Contact: +91 99725 24322 |
Menu
Menu
Quick summary: Explore the intricate dynamics of the global chilli value chain in our comprehensive blog. Delve into the cultivation, trade, and processing of chillies, and uncover the challenges and opportunities present in this dynamic industry.
The chili industry plays a vital role in global food production and culinary traditions, providing flavor, color, and heat to dishes across cultures. However, like any agricultural commodity, the chili value chain is rife with challenges. For chili producers, exporters, and distributors, managing quality control and ensuring traceability can make or break the success of their operations.
From pest management to post-harvest processing, the road to delivering consistent, high-quality chilies is filled with hurdles that require careful attention and innovative solutions. In this blog post, we’ll explore the key challenges in the chili value chain, particularly around quality control and traceability, and how modern solutions can help address these issues.
Key Takeaways
The global chili market is characterized by significant production, consumption, and trade, with chili being one of the most widely used spices worldwide. Chili is cultivated across various regions, with major producers including India, China, Mexico, and Thailand. The demand for chili is driven by its versatile culinary applications, including seasoning, sauces, and condiments, as well as its use in pharmaceuticals and cosmetics. The market is influenced by factors such as changing consumer preferences, dietary trends, and the increasing popularity of spicy cuisine globally. Additionally, chili trade is significant, with countries importing and exporting chili products to meet domestic demand and capitalize on international market opportunities. Overall, the global chili market is dynamic and diverse, offering opportunities for producers, processors, traders, and consumers alike.
India, known as the “Land of Spices,” holds the title of being the foremost producer and exporter of chillies globally. It boasts the largest cultivation area and is both the largest producer and consumer of dry chillies worldwide. Dry chillies rank among the most widely cultivated spices in India.
Chilli stands out as a highly prized spice crop. India ranks as the foremost producer, consumer, and exporter of Chilli, accounting for approximately 40% of global production. Within India, Andhra Pradesh is the top state for Chilli cultivation.
The initial cultivation and harvesting operations include choosing the suitable chilli kinds, preparing the soil, planting seeds or seedlings, and executing appropriate cultivation measures like irrigation and insect control. Harvesting usually occurs when chilies reach their peak maturity, and it requires precise plucking to assure quality and minimise damage.
The processing and packaging processes begin with cleaning and sorting the harvested chilies, which are then processed using methods such as drying, grinding, or preservation. These methods attempt to improve flavour, texture, and shelf life while adhering to hygienic regulations. Packaging entails selecting appropriate materials and labelling products with critical information like expiration dates and batch numbers to aid traceability and consumer communication.
Distribution and retailing include delivering packaged chilli products to wholesalers, retailers, and straight to customers. Proper handling, storage, and transportation conditions are critical for maintaining product quality and safety during distribution. To match consumer expectations and develop trust in the supply chain, retailers must display chilli items attractively, provide correct product information, and ensure compliance with food safety requirements.
The intermediaries involved in the chilli supply chain are:
Producers play a crucial role in marketing by conducting essential practices such as drying, cleaning, grading, and packing, which significantly impact the value chain. These practices directly influence the price of the produce, which is the ultimate objective of any marketing endeavor. Chilli farmers bring their produce to market only after meticulously drying, grading, and packing them in gunny bags.
Licensed commission agents operate within regulated markets, charging a 2% commission from farmers for their services. They facilitate the trade process by fostering a competitive environment among traders, wholesalers, and processors during price negotiations. While they do not directly engage in trading, commission agents play a crucial role in facilitating trade transactions.
Traders and exporters act as intermediaries in the chili trade, purchasing produce on behalf of wholesalers, exporters, and processors. Their role is pivotal as they ensure a consistent supply of chili throughout the year, requiring cold storage facilities to preserve quality. These intermediaries procure produce based on in-person orders, storing them in nearby cold storage facilities to maintain freshness and meet market demand year-round.
Wholesalers are key players in the chili trade, purchasing large quantities of produce and distributing them in bulk to retailers. While local wholesalers actively participate, those from distant areas rely on traders for procurement due to storage constraints, as they lack cold storage facilities and are dispersed geographically.
Processors are pivotal in the chili value chain, particularly in value addition processes like chili powder production. While Kurnool hosts mainly small-scale processors focusing on powder production, larger corporations such as Priya Foods Ltd, ITC, and MTR also operate, often sourcing directly from farmers or through regulated markets during shortages. Processors in remote areas typically rely on traders to procure chili, ensuring specific quality standards and handling tasks like cleaning, grading, and transportation to the processing facilities, offering convenience to both parties.
Retailers serve as intermediaries between wholesalers, processors, and consumers, receiving chili products in bulk and distributing them in smaller quantities to end consumers across the country. With their widespread presence, retailers act as the primary touchpoint for consumers in accessing chili and chili powder products.
Despite its status as the world’s largest chilli producer, the Indian chilli industry faces a significant challenge in generating substantial trade value. This challenge stems from a lack of awareness about quality standards and reliance on traditional processes, leading to manual errors, insufficient quality production, food loss, unfair trade practices, and human biases in the chilli supply chain.
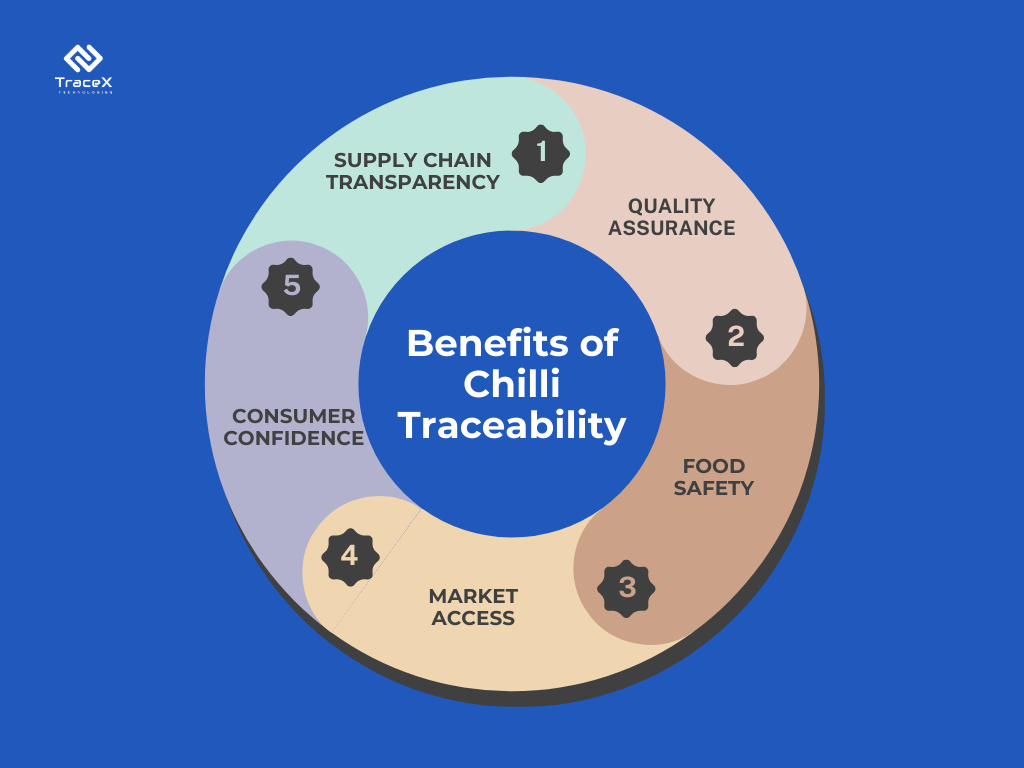
Food safety and quality are critical in the chilli sector for protecting consumers from health concerns and maintaining the reputation of chilli products. Implementing stringent quality control procedures across the supply chain, from cultivation to distribution, helps to avoid contamination, adulteration, and other dangers, ensuring that only safe and high-quality chilies reach the market.
Chilli producers and distributors must meet regulatory requirements and obtain certificates to indicate compliance with food safety standards and laws. Obtaining certifications such as ISO, HACCP, or GMP informs customers and stakeholders that chilli goods follow industry best practices and legal criteria, hence increasing trust and simplifying market access.
Building consumer trust and confidence requires transparent methods, credible information, and consistent product quality. Chilli businesses can boost brand reputation and loyalty by prioritizing food safety, following regulations, and maintaining open communication with customers.
Barcode and QR code technologies are widely utilised in the food business, especially the chilli sector, to provide for effective product tracking and traceability. These systems contain information like as batch numbers, manufacture dates, and origin, allowing stakeholders to rapidly access precise chilli product data via scanners or mobile devices.
Blockchain technology provides a decentralised and immutable ledger system that can transform chilli traceability. Each transaction or event in the chilli supply chain, from farming to sale, is securely and transparently recorded across several nodes, resulting in an immutable record of product history.
RFID tags and IoT devices provide real-time monitoring and tracking in the chilli industry. RFID tags implanted in chilli packaging or containers contain unique IDs that can be read remotely, allowing for accurate inventory management, temperature monitoring, and quality control across the supply chain.
Sustainable sourcing in the chili value chain is crucial because it ensures environmental protection, social equity, and economic viability for farmers. By focusing on sustainable practices, companies help preserve soil health, reduce chemical use, and promote biodiversity. It also supports ethical labor practices, improving the livelihoods of chili farmers. Sustainable sourcing can drive market access, traceability, and meet consumer demand for ethically produced goods while maintaining high-quality yields and minimizing negative environmental impacts. It strengthens supply chain resilience and builds long-term value for all stakeholders.
The TraceX farm management platform enhances traceability through comprehensive pre-harvest and post-harvest management capabilities.
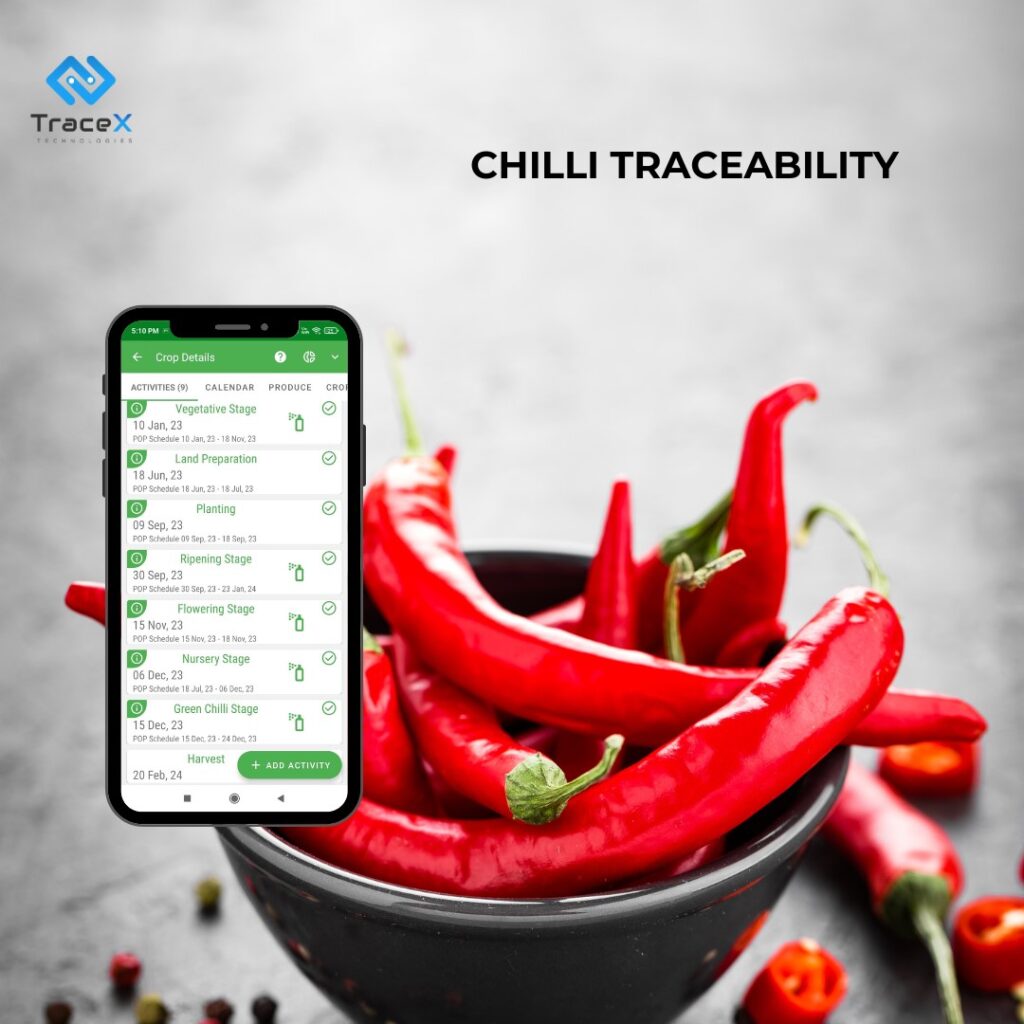
Pre-Harvest: The platform captures critical data such as seed variety, sowing dates, soil health, and agrochemical usage. By digitally recording these aspects, it establishes a strong foundation for traceability and sustainable practices. The TraceX farm management platform drives traceability during the pre-harvest phase through detailed farmer profiling, which includes data on individual growers, their practices, and certifications. It also incorporates farm plot management, mapping specific land parcels and soil data for precision insights.
Post-Harvest: The platform tracks activities like harvesting, processing, storage, and transportation, ensuring product transparency from farm to fork. By integrating data across these stages, it enables end-to-end visibility, fostering compliance, quality assurance, and consumer trust throughout the supply chain.
Overcoming quality control and traceability challenges in the chili value chain is critical for sustainable growth. Leveraging technology-driven traceability solutions enhances transparency, mitigates risk, and boosts trust across stakeholders. By focusing on quality standards, consumer confidence, and ethical sourcing, chili supply chains can drive industry transformation and empower producers.
Common issues include inconsistent grading, contamination risks, and uneven drying or processing methods that impact product standards.
Traceability offers end-to-end supply chain visibility, enhances quality control, reduces risk of adulteration, and increases consumer trust.
Yes, they ensure ethical sourcing, track environmental impacts, and promote fair practices, meeting consumer and regulatory demands.
