Contact: +91 99725 24322 |
Menu
Menu
Quick summary: Explore how the food and agriculture sectors play a pivotal role in advancing the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and driving global sustainability.

Being a complex web of activities, can the food and agriculture industry be transformed to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)? If you’re passionate about sustainability and want to make informed choices about the food you consume, you might be wondering how the industry can align with the SDGs.
In a world grappling with food security challenges, environmental concerns, and complex socio-economic issues, the pursuit of Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) is more crucial than ever. Food and agriculture, as two of the most fundamental elements of human existence, stand at the heart of this transformation.
From ending poverty and hunger to responding to climate change and sustaining our natural resources, food and agriculture lies at the very heart of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development.
Join us on a journey to explore how innovation, technology, and sustainable practices are coming together to reshape the landscape of food and agriculture, paving the way for a future where we can nourish the world while safeguarding the planet.
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are a set of 17 global objectives established by the United Nations to address pressing global challenges, including poverty, inequality, climate change, and environmental degradation. They serve as a universal call to action to promote economic, social, and environmental sustainability, guiding international efforts to create a more equitable and sustainable world by 2030.
Food and agriculture play a pivotal role in achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) by addressing hunger, promoting sustainable farming practices, and mitigating climate change. They contribute to ending poverty (SDG 1), ensuring zero hunger (SDG 2), promoting good health (SDG 3), and supporting economic growth (SDG 8). Sustainable agriculture practices also help conserve ecosystems and reduce inequalities (SDG 15) while combating climate change (SDG 13) through responsible land and water management.
Global food production holds immense significance as it sustains human life and impacts economies, health, and the environment worldwide. It ensures food security, influences international trade, and is central to livelihoods for billions. Sustainable practices are crucial for environmental preservation, biodiversity, and climate change mitigation, making food production a global priority in achieving the Sustainable Development Goals and addressing interconnected global challenges.
Agriculture significantly impacts environmental and social factors. It can lead to deforestation, water pollution, and habitat loss, contributing to climate change and loss of biodiversity. On the social front, it influences livelihoods, food security, and economic development, both positively and negatively. Sustainable agricultural practices are essential to mitigate negative environmental effects and improve social equity and well-being.
The 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are a universal call to action adopted by the United Nations to address global challenges by 2030. They encompass eradicating poverty, ending hunger, and promoting health and education (Goals 1-4). Additionally, the SDGs focus on gender equality, clean water, affordable and clean energy, decent work, industry, and innovation (Goals 5-9). They also address reducing inequalities, sustainable cities, responsible consumption and production, climate action, life below water, and life on land (Goals 10-15). Lastly, they emphasize peace, justice, and strong institutions, and partnerships for the goals (Goals 16-17), aiming to create a more equitable and sustainable world.
Several Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are directly related to food and agriculture. SDG 2 focuses on Zero Hunger, aiming to end hunger, achieve food security, improve nutrition, and promote sustainable agriculture. SDG 12, Responsible Consumption and Production, addresses sustainable food systems and reducing food waste. SDG 13, Climate Action, connects agriculture to climate change mitigation and adaptation. SDG 15, Life on Land, highlights the importance of protecting terrestrial ecosystems and biodiversity, often impacted by agriculture. These goals collectively underscore the pivotal role of food and agriculture in achieving broader sustainable development objectives.
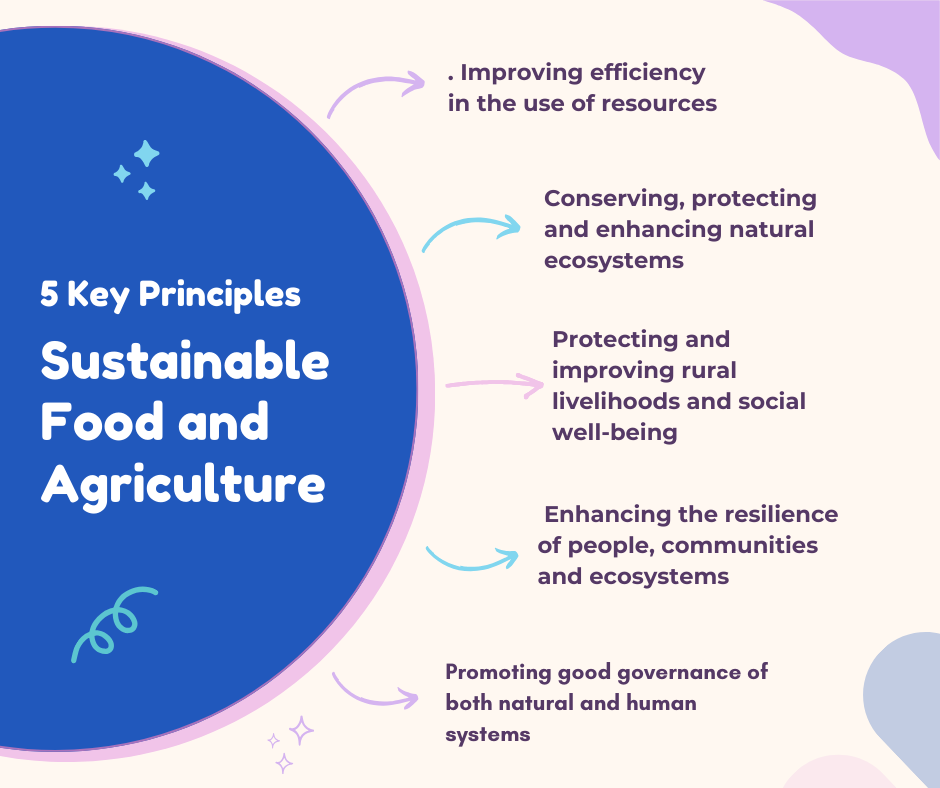
Adapting agriculture to climate change is essential for food security. This involves implementing resilient crop varieties, adjusting planting times, and managing water resources effectively. Sustainable practices, such as agroforestry and soil conservation, can help mitigate the impacts of changing climate conditions. By incorporating these strategies, agriculture can become more resilient and capable of producing food in the face of a shifting climate, ensuring global food security.
Climate-resilient techniques include crop diversification to reduce risks, water-saving technologies, such as drip irrigation, to manage scarce resources efficiently, and the adoption of drought-resistant crop varieties. Sustainable land management practices, like terracing and reforestation, help combat soil erosion and provide ecosystem services. These strategies collectively enhance the ability of agriculture to withstand climate fluctuations.
To reduce greenhouse gas emissions in agriculture, practices like no-till farming, improved manure management, and optimizing fertilizer use can lower methane and nitrous oxide emissions. Utilizing renewable energy sources for machinery, reducing food waste, and promoting sustainable land use can further mitigate the agricultural sector’s contribution to climate change.
Biodiversity and Ecosystems
Conserving biodiversity in agriculture involves practices like maintaining diverse crop varieties, preserving natural habitats within agricultural landscapes, and reducing the use of chemical pesticides and fertilizers. By promoting pollinator-friendly habitats and crop rotation, biodiversity is protected, and ecosystems are sustained, which benefits agriculture and the environment.
Agriculture can have significant impacts on ecosystems, including deforestation, habitat loss, and soil degradation. Pesticides and excessive water use can harm biodiversity, while livestock farming contributes to greenhouse gas emissions. Sustainable farming practices are essential to mitigate these negative effects and promote the coexistence of agriculture and healthy ecosystems.
Sustainable land management involves responsible use of resources to prevent soil erosion and degradation. Reforestation complements this by planting trees in degraded areas to restore forests and improve biodiversity. These practices contribute to climate mitigation, reduce desertification, and enhance ecosystem health, making them essential components of sustainable land management.
Addressing post-harvest losses is crucial to food security. It involves efficient handling, storage, and transportation of agricultural products to prevent spoilage and waste. Improved infrastructure, technologies, and better market access help reduce losses, ensuring more food reaches consumers and reducing the environmental impact of unnecessary production.
Responsible consumption and reducing food waste involve mindful use of resources. It includes efficient meal planning, better storage practices, and efforts to rescue surplus food for distribution. These strategies reduce the environmental footprint of food production and enhance sustainability by conserving resources and minimizing the negative impact of discarded food.
Technology plays a pivotal role in sustainable agriculture. Precision farming tools, like drones and sensors, improve resource management and reduce waste. Genetic engineering and biotechnology can create drought-resistant and disease-tolerant crops, enhancing resilience. Additionally, data analytics and blockchain enable supply chain transparency, ensuring ethical and sustainable practices in agriculture.
Innovative solutions for food production encompass vertical farming, hydroponics, and aquaponics to maximize yields in limited spaces. Genetic modification and gene editing enhance crop traits. Agtech platforms utilize data and AI for precision farming. Sustainable protein sources like lab-grown meat and insect farming reduce environmental impact. These innovations address the global food challenge sustainably.
TraceX blockchain traceability solutions play a pivotal role in transforming the food and agriculture sector to align with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). These solutions offer end-to-end visibility and transparency throughout the supply chain, ensuring responsible production and consumption. By tracking products from farm to table, they help in reducing food waste, enhancing sustainability, and fostering fair trade practices. Additionally, the data-driven insights provided by TraceX enable informed decision-making for more efficient resource management and sustainable agricultural practices. All of these contributions actively support various SDGs related to food security, sustainable agriculture, and responsible consumption and production.
Providers of technology solutions have the advantage of offering sustainable innovations to meet the increasing need for eco-friendly products, thus enhancing the overall well-being and adaptability of agricultural systems.
Partnerships and Collaboration
Governments play a central role in setting policies, regulations, and funding for SDGs. NGOs provide grassroots support, advocacy, and aid to implement SDG initiatives, fostering social equity. Businesses, through sustainable practices, innovation, and responsible supply chains, drive economic growth aligned with SDGs. Collaboration among these stakeholders is essential to address global challenges, as governments set the framework, NGOs drive community-level change, and businesses align profit motives with sustainability, collectively advancing progress toward the Sustainable Development Goals.
Collaborative efforts for sustainable food and agriculture involve partnerships between governments, farmers, NGOs, and the private sector. These collaborations promote responsible land and water management, reduce food waste, and encourage eco-friendly practices. They address issues like climate resilience, biodiversity preservation, and equitable access to resources, working together to ensure food security and environmental sustainability while advancing the Sustainable Development Goals.
Conclusion
In conclusion, sustainable food and agriculture practices are vital for addressing global challenges such as food security, environmental preservation, and climate change. By embracing responsible techniques, reducing waste, and fostering collaboration among governments, NGOs, and businesses, we can collectively work towards a more equitable and sustainable world, while advancing the Sustainable Development Goals and securing the well-being of current and future generations.
