Contact: +91 99725 24322 |
Menu
Menu
Quick summary: Explore how sustainable sourcing in agribusiness enhances environmental health, social equity, and economic viability. Learn about transparent supply chain practices, certified suppliers, and advanced technologies that help businesses meet global sustainability goals and drive positive change.

Agribusinesses today face a critical challenge: how to feed a growing population without depleting the planet’s resources. As consumers demand more transparency and sustainability, sourcing practices are under intense scrutiny. The hook? Sustainable sourcing isn’t just a “nice to have” anymore—it’s a business necessity.
Unsustainable farming practices are leading to deforestation, soil degradation, and water scarcity, threatening the long-term viability of the very resources agribusinesses depend on. Without a shift to sustainable sourcing, the future of food security—and your business—hangs in the balance.
Is your supply chain part of the solution, or contributing to the problem?
According to a recent study, 87 % of consumers are willing to purchase products that are sustainably sourced.
Key Takeaways
Sustainable sourcing is the practice of selecting suppliers, materials, and processes that minimize harm to the environment while supporting social and economic well-being. It’s about ensuring that every stage of the supply chain—whether it’s growing, harvesting, processing, or distributing—follows practices that are responsible, ethical, and sustainable for the long term. Sustainable sourcing helps reduce the carbon footprint by prioritizing low-impact practices and materials, thereby minimizing greenhouse gas emissions throughout the supply chain.
1.Environmental Protection: This involves choosing methods that reduce pollution, conserve natural resources, and promote biodiversity. For example, sourcing materials from farms that avoid deforestation or use water-saving technologies is a step towards sustainability. Sustainable sourcing fosters low carbon supply chains by selecting eco-friendly materials and practices that reduce overall greenhouse gas emissions.
2. Social Responsibility: Sustainable sourcing ensures fair labor practices, supports local communities, and promotes the well-being of workers. It’s about ensuring that people involved in the supply chain are treated fairly and have safe working conditions.
3. Economic Viability: For sustainable sourcing to be effective, it must also make financial sense. This means creating resilient supply chains that can adapt to changes, reduce long-term costs, and ensure that everyone involved—from producers to consumers—benefits economically.
Achieving sustainable sourcing isn’t just about focusing on one aspect. It requires finding the right balance between environmental protection, social responsibility, and economic growth. For example, while organic farming might be better for the environment, it also needs to ensure fair wages for farmers and affordable prices for consumers. Striking this balance ensures that sustainability is truly impactful and long-lasting.
Sustainable sourcing is more than just a corporate responsibility; it aligns with global sustainability efforts like the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and the Paris Agreement. These frameworks call for reducing environmental impact, addressing climate change, and ensuring equitable growth. By embracing sustainable sourcing, companies can contribute to goals such as combating climate change (SDG 13), ensuring responsible consumption and production (SDG 12), and promoting decent work and economic growth (SDG 8).
Sustainable sourcing is not just about making the right choice today; it’s about ensuring a healthier planet and a more equitable world for future generations.
Sustainable sourcing isn’t just about doing what’s right for the environment—it’s also about meeting critical regulations that are shaping the future of global trade. With growing awareness around deforestation, climate change, and ethical labor practices, governments and international bodies have implemented strict rules to ensure companies adopt responsible sourcing practices. Two major frameworks that businesses in agribusiness and other industries must comply with are the EU Deforestation Regulation (EUDR) and Union for Ethical BioTrade (UEBT) standards.
The EUDR aims to curb deforestation driven by the production of certain commodities, like soy, palm oil, beef, and coffee, by ensuring that products entering the European market do not contribute to illegal deforestation. Under this regulation, businesses must:
For agribusinesses, this means keeping a close eye on where raw materials are sourced, ensuring transparency from farm to market, and using technology like blockchain to trace the journey of their products. Compliance with EUDR is essential not just for avoiding penalties but also for aligning with European consumers’ increasing demand for environmentally responsible products.
UEBT is another crucial certification focused on ethical sourcing of biodiversity-based products. It ensures that companies are sourcing ingredients in a way that respects people and biodiversity, by:
Meeting UEBT standards is essential for businesses committed to ethical sourcing, ensuring that they are both protecting the ecosystems they rely on and supporting local communities. This certification is particularly relevant for businesses in sectors like agriculture, cosmetics, and food.
With these regulations in place, compliance is no longer optional—it’s a necessity. Companies must:
By aligning with global standards like the EUDR and UEBT, businesses can not only avoid regulatory risks but also build consumer trust, boost brand reputation, and position themselves as leaders in the sustainability movement. Sustainable sourcing is about creating long-term value for both the business and the planet, ensuring that future generations can thrive.
Adopting sustainable sourcing is a crucial step for agribusinesses aiming to minimize their environmental impact and meet regulatory standards. However, the journey to sustainability is fraught with challenges that can make the transition daunting.
Agribusinesses often operate within vast and intricate supply chains that span multiple countries and involve numerous intermediaries. Tracking the journey of raw materials from farms to consumers can be incredibly complex, particularly when dealing with global networks. Lack of transparency in these supply chains makes it difficult to ensure that every step adheres to sustainable practices. Without clear visibility, it’s challenging to verify whether suppliers are following ethical and environmental standards, leading to potential risks of non-compliance and greenwashing.
Obtaining certification for sustainable practices—such as organic or fair-trade labels—can be costly and resource-intensive. These certifications often require significant investments in new technologies, process changes, and rigorous audits. For many agribusinesses, especially smaller operations, the financial burden and administrative requirements can be overwhelming. Additionally, there’s often a learning curve involved in understanding and implementing these standards, which can further strain resources.
Many agribusinesses source materials from smallholder farmers and suppliers located in remote or developing regions. Engaging with these suppliers poses its own set of challenges. Smallholder farmers might lack the resources or knowledge to adopt sustainable practices, and logistical issues can complicate supply chain management. Building relationships with these farmers requires significant effort, support, and investment in capacity-building to ensure they can meet sustainability requirements. Additionally, infrastructure limitations in remote areas can hinder the ability to implement and monitor sustainable practices effectively.
In the quest for sustainable sourcing, technology plays a pivotal role in transforming how agribusinesses manage their supply chains.
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing the way we track and verify the origins of products. Think of it as a digital ledger where every transaction—from farm to table—is recorded in a secure, immutable way. This means that every step a product takes can be traced back, ensuring that it meets all sustainability and ethical standards. For agribusinesses, this transparency is crucial. It helps in verifying that suppliers are complying with environmental regulations, preventing fraud, and building trust with consumers. With blockchain, companies can confidently assure their customers that their products are truly sustainably sourced.
Satellite and AI technologies offer powerful tools for monitoring and managing agricultural practices from space. Satellites provide real-time data on land use, deforestation, crop health, and water usage, giving businesses a bird’s-eye view of their environmental impact. AI algorithms can analyze this vast amount of data to predict trends, identify potential issues, and optimize resource use. For agribusinesses, this means they can proactively manage their environmental footprint, detect illegal deforestation activities, and ensure that land management practices are sustainable. These technologies make it possible to monitor and adjust practices on the fly, promoting greater environmental stewardship.
Digital Monitoring, Reporting, and Verification (MRV) systems are transforming how companies track and report their carbon emissions and sustainability efforts. These systems use advanced technologies to collect data on greenhouse gas emissions, energy use, and other environmental metrics in real time. This data is then analyzed to ensure that sustainability goals are being met and to provide accurate, transparent reporting. For agribusinesses, Digital MRV simplifies compliance with regulations and helps demonstrate their commitment to reducing carbon footprints. It also provides actionable insights to improve sustainability practices and make data-driven decisions.
Transitioning to sustainable sourcing can seem like a daunting task, but breaking it down into manageable steps can make the process smoother and more effective.
1. Mapping the Supply Chain for Sustainability Risks
The first step in transitioning to sustainable sourcing is understanding where your products come from and how they’re produced. This means mapping out your entire supply chain—from the raw materials at the farm level to the final product that reaches consumers. By identifying every link in the chain, you can pinpoint potential risks related to environmental impact, labor practices, and supply chain disruptions. For example, you might discover that a key supplier is involved in deforestation or that certain production practices are leading to excessive water use. This visibility allows you to address these issues directly, prioritize areas for improvement, and ensure that your sourcing practices align with sustainability goals.
2. Building Partnerships with Certified Sustainable Suppliers
Once you’ve mapped out your supply chain and identified risks, the next step is to build relationships with suppliers who meet sustainable and ethical standards. Look for suppliers who have certifications from recognized organizations, such as organic, fair-trade, or other sustainability certifications. These certifications ensure that the suppliers adhere to specific environmental and social practices. Establishing strong partnerships with these certified suppliers not only helps you meet your sustainability targets but also fosters a more resilient supply chain. Working together with these suppliers, you can collaborate on improvements, share best practices, and drive innovation in sustainable sourcing.
3. Implementing Technology for Monitoring and Transparency
To ensure that your sustainable sourcing practices are effectively managed and communicated, technology is your best ally. Implementing tools such as blockchain for traceability, satellite and AI for monitoring land use, and digital MRV systems for carbon tracking can greatly enhance transparency and accountability. These technologies allow you to track the journey of your products in real-time, verify that sustainability standards are being met, and make data-driven decisions. For instance, blockchain can provide an unalterable record of each transaction in your supply chain, while AI can help analyze environmental impact and identify areas for improvement. By integrating these technologies, you can maintain a high level of transparency, manage risks more effectively, and demonstrate your commitment to sustainability to both regulators and consumers.
TraceX’s EUDR Compliance and Digital MRV (DMRV) platforms are pivotal tools in ensuring that sustainable sourcing practices are not only implemented but also validated with precision.
TraceX’s EUDR Compliance platform is designed to help businesses meet the stringent requirements of the EU Deforestation Regulation (EUDR). This platform provides comprehensive tools for:
The platform utilizes blockchain technology to create an immutable and transparent record of every step in the supply chain. From farm to final product, every transaction is recorded, allowing businesses to verify that their products are sourced from deforestation-free areas.
The platform enables businesses to map their entire supply chain, identifying potential risks related to deforestation and land use. By providing detailed insights into where materials are sourced and how they are processed, the platform helps businesses manage and mitigate sustainability risks effectively.
The platform supports the verification of compliance with EUDR by providing robust reporting tools. Businesses can generate detailed reports showing adherence to deforestation-free requirements, helping to ensure that they meet regulatory standards and can provide evidence of their sustainable sourcing practices.
TraceX’s Digital MRV (DMRV) platform plays a crucial role in managing and validating carbon emissions within sustainable sourcing practices.
DMRV technology allows for real-time monitoring of carbon emissions and other environmental metrics. By collecting and analyzing data from various sources, the platform helps businesses track their carbon footprint and ensure that their sourcing practices are aligned with sustainability goals. The platform facilitates accurate reporting of carbon emissions and sustainability efforts. With detailed, verifiable data, businesses can demonstrate their commitment to reducing their environmental impact and comply with reporting requirements set by regulations and standards.
DMRV provides actionable insights into how sourcing practices affect carbon emissions and environmental performance. This information helps businesses make informed decisions to optimize their practices, reduce their carbon footprint, and enhance their overall sustainability efforts.
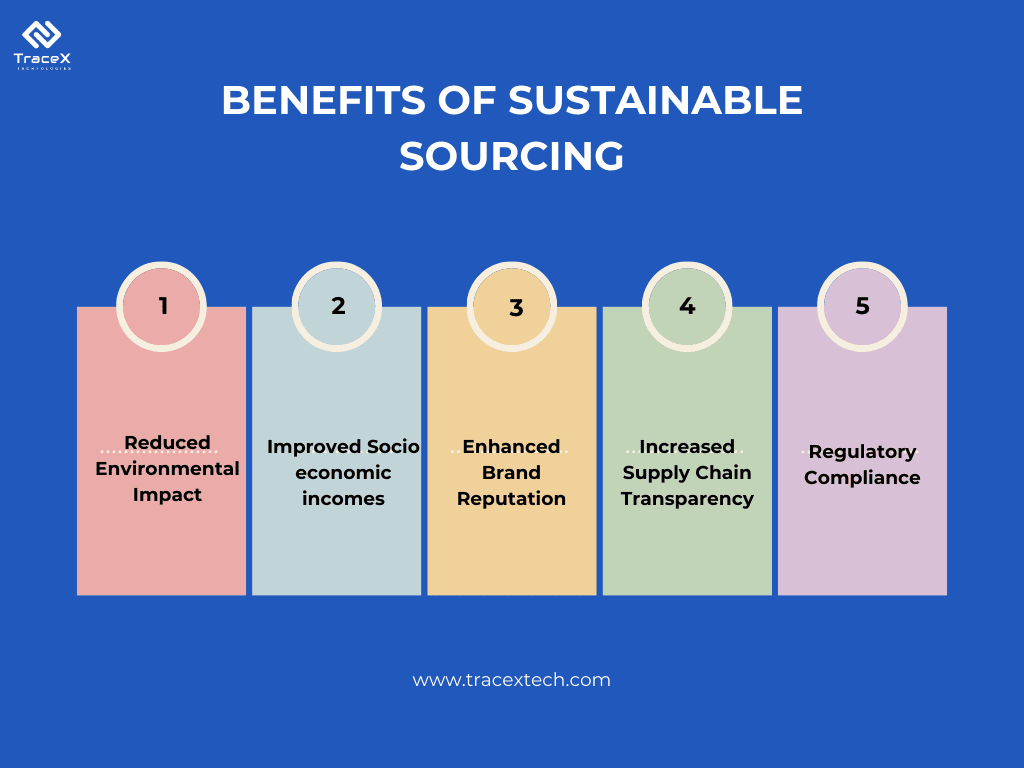
Sustainable sourcing in agribusiness is a critical strategy for ensuring long-term environmental health, social equity, and economic viability. By integrating transparent supply chain practices, partnering with certified suppliers, and adopting advanced technologies, agribusinesses can effectively manage their environmental impact and meet global sustainability goals. Sustainable sourcing not only helps in complying with regulations but also enhances brand reputation and fosters consumer trust. As the industry continues to evolve, embracing these practices will be key to driving positive change and securing a sustainable future for all stakeholders.
Sustainable sourcing in agribusiness involves selecting and managing suppliers and materials in a way that minimizes environmental impact, supports social equity, and ensures economic viability. It includes practices such as using resources efficiently, reducing carbon footprints, and ensuring fair labor practices. By adopting sustainable sourcing, businesses can contribute to environmental conservation, support local communities, and meet regulatory standards while enhancing their brand reputation.
To ensure sustainable sourcing, agribusinesses should map their entire supply chain to identify and manage risks. This involves engaging with certified suppliers who adhere to sustainability standards, such as organic or fair-trade certifications. Implementing advanced technologies, such as blockchain for traceability and digital monitoring systems for tracking environmental impact, can provide transparency and help businesses verify that their sourcing practices align with sustainability goals.
Adopting sustainable sourcing practices offers multiple benefits, including improved environmental performance, enhanced brand reputation, and increased consumer trust. It helps businesses comply with regulations, such as the EU Deforestation Regulation (EUDR), and can lead to cost savings through more efficient resource use. Additionally, sustainable sourcing fosters better relationships with suppliers and local communities, supports long-term business viability, and contributes to global sustainability efforts.
