Contact: +91 99725 24322 |
Menu
Menu
Quick summary: Discover how LCA (Life Cycle Assessment) of agriculture value chains offers valuable insights into environmental impacts. Explore the benefits of Trace Carbon, a sustainability and carbon management platform, in accurately measuring and managing sustainability in agricultural activities.

Agriculture is at the heart of our daily lives, but its environmental impact is a growing concern. As the world demands more food with fewer resources, sustainability has become the focal point of innovation. Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) in agriculture is a powerful tool that evaluates the environmental impact of farming practices, from planting seeds to delivering food to the table.
However, there’s a challenge that many in the agricultural sector face. Farmers and agribusinesses often struggle to understand where their biggest environmental impacts lie. Without clear insights, making meaningful changes to improve sustainability feels like shooting in the dark. By uncovering hidden inefficiencies and environmental costs, LCA empowers agriculture to become more sustainable and future-proof, all while meeting the increasing consumer demand for eco-friendly practices.
Key Takeaways
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) is a scientific method used to measure the environmental impact of a product, process, or system throughout its entire lifecycle. In agriculture, this means evaluating every stage of a product’s journey—from planting seeds to harvesting crops, processing, transportation, and even the disposal of waste.
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) plays a significant role in enhancing climate resilience in agriculture by providing a holistic view of the environmental impacts across the entire agricultural supply chain. Understanding LCA helps identify inefficiencies and environmental hotspots in agricultural processes. For example, a farmer might discover that most emissions come from fertilizer use or that water consumption could be reduced with better irrigation practices. By focusing on these areas, agribusinesses can reduce their environmental footprint, save costs, and align with global sustainability goals.
This holistic approach provides actionable insights to create more sustainable food systems, benefiting both producers and consumers.
LCA helps to quantify and assess the carbon footprint, water usage, and other environmental factors tied to agricultural practices. By identifying areas where climate risks, such as water scarcity or high carbon emissions, are most pronounced, farmers can adjust their practices to build resilience against climate impacts. For instance, LCA can highlight areas where switching to more water-efficient irrigation methods or reducing fertilizer usage could mitigate the risk of drought or soil degradation, which are exacerbated by climate change.
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) is a powerful tool for quantifying the environmental impact of agricultural practices. It allows stakeholders to measure key sustainability metrics such as greenhouse gas emissions, water usage, and energy consumption across the entire agricultural lifecycle. For example, farmers can identify which processes, like fertilizer use or transportation, contribute the most to their carbon footprint. Policymakers can use LCA data to create informed regulations and incentives that promote sustainable farming. Meanwhile, consumers benefit from greater transparency, enabling them to make eco-friendly choices when purchasing food.
LCA supports decisions that promote sustainable land management, such as crop rotation, agroforestry, and reduced tillage. These practices improve soil health and increase its ability to store carbon, thus enhancing resilience to climate shocks like floods, droughts, and heatwaves. By assessing the full environmental impact of farming practices, LCA helps identify practices that not only reduce emissions but also strengthen land and ecosystem health, making them more resilient to changing weather patterns.
LCA plays a critical role in meeting global sustainability objectives like the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). By highlighting areas for improvement in resource use and emissions, LCA directly supports goals like Climate Action (SDG 13) and Responsible Consumption and Production (SDG 12). Additionally, it aligns with climate action initiatives like carbon neutrality pledges, helping agribusinesses reduce their environmental impact while meeting international sustainability standards.
For businesses, adopting LCA practices isn’t just about compliance; it’s a strategy to stand out. Demonstrating a commitment to sustainability enhances brand value, builds consumer trust, and opens doors to new markets that prioritize eco-friendly products. Agricultural products with proven sustainable credentials often fetch a premium price, creating financial benefits for producers and brands alike. Whether it’s marketing a product as carbon-neutral or emphasizing water-efficient farming methods, the insights from LCA can transform sustainability into a unique selling point.
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) equips farmers with actionable insights to make smarter decisions on resource use. By pinpointing inefficiencies—such as excessive fertilizer application or water wastage—LCA helps optimize these inputs, leading to lower operational costs. Additionally, better resource management enhances soil health and reduces water contamination, creating long-term benefits for farm productivity and environmental stewardship. It’s a win-win for farmers: reduced expenses coupled with improved sustainability.
For agribusinesses, LCA is a crucial tool for staying compliant with increasingly strict environmental regulations and sustainability standards. It helps in identifying and mitigating the environmental impacts of their supply chain, from sourcing raw materials to distributing products. By improving transparency, businesses can demonstrate accountability to stakeholders and gain a competitive edge in markets where sustainability is a key differentiator. LCA also aids in achieving certifications and eco-labels, further boosting brand credibility.
Today’s consumers demand more transparency about how their food is produced. LCA allows agribusinesses to share detailed insights into the environmental footprint of their products, fostering trust and loyalty. When consumers know they’re purchasing items that are sustainably produced, it aligns with their values, encouraging them to support brands that care for the planet. This informed choice creates a deeper connection between consumers and producers, driving demand for sustainable products.
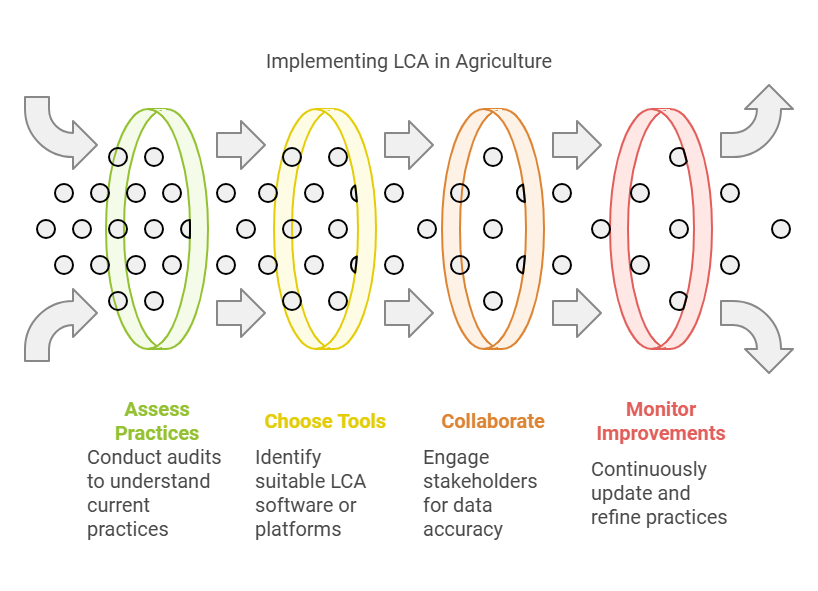
Blockchain technology is transforming how Life Cycle Assessments (LCA) are conducted in agriculture by providing end-to-end transparency across supply chains. With blockchain, every stage of a product’s journey—from sourcing raw materials to its final distribution—can be securely documented and traced. This ensures that all data inputs used for the LCA are accurate, verifiable, and tamper-proof. For example, farmers can log their use of fertilizers or water resources, and processors can record their energy consumption, creating a complete and trustworthy dataset for environmental impact analysis.
Satellite technology is another game-changer for LCA in agriculture. Satellites provide real-time data on various environmental metrics, such as land use, soil health, crop growth, and water consumption. This data offers a macro-level view of agricultural practices and helps quantify impacts like deforestation, carbon emissions, or water depletion. By integrating satellite imagery with LCA tools, stakeholders can identify high-impact areas and prioritize sustainability efforts more effectively. For instance, a farmer using satellite data can monitor soil quality and make data-driven decisions to reduce over-fertilization.
TraceX Farm Management Platform: Enhancing Data Accuracy and Transparency
The TraceX Farm Management Platform provides a unified solution to track and document every stage of agricultural production, ensuring precise and verifiable data for LCA. Key features include:
By streamlining data collection and verification, the platform eliminates one of the major challenges in LCA—reliable data.
The Digital Monitoring, Reporting, and Verification (DMRV) platform is tailored to quantify and report environmental impacts effectively.
Together, these platforms empower stakeholders in agriculture to adopt LCA seamlessly, providing actionable insights to enhance sustainability while maintaining compliance with environmental goals.
In conclusion, Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) serves as a powerful tool in measuring the environmental impact of agricultural practices, offering valuable insights to help the sector move toward sustainability. By assessing inputs, processes, and outcomes from “cradle to grave,” LCA allows farmers, agribusinesses, and policymakers to identify areas for improvement in resource use, carbon emissions, water consumption, and biodiversity conservation. As the global demand for sustainable practices grows, adopting LCA in agriculture not only helps meet regulatory requirements but also enhances brand reputation, reduces environmental footprints, and fosters long-term sustainability for the planet and future generations.
LCA in agriculture is a method used to assess the environmental impacts of agricultural products or practices throughout their entire life cycle—from production to disposal. It evaluates factors such as carbon footprint, water usage, and ecosystem health.
LCA helps farmers identify areas where resources are being wasted, such as water, energy, and fertilizers, which can then be optimized. This leads to cost savings, more efficient resource use, and healthier soil and crops.
The key environmental impacts assessed by LCA include carbon emissions, water consumption, energy use, land use, and effects on biodiversity. By identifying these impacts, farmers can make more informed decisions to mitigate negative effects on the environment. Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) strongly advocates for climate-smart agriculture (CSA) by providing a framework to measure and minimize the environmental impacts of agricultural activities.
