Contact: +91 99725 24322 |
Menu
Menu
Quick summary: Explore how ESG in agriculture is driving sustainable food production by promoting environmental responsibility, social equity, and transparent governance for long-term sustainability.

Agriculture sits at the crossroads of feeding the world and preserving the planet. While striving to meet ever-growing food demands, many agribusinesses grapple with ESG in agriculture—balancing environmental impact, social responsibility, and governance standards.
A survey by Accenture found that 72% of agribusiness executives believe that implementing ESG practices can create new business opportunities and drive innovation.
Integrating Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) principles isn’t a mere goal; it’s a necessity. Yet, the challenge? Achieving sustainable impact without disrupting productivity or profitability remains a formidable hurdle. Here’s how ESG strategies can transform this balance, ensuring agricultural resilience and ethical practices.
Key Takeaways
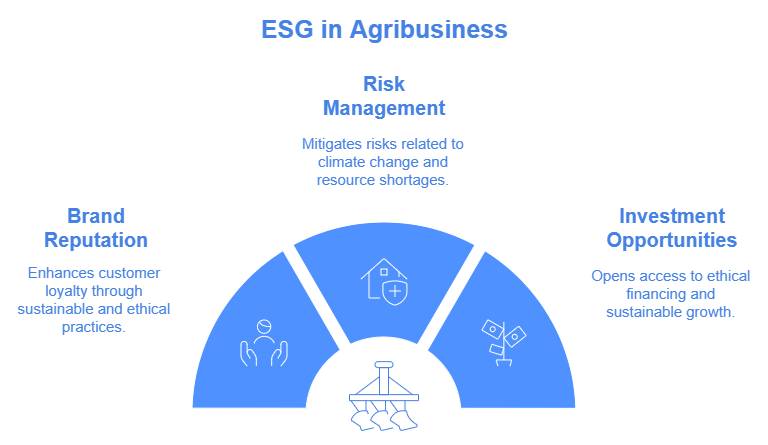
Consumers are becoming more mindful about where their food comes from and how it’s produced. This means agribusinesses need to show they care about the planet and the people behind their products. If you’re a procurement head, this might mean proving ethical sourcing, reducing carbon footprints, or aligning with sustainable standards. When your customers see your efforts, they’re more likely to trust and stay loyal to your brand.
For compliance heads and supply chain managers, the tightening web of global regulations around sustainability can be a real challenge. New laws can require proving ethical labor practices, minimizing emissions, or traceable sourcing. Non-compliance can lead to fines or market exclusion. Adopting ESG measures provides a path to staying ahead of regulations, ensuring your supply chain aligns with emerging standards, and keeping business operations smooth and penalty-free.
ESG integration encourages sustainability, fosters stakeholder trust, improves risk management, and satisfies consumer desires for morally and environmentally responsible products. Embracing sustainability and responsible practices not only helps mitigate environmental challenges but also fosters social inclusion, economic stability and supply chain resilience. By prioritizing ESG considerations, agriculture companies can contribute to a more sustainable and prosperous future for the industry, stakeholders and the planet as a whole.
Reducing Carbon Footprints
Reducing emissions has become a top concern for agribusinesses. Sustainability officers are tasked with finding ways to cut down carbon output from production, processing, and transport. Embracing renewable energy, reducing chemical inputs, and streamlining logistics can help significantly. This can be challenging but essential for meeting internal sustainability goals and market demands.
Sustainable Land and Resource Management
Overuse of land and water threatens long-term productivity. For farmers and agronomists, managing resources sustainably—through crop rotation, soil health measures, or water conservation—is key to thriving ecosystems and better yields.
Climate Change Mitigation Efforts
Agriculture faces direct impacts from climate shifts—unpredictable weather, pests, and droughts. For sustainability leaders, adopting resilient practices like climate-smart crops or precision farming offers both mitigation of climate risks and enhanced productivity, securing a future for all involved.
Ensuring Fair Labor Practices and Rural Development
For agribusiness leaders, addressing fair labor practices is more than compliance—it’s about ethical responsibility. Workers deserve safe conditions, fair wages, and opportunities for growth. Improving these areas also fosters local economic stability and reduces turnover.
Promoting Farmer Welfare and Community Engagement
Agricultural sustainability depends on thriving communities. Procurement and sustainability heads often prioritize farmer welfare programs, offering education, fair pricing, or healthcare support. Engaging with local communities drives trust, improves supply resilience, and supports social equity, ultimately strengthening long-term partnerships and productivity.
Traceability and Supply Chain Transparency
For procurement and sustainability leaders, knowing the origins of agricultural products is crucial. It ensures product quality, aligns with consumer demand for ethical sourcing, and addresses compliance needs. Technologies like blockchain can offer a transparent record, reducing the risk of fraud and bolstering trust across the supply chain.
Ethical Practices and Anti-Corruption Measures
Ethical governance means implementing robust anti-corruption protocols and setting clear standards for fair business practices. This reduces risk, strengthens supplier relationships, and ensures compliance, helping businesses build resilient, reputable supply chains.
In the age of digitization, technology stands out as a game-changer, presenting Farm Management Software (FMS) as a potent instrument to navigate the intricacies of contemporary agriculture. Sustainable farming necessitates more than just sowing seeds; it requires intelligent and effective farm management. From streamlining resource utilization to boosting productivity and environmental responsibility, FMS emerges as a key player. Crucially, farm management software contributes significantly to the progress of sustainable agriculture by elevating efficiency, optimizing resource deployment, and facilitating informed decision-making. It empowers farmers to maximize crop yields, monitor environmental impact, and champion responsible practices, thereby fostering long-term agricultural sustainability.
A leading spice processor, known for its dedication to quality and sustainability, operates from Karnataka, India, with a global reach extending to Vietnam and Turkey. Facing increasing demands for product authenticity and safety, they adopted TraceX’s Sustainability Platform to revolutionize their traceability and compliance efforts.
By leveraging blockchain-driven traceability, the processor achieved transparent end-to-end visibility of its spice supply chain, from farm to fork. This ensured authenticity, enhanced safety measures, and reduced inefficiencies across multiple regions. Additionally, the platform helped align with ESG goals by validating ethical sourcing and sustainable practices.
The results? Improved trust with global partners, streamlined compliance processes, and a robust framework for sustainable growth—setting a new standard in the spice industry.
In the current business environment, considerations related to environmental, social, and governance (ESG) have become pivotal in driving sustainable practices and meeting stakeholder expectations. With the introduction of the Corporate Sustainability and Reporting Directive (CSRD) in the European Union and the associated reporting requirements outlined in the ESRS, there is an increased emphasis on companies enhancing their ESG reporting. This includes transparent disclosure of resource usage, waste management, greenhouse gas emissions, labor conditions, and supply chain transparency.
The landscape of food production is shifting, driven by a rising tide of ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) regulations. From sustainable sourcing and resource usage to fair labor practices and board diversity, food companies must adapt to a new era of transparency and accountability. Understanding these regulations is crucial for ensuring compliance, minimizing operational risks, and seizing the opportunities presented by ethical and sustainable practices. By embracing ESG principles, food companies can build trust with consumers, attract investors, and ultimately contribute to a healthier planet and food system.
The prevalence of data brings about a significant challenge – the fragmentation of data within organizations. Crucial information is scattered across various business functions and systems, making it difficult to integrate and convert into actionable insights. This disjointed data landscape presents multiple business hurdles, especially for organizations striving to enhance business outcomes and harmonize their operations with environmental, social, and governance (ESG) commitments.
Simultaneously, certain companies are proactively collecting specific ESG data, particularly concerning greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. This initiative is driven by the anticipation of upcoming regulations that demand more extensive climate and environmental sustainability disclosures, such as the forthcoming SEC scope 3 emissions disclosure and the EU’s Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD).
However, these regulatory requirements should not be perceived merely as compliance exercises.
Harnessing technology to efficiently extract the necessary information for current and future disclosures empowers organizations to base decision-making on real-time data. Navigating the complex terrain of ESG compliance can be messy, but technology stands as your compass. From automating data collection to streamlining reporting, smart solutions empower you to meet and exceed ESG standards – ensuring sustainability, transparency, and a competitive edge. Embrace tech, chart your course towards responsible practices, and build a future where business thrives alongside our planet and people.
TraceX’s Sustainability platform plays a pivotal role in addressing ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) challenges in agriculture by offering innovative technology solutions that enable traceability, transparency, and accountability across supply chains
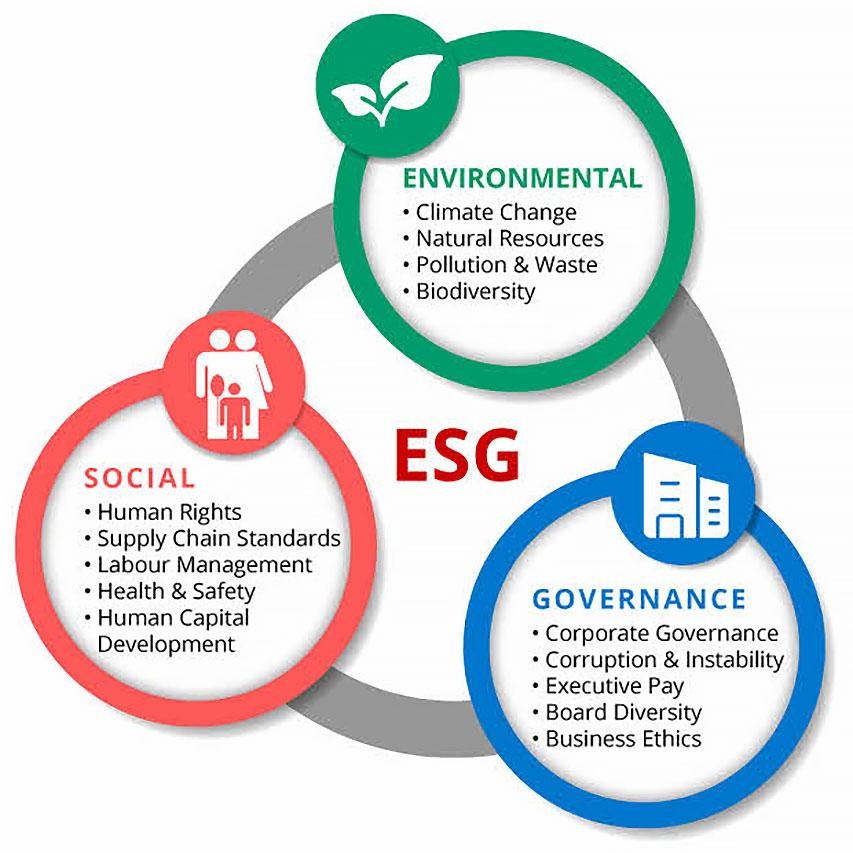
1. Environmental Impact (E):
2. Social Impact (S):
3. Governance (G):
In conclusion, ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) principles are transforming the way agriculture approaches sustainability, driving the industry toward more responsible and ethical food production. By focusing on environmental stewardship, social equity, and transparent governance, agriculture can mitigate its ecological impact, empower local communities, and create more resilient and ethical supply chains. As ESG frameworks continue to gain importance, they offer a roadmap for fostering long-term sustainability in food production, ensuring that future generations benefit from a healthier planet, fairer working conditions, and more secure food systems.
ESG in agriculture refers to the integration of Environmental, Social, and Governance principles in farming and food production practices. It is important because it helps mitigate environmental harm, supports fair labor practices, and ensures compliance with regulations, driving the industry toward more sustainable and ethical practices.
ESG practices improve environmental sustainability by promoting responsible land use, reducing carbon emissions, and encouraging sustainable farming methods. These practices help reduce deforestation, protect biodiversity, and manage water and soil resources more efficiently.
ESG frameworks benefit farmers and agribusinesses by providing access to new markets, improving operational efficiency, ensuring compliance with regulations, and enhancing brand reputation. They also foster better working conditions for farmworkers and create a more transparent, ethical food supply chain.
