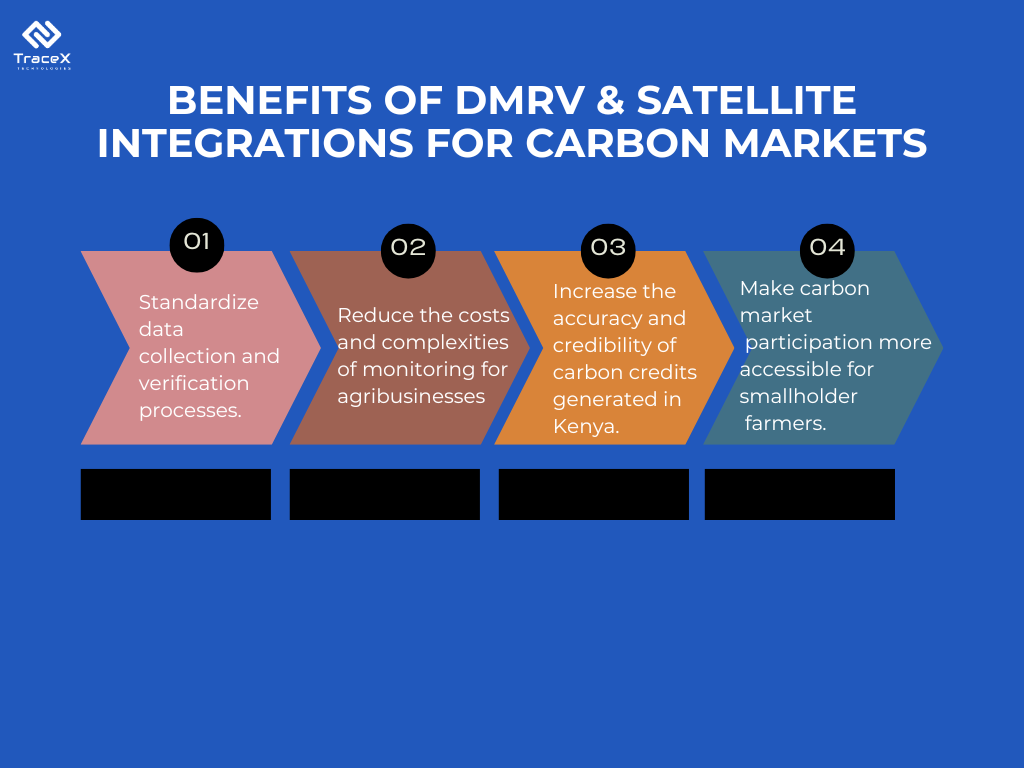
TraceX DMRV platform tackles data verification and accessibility challenges in the Kenyan carbon market. TraceX offers a user-friendly platform that streamlines the Measurement, Reporting, and Verification (DMRV) process for agribusinesses. It guides them in collecting and reporting data on sustainable practices like improved soil management or renewable energy adoption. This data can be verified by independent third parties, ensuring the legitimacy of the carbon credits generated. Additionally, TraceX can leverage satellite imagery to monitor land-use changes and track the effectiveness of these practices on smallholder farms. By simplifying data collection, verification, and even incorporating satellite monitoring, TraceX empowers Kenyan agribusinesses, particularly smallholders, to actively participate in the carbon market and benefit from the economic rewards of sustainable practices.
In conclusion, Kenya’s carbon market presents a dynamic landscape brimming with both opportunities and challenges for the nation’s agribusiness sector. While navigating complexities like market fluctuations and ensuring equitable access may require ongoing efforts, the potential rewards are substantial. By embracing technological solutions like DMRV platforms and satellite monitoring, agribusinesses can overcome these hurdles and unlock new revenue streams, expand market access, and solidify their role as sustainability leaders. As Kenya continues to refine its carbon market framework and fosters innovation, a future where environmental responsibility and economic growth go hand-in-hand becomes a distinct possibility. This paves the way for a thriving carbon market that empowers Kenyan agribusinesses to become global champions of sustainable and climate-smart agriculture.
