Contact: +91 99725 24322 |
Menu
Menu
Quick summary: Explore the world of carbon accounting and its pivotal role in mitigating climate change. Discover key strategies, methodologies, and best practices to embrace sustainability and reduce carbon footprints. Dive into the journey towards a greener, more responsible future.

Did you know that over 90% of a company’s emissions often lie hidden in supply chains? This staggering figure highlights a critical challenge: tracking emissions accurately across complex operations. Businesses today face a mounting pressure to measure, manage, and reduce their carbon emissions and navigate the carbon accounting maze.
According to BCG 2021 survey, only 9% of organizations could comprehensively and accurately measure their total GHG.
For many businesses, manual processes, fragmented data, and inconsistent reporting standards makes carbon accounting feel very complex. With the right tools and strategies, you can turn this challenge into a pathway to growth and sustainability. This guide provides actionable insights into simplifying carbon accounting and aligning with global standards.
Key Takeaways
Carbon accounting is like keeping a financial ledger—but instead of tracking money, you’re keeping tabs on the greenhouse gases your business emits. It’s the foundation for any sustainability strategy because you can’t manage what you don’t measure.
Think of it this way: if your goal is to reduce emissions, carbon accounting helps you understand where those emissions are coming from and how big they are. It’s a critical step toward making informed decisions that benefit both your business and the planet.
Carbon emissions are divided into three categories, or “scopes,” to make it easier to track where they come from:
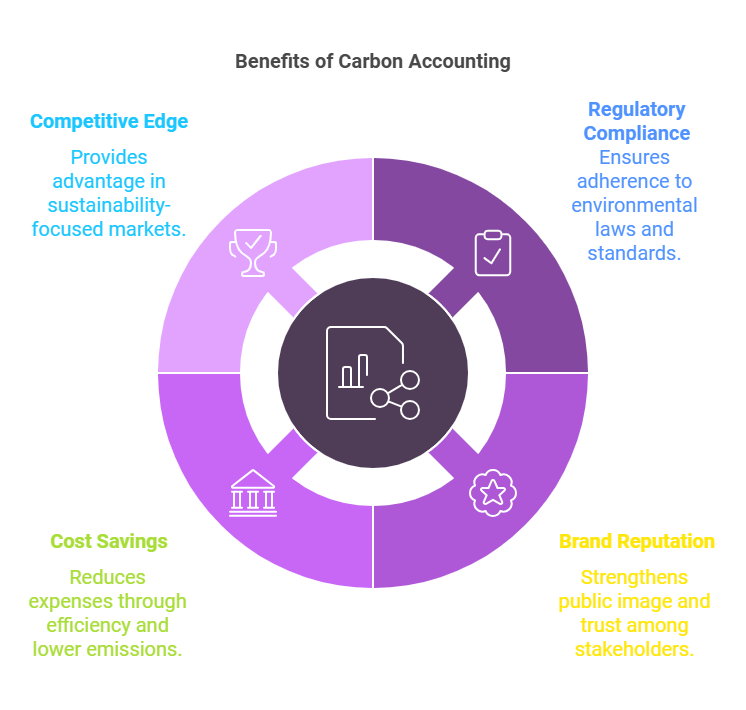
Understanding these concepts isn’t just about compliance—it’s about staying competitive in a world that values sustainability. Whether you’re looking to attract eco-conscious customers, meet regulatory requirements, or create long-term value, carbon accounting is the key to unlocking your business’s greener future.
World is committed to limit global temperature rises to 1.5˚C above pre-industrial levels to counter the climate change GHG emissions need to be halved by 2030 and net zero emissions need to be hit by 2050.
Governments and international organizations are tightening emissions regulations. Carbon accounting helps businesses comply with standards like the EU’s Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) or frameworks like the Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Protocol. Without accurate data, compliance becomes a guessing game.
Sustainability is a competitive advantage. Customers, investors, and partners increasingly favor businesses that demonstrate environmental responsibility. Carbon accounting showcases your commitment to reducing emissions, strengthening trust and brand value.
Measuring emissions often highlights inefficiencies. Whether it’s wasted energy or excessive fuel consumption, carbon accounting helps identify areas to cut costs while reducing your carbon footprint. It’s a win-win for your bottom line and the environment.
With ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) investing on the rise, businesses with transparent carbon data are more likely to attract funding. Carbon accounting signals to investors that you’re serious about sustainability and long-term growth.
As industries evolve toward greener practices, businesses that lag risk falling behind. Carbon accounting positions your company as a leader, ensuring you stay ahead in an increasingly eco-conscious market.
Carbon accounting is the foundation for setting and achieving emissions reduction goals. By understanding your carbon footprint, you can implement strategies aligned with science-based targets, helping combat climate change effectively.
Climate risks like resource scarcity, extreme weather, and regulatory changes are becoming more pressing. Carbon accounting prepares businesses to adapt to these challenges, making operations more resilient and sustainable in the long run.
Carbon accounting isn’t just about numbers—it’s about action. By understanding and managing your emissions, your business can save money, build trust, and create a meaningful impact on the planet. It’s the smart choice for businesses aiming to grow sustainably.

Carbon accounting is a crucial step toward sustainability, but let’s face it—it’s no walk in the park. Many businesses stumble upon challenges that make accurate emissions tracking feel like solving a massive jigsaw puzzle.

The first challenge is sourcing accurate emissions data. With multiple departments, suppliers, and locations involved, data is often scattered, incomplete, or inconsistent.
Why it’s tough: Imagine trying to calculate your monthly expenses, but half the receipts are missing, and some are in a foreign language. That’s what emissions data collection can feel like for many businesses.
How to overcome it: Digital monitoring tools like Digital MRV (Monitoring, Reporting, and Verification) come to the rescue. They centralize data collection, automate processes, and ensure real-time accuracy, making this daunting task much more manageable.
Scope 3 emissions—those indirect emissions from your supply chain—are often the largest and trickiest to track. From raw material suppliers to end-user transportation, the web is vast and tangled.
Why it’s tough: Tracking Scope 3 emissions is like tracing the origin of every ingredient in a recipe served at a buffet. It’s complicated, overwhelming, and prone to errors.
How to overcome it: Digital solutions that offer supply chain mapping and automated data inputs simplify Scope 3 accounting. These tools help you identify hotspots, engage suppliers, and accurately calculate emissions at every stage.
Industries with fragmented supply chains often lack a unified approach to carbon reporting, leading to confusion and inefficiencies.
Why it’s tough: Imagine a group project where everyone uses different formats and languages—it’s chaos. That’s the reality of carbon accounting in many industries.
How to overcome it: Align your practices with globally recognized standards like the GHG Protocol or ISO 14064. Many digital platforms are designed to integrate these frameworks, ensuring consistency and credibility in your reporting.
Digital tools like Digital MRV are game-changers in carbon accounting.
By addressing these challenges head-on, businesses can turn carbon accounting from a headache into a strategic advantage. With the right tools and a clear plan, you’re not just counting carbon—you’re building a roadmap to sustainability, credibility, and long-term success.
When it comes to tackling carbon emissions, a solid framework is your compass. Carbon accounting standards and frameworks guide businesses in measuring, managing, and reporting emissions consistently and credibly.

The Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Protocol is the gold standard for carbon accounting. Think of it as the universal language for emissions measurement.
ISO 14064 provides detailed standards for quantifying and verifying greenhouse gas emissions.
The Science-Based Targets initiative (SBTi) helps businesses set emission reduction goals aligned with climate science.
CDP encourages companies to disclose their carbon emissions, risks, and reduction efforts publicly.
Aligning with global standards like these isn’t just about ticking boxes—it’s about doing things right.
Carbon accounting standards are like a GPS for your sustainability journey. They guide you in the right direction, ensure you don’t take shortcuts, and help you reach your destination with confidence. For businesses serious about tackling emissions and achieving sustainability goals, these frameworks are essential companions.
Start with the basics: Why are you doing carbon accounting? Are you aiming to meet regulatory requirements, enhance your brand’s sustainability, or prepare for investor scrutiny? Clear objectives will shape your strategy.
Next, determine the emissions scope you’ll track:
Data collection is the backbone of carbon accounting. You’ll need input from various departments, suppliers, and logistics partners. This step can be challenging, especially if data is siloed or incomplete.
Gone are the days of managing emissions data with spreadsheets! Technology like Digital MRV platforms simplifies the process by:
Adopt globally recognized frameworks like the GHG Protocol or ISO 14064 to ensure your data is credible and comparable. These standards provide a structured approach to measuring and reporting emissions, making it easier to communicate your efforts to stakeholders.
Transparency is key to building trust with stakeholders. Share your carbon accounting results through sustainability reports, investor presentations, or public disclosures. Partner with third-party auditors to validate your findings, ensuring credibility.
Carbon accounting can seem like an uphill battle, especially when dealing with vast amounts of data from different sources. Enter technology—a game-changer in simplifying and streamlining the process. Let’s explore how digital solutions like TraceX’s Digital MRV platform make carbon tracking not just easier, but smarter.
Traditional methods of tracking emissions often involve manual spreadsheets, endless emails, and data scattered across departments. This is not only time-consuming but also prone to errors. Digital tools like TraceX’s Digital MRV platform centralize all your data in one place, automating the process and reducing manual effort.
Real-time insights are crucial for sustainability heads. With digital platforms, you can monitor your emissions as they happen, enabling quicker decision-making. Imagine spotting a potential issue in your supply chain today instead of discovering it months later in a report.
Reporting emissions for compliance or internal tracking can be a nightmare if done manually. Digital MRV platforms automatically generate accurate reports, formatted to meet global standards like the GHG Protocol. This not only saves time but also ensures consistency and credibility.
One of the biggest challenges in carbon accounting is verifying your emissions data. Digital MRV platforms simplify this by providing structured, transparent data that can be easily reviewed and validated by third-party auditors. This adds credibility to your carbon reduction claims and boosts stakeholder trust.
Tools like TraceX’s Digital MRV platform empower businesses to:
When it comes to carbon accounting, success doesn’t just happen on its own. It requires a strategic approach and commitment from every part of the business.
Carbon accounting isn’t a task that can be handled in isolation. To truly track and reduce emissions, you need to involve everyone in your supply chain. This means collaborating with your suppliers to gather accurate data on their emissions and engaging your customers by providing them with transparent, reliable carbon data.
The world of carbon accounting is full of jargon and complex calculations. To make sure everyone is on the same page, it’s crucial to use standardized metrics and frameworks like the GHG Protocol or ISO 14064. These frameworks help businesses measure, report, and manage their emissions in a consistent and globally recognized way.
Carbon accounting isn’t a one-time effort—it’s a continuous journey. Regular reviews help ensure your strategies remain effective, up-to-date, and aligned with your emissions reduction goals. As your business grows and changes, your carbon accounting strategy needs to evolve too.
Transparency is key when it comes to carbon accounting. Businesses that are open about their emissions, how they’re measured, and their reduction strategies tend to build more trust with customers, investors, and other stakeholders. Regularly sharing progress and challenges demonstrates commitment and builds credibility.
Adopting carbon accounting is no longer just a compliance requirement but a strategic approach to sustainable growth. By accurately measuring, reporting, and reducing emissions, businesses can unlock operational efficiencies, build trust with stakeholders, and contribute to global sustainability goals. The right carbon accounting strategy will not only reduce environmental impact but also enhance your reputation and prepare your business for future challenges. Start today by integrating carbon accounting into your business strategy and be a part of the solution for a greener tomorrow.
Carbon accounting is the process of measuring, reporting, and managing greenhouse gas emissions produced by a business. It is important because it helps businesses track their environmental impact, comply with regulations, and improve operational efficiency while enhancing sustainability.
Businesses can implement carbon accounting by defining their emissions scope (Scope 1, 2, and 3), collecting data from across operations, using technology like Digital MRV for accurate calculations, and aligning with global standards like GHG Protocol for consistency and credibility.
Carbon accounting provides businesses with the insights needed to measure and reduce emissions effectively. By identifying high-emission areas, businesses can target improvements, set reduction goals, and track progress toward sustainability targets, enhancing both environmental and financial performance.
