Contact: +91 99725 24322 |
Menu
Menu
Quick summary: Unveiling the silent threat: Agricultural methane emissions are a major contributor to climate change, impacting our environment, health, and food security. Discover the sources, impacts, and solutions for a sustainable future.

Our food system is facing a silent threat – methane emissions from agriculture. These potent greenhouse gasses contribute significantly to climate change, packing a punch 25 times more powerful than carbon dioxide in the short term. This invisible enemy lurks throughout the agricultural process, from the burps of cows and sheep to the decomposition of rice paddy waste.
The challenge lies in its widespread nature – agriculture accounts for a staggering 32% of human-caused methane emissions globally.
These emissions pose a significant threat not only to the environment but also to the very industry they stem from. Climate change disrupts weather patterns, leading to droughts, floods, and unpredictable growing seasons. This directly impacts crop yields and livestock health, jeopardizing food security and livelihoods for millions. The urgency is clear – we need innovative solutions to tackle agricultural methane emissions and build a more sustainable food system for the future.
While carbon dioxide often dominates climate change discussions, methane emissions from agriculture pose a significant and often overlooked threat. These potent greenhouse gasses, emanating from livestock enteric fermentation (burps and flatulence) and rice cultivation practices, contribute a staggering 32% of human-caused methane emissions globally. Packing a punch 25 times more powerful than carbon dioxide over a 20-year period, their impact on global warming is undeniable. The consequences of inaction go far beyond environmental damage. Climate change, fuelled in part by agricultural methane, disrupts weather patterns, leading to unpredictable growing seasons and extreme weather events like droughts and floods. This directly impacts crop yields and livestock health, jeopardizing global food security and the livelihoods of millions of farmers.
The effects of agricultural methane emissions are not limited to the environment and food security. There’s a clear economic dimension at play as well. Climate change can lead to rising sea levels and disrupted transportation routes, further impacting economic stability in vulnerable regions. Additionally, the methane itself can have detrimental health effects, contributing to respiratory issues in populations exposed to high concentrations. Given their potent environmental impact, disruptive influence on food security, and potential for economic and health complications, methane emissions from agriculture necessitate immediate and comprehensive action. Implementing innovative mitigation strategies is crucial to protect our planet, ensure reliable food production, and safeguard the well-being of populations worldwide.
Agricultural methane emissions are a significant contributor to climate change, a phenomenon causing the Earth’s average temperature to rise. While carbon dioxide is often the central focus, methane plays a critical and often underestimated role.
Over a 20-year period, methane is 25 times more potent at trapping heat than carbon dioxide. While it breaks down faster than CO2, its immediate impact on global warming is substantial. As methane and other greenhouse gasses accumulate in the atmosphere, they trap heat that would normally radiate back into space. This imbalance disrupts global weather patterns, leading to:
The impact of agricultural methane emissions goes beyond temperature increases. Methane contributes to the formation of tropospheric ozone, a ground-level air pollutant. This pollutant can exacerbate respiratory problems like asthma and contribute to smog formation, especially in regions with high agricultural activity.
These environmental consequences of agricultural methane emissions create a ripple effect, impacting everything from agricultural productivity and food security to human health and the overall health of ecosystems. Addressing these emissions is crucial for mitigating climate change and ensuring a sustainable future for our planet.
While the environmental consequences of agricultural methane emissions are significant, the threat extends to human health as well. Methane itself isn’t directly harmful in low concentrations. However, its breakdown in the atmosphere contributes to the formation of ground-level ozone, a potent air pollutant. Ozone irritates the lungs, triggering respiratory problems. Studies suggest a potential link between long-term exposure to air pollutants like ozone and an increased risk of lung cancer. Although less well-understood, some research suggests a possible link between long-term exposure to air pollution and neurological problems.
These health impacts are particularly concerning for populations residing in areas with high concentrations of agricultural methane emissions, such as communities near large livestock farms or rice paddies.
Beyond the environmental and health consequences, agricultural methane emissions pose a significant economic threat:
Climate change, fueled in part by methane emissions, disrupts weather patterns and increases the frequency of extreme weather events. This can lead to:
The combined effects of climate change on crops and livestock can significantly reduce agricultural productivity. This translates to lower output, decreased revenue for farmers, and potential disruptions in global food supply chains. Reduced agricultural productivity due to climate change can lead to food shortages and price hikes, particularly in vulnerable regions. This threatens global food security and can trigger social unrest and economic instability in countries heavily reliant on food imports.
The economic impact of agricultural methane emissions is far-reaching. It affects the livelihoods of farmers, disrupts food supply chains, and creates potential for food shortages and economic hardship. Implementing effective mitigation strategies can help safeguard the agricultural sector, promote food security, and create a more stable global economy.
While agriculture plays a crucial role in feeding the world, it also harbours hidden sources of potent greenhouse gases. Methane emissions are a major concern, and understanding their origins is the first step towards effective mitigation strategies.
1. Livestock (Ruminant Animals):
2. Rice Cultivation:
3. Manure Management:
4. Soil Management:
By understanding these key sources of agricultural methane emissions, we can develop targeted mitigation strategies. This can involve improvements in animal feed management, manure handling practices, rice cultivation techniques, and soil management approaches. Addressing these emissions is crucial for creating a more sustainable food system and safeguarding our planet.
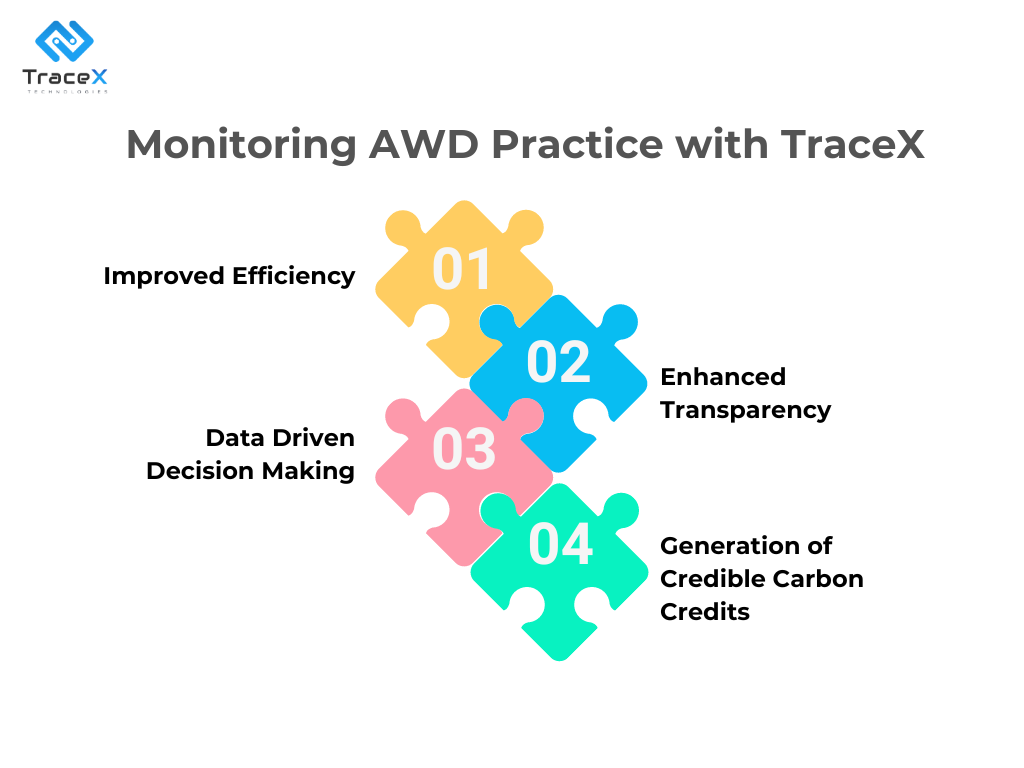
TraceX’s data collection, monitoring, and reporting capabilities, farmers can effectively implement AWD irrigation practices, conserve precious water resources, and contribute to a more sustainable rice production system that minimizes methane emissions.
This allows for real-time data collection on water levels within the paddy, providing farmers and stakeholders with a clear picture of irrigation practices.
Based on pre-defined parameters for AWD practices, TraceX can trigger alerts if water levels deviate significantly from the intended drying and re-wetting cycles. This real-time feedback allows farmers to adjust irrigation practices promptly and ensure proper implementation of AWD.
TraceX utilizes blockchain technology, which creates an immutable record of all data collected. This eliminates the possibility of data manipulation and ensures verifiable proof of AWD implementation. This is crucial for ensuring transparency within the supply chain and verifying claims of sustainable rice production practices.
The sustainability platform can compile and analyze data on AWD practices across various rice farms. This data can be used to generate reports that track adherence to AWD protocols, identify areas for improvement, and measure the overall effectiveness of the practice in reducing water usage and methane emissions.
The impact of methane emissions from agriculture is a complex and multifaceted challenge. It threatens our environment, disrupts weather patterns, jeopardizes food security, and poses health risks. However, despair is not an option. The solutions exist, ranging from improved agricultural practices and innovative manure management techniques to the power of technology platforms.
By embracing these solutions and fostering collaboration between farmers, researchers, policymakers, and consumers, we can build a more sustainable future for agriculture. A future where food production doesn’t come at the cost of environmental degradation, but rather contributes to a healthier planet for generations to come. The time to act is now. Let’s work together to break free from methane’s grip and cultivate a more sustainable future for us all.
