Contact: +91 99725 24322 |
Menu
Menu
Quick summary: Discover the essential steps importers need to take for compliance with the EU Deforestation Regulation (EUDR). Learn how to navigate the challenges, ensure traceability, and meet sustainability standards to protect your business and the environment.

As an importer, you’re likely no stranger to the complexities of international trade. But with the European Union’s Deforestation Regulation (EUDR) now in effect, you may be wondering how to ensure your business is compliant. (European Union Deforestation Regulation) EUDR requirements for importers can be daunting for forest-risk commodities. With stringent rules now in place, the stakes are high—non-compliance could mean losing access to a crucial market.
Many importers find themselves overwhelmed by the complexity of supply chains, the need for full traceability, and the pressure to ensure their products are deforestation-free. But with the right tools and a proactive approach, staying compliant is not only possible but can also protect your business’s future.
Large importers and SMEs are prohibited from bringing products into the EU if they originate from agricultural lands deforested after December 30, 2020. By the December 30, 2024 deadline, traders and operators of these products must begin declaring their product components to prove they are not connected to deforested areas.
The EUDR is a groundbreaking regulation aimed at preventing deforestation and promoting sustainable land use practices worldwide. Enacted in response to increasing environmental concerns, the regulation aims to halt the import of products linked to deforestation into the European Union. It applies to a range of products, from timber and soy to palm oil, cattle, rubber, cocoa and coffee. In essence, the EUDR prohibits the sale of products linked to deforestation or forest degradation in the EU market. This law is not just about protecting forests but also about addressing broader environmental challenges, such as climate change and biodiversity loss, which are closely linked to deforestation.
This regulation is significant because it shifts the responsibility onto importers and businesses, making them accountable for ensuring that their supply chains are free from deforestation.
In today’s global marketplace, sustainability is no longer just a buzzword—it’s a necessity. Consumers are increasingly demanding products that are ethically sourced and environmentally friendly. Companies, in turn, are under pressure to prove that their products are sustainable, not just in terms of carbon footprint but also in how they impact the world’s forests. Global trade is at a crossroads where the demand for transparency and accountability is reshaping how businesses operate. As consumers become more informed, they are making choices that reflect their values, opting for products that do not contribute to environmental harm. The EUDR is a response to this shift, emphasizing the need for sustainable sourcing practices that go beyond mere compliance but are integral to a company’s reputation and success.
For importers of forest-risk commodities, EUDR compliance is not just a legal requirement—it’s a critical component of doing business in the EU. Non-compliance can lead to severe penalties, including fines and the prohibition of products from entering the EU market. But beyond the legal ramifications, there is a reputational risk. Companies found to be contributing to deforestation face public backlash, loss of consumer trust, and damage to their brand. Moreover, as global awareness of environmental issues grows, compliance with regulations like the EUDR is becoming a competitive advantage. Importers who can demonstrate that their products are deforestation-free are more likely to win contracts, retain customers, and enter new markets. In essence, EUDR compliance is about securing the future of businesses in a world where sustainability is increasingly non-negotiable.
The regulation distinguishes between large importers and small- and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). Large importers, defined as those with more than 250 employees, a turnover exceeding 50 million euros, or a balance sheet total over 43 million euros, must fulfill comprehensive due diligence and information obligations for all products they import or trade.
On the other hand, SME importers are generally exempt from the full due diligence requirements but are still required to provide specific information. They must demonstrate, for instance, through references, that the products they import were sourced from suppliers not involved in deforestation.
EU countries will conduct on-site checks and risk analyses for EUDR compliance, focusing on high-risk areas for deforestation. Non-compliance could result in fines of up to 4% of the previous year’s sales, confiscation of revenues, or the seizure and refusal of prohibited products at the border.
The EU Deforestation Regulation (EUDR) is a comprehensive framework designed to address the environmental impact of deforestation, particularly in relation to global trade. Understanding its scope is essential for importers who need to navigate this complex regulation while ensuring that their supply chains remain compliant and sustainable.
The EUDR targets specific commodities known to be significant drivers of deforestation. These include:
Soy: Widely used in animal feed and food products, soy production has been linked to large-scale deforestation, especially in regions like the Amazon and Cerrado in Brazil.
Palm Oil: A common ingredient in many everyday products, palm oil production is a leading cause of deforestation in Southeast Asia, affecting biodiversity and contributing to greenhouse gas emissions.
Coffee and Cocoa: Cultivated in tropical regions, the expansion of coffee and cocoa plantations has often led to the clearing of forests, impacting local ecosystems and communities.
Rubber: A critical raw material in the automotive and manufacturing industries, rubber production, particularly in Southeast Asia, has been associated with significant deforestation. Expanding rubber plantations in countries like Indonesia, Thailand, and Vietnam often encroach on tropical forests, leading to habitat destruction, loss of biodiversity, and increased carbon emissions.
Wood: As a raw material, wood is integral to many industries, but unsustainable logging practices have contributed to the depletion of forests worldwide.
Beef and Leather: The cattle industry is another major driver of deforestation, particularly in South America, where forests are cleared for grazing land.
The regulation also extends to partially processed and derivative products, such as leather, chocolate, furniture, paper, beef, and charcoal.
These commodities are targeted by the EUDR because their production processes are closely linked to the loss of forests, which are crucial for maintaining ecological balance. Forests play a vital role in absorbing carbon dioxide, supporting biodiversity, and regulating the water cycle. By focusing on these commodities, the EUDR aims to reduce the EU’s contribution to global deforestation and encourage more sustainable production practices. The EUDR imposes significant responsibilities on importers of the targeted commodities. The regulation requires importers to ensure that the products they bring into the EU do not contribute to deforestation. This involves implementing robust due diligence processes to trace the origin of commodities and verify that they are sourced sustainably.
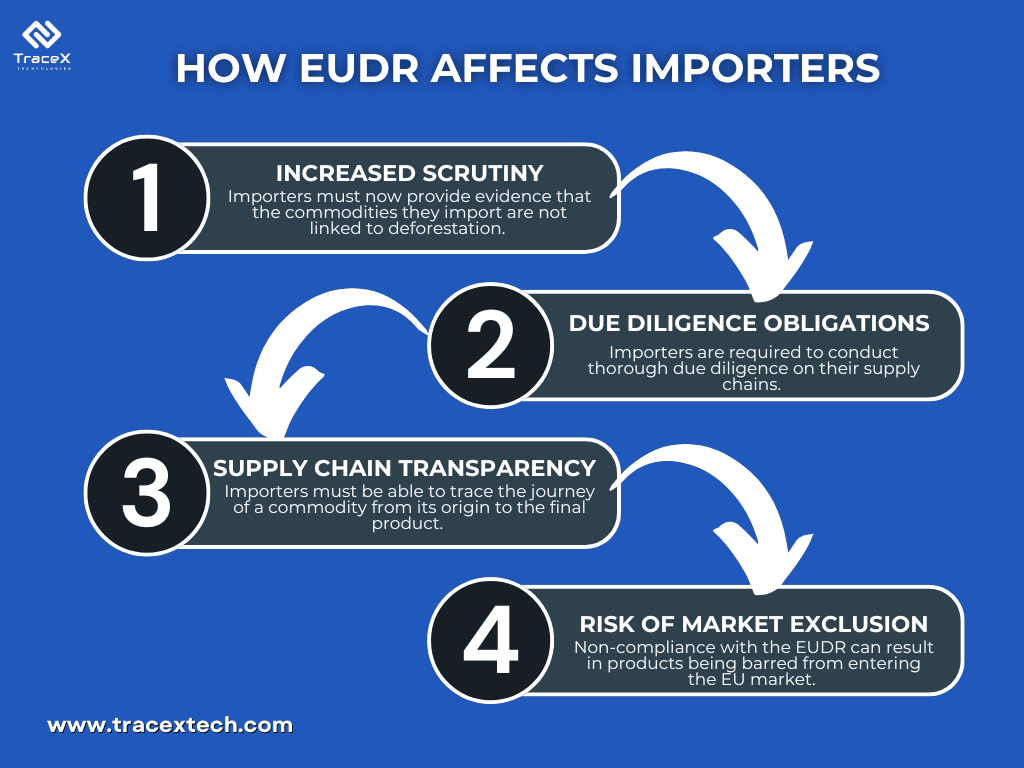
To comply with the EUDR, importers must adopt stringent due diligence measures. This involves identifying the entire supply chain from the point of origin to the final product, evaluating the likelihood that a product has been produced in a way that contributes to deforestation, working closely with suppliers to ensure they adhere to sustainable practices and provide the necessary documentation and utilizing advanced technologies, such as blockchain and satellite monitoring, to enhance traceability and ensure compliance.
Geolocation data is the cornerstone of ensuring that commodities are sourced from deforestation-free areas. For importers under the EUDR, it’s not just about knowing where products originate—it’s about proving it with precision. Importers must collect accurate geolocation coordinates for each plot of land where commodities like soy, coffee, or rubber are produced. This data must be submitted in specific formats, such as GeoJSON, which allows for the precise mapping of land areas. By providing detailed geolocation information, companies can demonstrate that their supply chains do not contribute to deforestation, thereby fulfilling one of the core requirements of the EUDR.
A due diligence statement is a critical document that importers must submit under the EUDR. This statement serves as a formal declaration that the products being imported comply with deforestation-free requirements. It involves rigorous documentation, including the sourcing of raw materials, proof of geolocation, and verification processes. The due diligence statement is not just a bureaucratic formality; it’s a legal requirement that holds companies accountable. Importers must ensure that all necessary documentation is accurate, up-to-date, and readily available for inspection by authorities. This step is crucial for maintaining transparency and demonstrating a commitment to ethical sourcing.
Traceability is the backbone of EUDR compliance, ensuring that every step in the supply chain can be tracked and verified. Importers must implement robust traceability systems that can monitor the movement of commodities from the point of origin to the final product. This involves the use of advanced technologies such as blockchain, which provides a secure and immutable record of transactions. Best practices for achieving traceability include working closely with suppliers to maintain accurate records, utilizing digital platforms for real-time tracking, and regularly auditing supply chains to identify and mitigate risks. By adhering to these traceability standards, companies can ensure that their products are not only deforestation-free but also aligned with broader sustainability goals.

Traceability is at the heart of EUDR compliance, and blockchain excels in this area. By using blockchain, companies can create a digital thread that follows a commodity from its origin to the final product. Every step, from the harvesting of raw materials to the transportation and processing stages, is recorded on the blockchain. This makes it possible to track and verify the entire journey of a product with precision. For instance, if a batch of coffee is sourced from a farm in Brazil, blockchain can verify that the farm meets EUDR standards by providing geolocation data and other relevant information. This data is then permanently recorded, ensuring that any claims about the product’s sustainability can be verified at any point. Blockchain’s role in enhancing traceability thus empowers companies to meet regulatory requirements, avoid penalties, and build consumer trust by offering irrefutable proof of their sustainable practices.
The TraceX EUDR compliance platform is designed to address the complex challenges importers face under the EU Deforestation Regulation. It simplifies the daunting task of managing and verifying the intricate data required to prove that imported commodities are deforestation-free. By leveraging blockchain technology, the platform ensures transparency and traceability across the entire supply chain, from farm to shelf. This helps importers meet strict due diligence requirements, manage geolocation data with precision, and stay up-to-date with evolving regulatory standards. Ultimately, TraceX provides a comprehensive, trustworthy solution that mitigates the risk of non-compliance and builds confidence among stakeholders and regulators.
The complexities of EUDR compliance is a significant challenge for importers, but it’s a crucial step towards sustainable and responsible sourcing. The regulation emphasizes transparency and accountability, requiring businesses to implement rigorous due diligence practices. By understanding and adhering to these requirements, importers not only safeguard their market access but also contribute to the global fight against deforestation. Embracing this responsibility will ultimately foster trust and resilience in your supply chain, aligning your business with the growing global demand for sustainability.
