Contact: +91 99725 24322 |
Menu
Menu
Quick summary: Explore the journey of tobacco from farm to consumer, uncovering key steps, challenges, and solutions for a more sustainable and ethical tobacco supply chain.
Every puff, pinch, or chew of tobacco connects back to a vast and complex network with far-reaching consequences. While tobacco is one of the world’s most widely consumed commodities, it’s more than just a crop—it’s the backbone of a multi-billion-dollar industry with both beneficial and troubling impacts on global economies, public health, and our planet. What happens before a cigarette land on a shelf, or a cigar is lit at a celebration? The journey of tobacco supply chain starting from seed to consumer is tangled with economic powerhouses, family farms, stringent regulations, and deep-rooted ethical dilemmas.
By exploring the tobacco supply chain in depth, we can tackle pressing challenges, embrace innovative solutions, and ensure every player, from smallholder farmers to multinational corporations, contributes to a more ethical and environmentally responsible industry. The stakes are high, but the potential for meaningful change is real—and long overdue.
Key Takeaways
To understand the true impact and opportunities for change, it’s vital to dissect the key stages of the tobacco supply chain:
Understanding this journey isn’t just about scrutinizing a product. It’s about transparency, accountability, and creating a fairer, healthier, and more sustainable future for all.
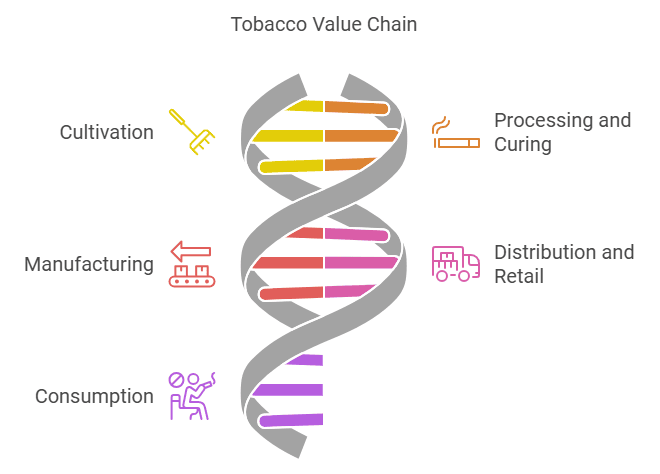
Tobacco cultivation spans across diverse regions and climates, and understanding its journey from seed to harvest sheds light on the crop’s significant role in global trade—and its impact on communities and the environment.
Tobacco thrives in various climates, but it grows best in subtropical and temperate regions with a balance of warmth, sunlight, and rainfall. Countries like China, India, Brazil, and the United States lead in production. Each region’s climate influences the type of tobacco grown and its distinctive characteristics, which ultimately shape the final product. For example, Cuban tobacco is famous for cigars due to the island’s rich soil and humid climate, while Virginia tobacco, grown widely in the U.S., produces lighter, milder flavors.
The tobacco cultivation journey starts with small seeds—among the tiniest in the agricultural world. Farmers typically plant seeds in controlled nurseries and carefully tend to them before transplanting the young seedlings to the field. Growing tobacco requires significant manual labor. Farmers must regularly weed, fertilize, and monitor for pests. After months of careful nurturing, the leaves mature, turning thick and dark green, indicating they’re ready for harvest.
While tobacco farming sustains many livelihoods, it also raises pressing challenges. Environmentally, the crop depletes soil nutrients, often leading to deforestation for new arable land. Additionally, the high use of pesticides can pose risks to ecosystems and human health. Socially, many farmers, particularly in low-income regions, are caught in cycles of poverty, struggling to earn fair wages due to market pressures. Labor exploitation, including child labor, is another concern that has attracted significant international attention.
Sustainable tobacco initiatives aimed at promoting ethical practices, reducing environmental damage, and supporting fair trade are emerging. By understanding the complexities of tobacco cultivation, we can better appreciate the challenges and potential paths toward positive change.
The journey of a tobacco leaf doesn’t end with cultivation—it’s just beginning. The way leaves are harvested, cured, and processed is critical to ensuring their quality and marketability.
Harvesting tobacco is all about timing. Farmers must wait until the leaves reach their peak maturity—when they’re full, thick, and show specific color changes. There are two main ways to harvest tobacco: hand-picking and mechanical harvesting.
Freshly harvested tobacco leaves are full of moisture, making them unsuitable for use right away. Enter the curing process, where leaves are dried to develop their flavor, aroma, and texture.
Once cured, the leaves move into the processing phase, which involves sorting, grading, and preparing them for various products. Labor plays a huge role here. Workers inspect and sort leaves by quality, color, and size. This manual inspection ensures that only the best leaves are used for premium products.
Quality control is essential, as any imperfections or inconsistencies can affect the entire batch. Tobacco processors follow strict protocols to maintain high standards, and often, experienced workers handle these tasks to ensure consistency and quality.
The journey of a tobacco leaf doesn’t stop after it’s cured and sorted. The next stage transforms these leaves into various tobacco products that consumers use worldwide, including cigarettes, cigars, and smokeless products like chewing tobacco. This process is intricate, heavily regulated, and increasingly driven by technology.
Every product undergoes rigorous testing to ensure consistency in taste, safety, and compliance with regulations.
Tobacco manufacturing is one of the most heavily regulated industries worldwide, and for good reason. Governments enforce stringent rules to protect consumer health and safety:
Compliance is complex, with frequent updates and varying rules from one country to another. For manufacturers, staying informed is critical to avoid penalties and maintain consumer trust.
Modern tobacco production relies heavily on technology to increase efficiency and maintain consistent product quality:
In the world of distribution and logistics, it’s all about moving products efficiently from one point to another. Whether it’s a domestic shipment or international trade, effective supply chain management plays a key role in making sure that goods get where they need to be, on time and in good condition.
In today’s world, customers and regulators want to know where products come from and how they were made. This has led to increased efforts in traceability and ethical sourcing, especially in industries like tobacco.
1. Traceability: Using blockchain technologies , companies can track every step of the product’s journey, from the farm where tobacco is grown to the final retailer. This ensures that businesses can prove where their products come from and that they’re complying with regulations, especially concerning issues like illegal tobacco trade or the exploitation of workers.
2. Ethical Sourcing: Many tobacco companies are now focusing on sourcing tobacco in a way that supports fair labor practices and environmental sustainability. This includes working with farmers who follow ethical farming methods and ensuring workers are treated fairly. Ethical sourcing practices are becoming more important to consumers who want to make responsible choices.
The tobacco supply chain is complex, and it faces several key challenges that impact both businesses and society as a whole. From environmental concerns to labor practices, and compliance with global regulations, these issues require careful attention.
TraceX has partnered with VST (a leading tobacco company) to track the journey of its tobacco from farm to factory, ensuring sustainable procurement and efficient farmer management. By leveraging TraceX’s platform, VST gains full transparency into every stage of the supply chain, from the farming process to processing and distribution.
The platform enhances sustainability by monitoring farming practices, ensuring that they adhere to ethical and environmental standards. It also improves efficiency by providing real-time data on farm activities, which helps optimize resource use and reduce waste.
For VST, the TraceX solution ensures responsible sourcing, strengthens compliance with regulatory standards, and builds trust with stakeholders by offering clear visibility of the entire tobacco supply chain. This integration of technology allows VST to enhance farmer engagement, manage procurement efficiently, and contribute to more sustainable practices in the tobacco industry.
The tobacco supply chain, like many industries, is undergoing significant change thanks to technological advancements. Technologies like blockchain, artificial intelligence (AI), and various digital tools are transforming how tobacco is produced, tracked, and sold. These innovations are helping to improve traceability, ensure sustainability, and enhance compliance with regulations.
One of the biggest challenges in the tobacco supply chain is knowing exactly where the product comes from and how it moves through the system. Blockchain technology has become a game-changer in this area. Blockchain is a digital ledger that records transactions in a secure, transparent way. By using blockchain, tobacco companies can trace every step of a product’s journey — from the farm where the tobacco is grown to the final sale in stores. This not only helps ensure that products are genuine but also ensures that companies are adhering to regulatory standards and preventing illegal activities, like counterfeit tobacco or tax evasion.
Digital tools, like mobile apps and cloud-based systems, are also playing a big role in modernizing the supply chain. These tools allow for real-time monitoring and tracking of shipments, reducing delays and helping businesses stay on top of the movement of goods. They can also be used for compliance management, ensuring that all the necessary paperwork is completed and regulations are met. Digital platforms also allow companies to track and report on sustainability initiatives, which is important for meeting the growing demand for transparency from consumers and regulators.
Technology helps combat the illegal tobacco trade, which is a major issue in many parts of the world. Blockchain provides a secure way to verify the authenticity of tobacco products, preventing counterfeit goods from entering the market. Digital tracking also helps authorities identify and stop the smuggling of illegal tobacco.
TraceX is a technology platform designed to streamline traceability and farm management processes in agricultural supply chains. By leveraging advanced technologies like blockchain and real-time data tracking, TraceX provides businesses with the tools they need to ensure transparent, efficient, and sustainable operations. Specifically, it helps address the challenges faced by companies in ensuring traceability, ethical sourcing, and sustainable procurement in industries like tobacco, agriculture, and beyond.
The tobacco supply chain is complex, spanning from cultivation to consumer. Each step, from farming to processing, transportation, and retail, carries significant environmental, ethical, and regulatory challenges. Addressing these challenges requires a commitment to sustainable practices, transparency, and compliance with global standards. With technologies like blockchain and data-driven solutions, businesses can enhance traceability, ensure responsible sourcing, and engage with stakeholders more effectively. As the demand for sustainability grows, the tobacco industry must evolve to meet these expectations, balancing profitability with ethical responsibility.
Technology, such as blockchain and AI, can provide end-to-end visibility in the tobacco supply chain, ensuring that each step—from cultivation to processing—can be traced for ethical sourcing, compliance, and sustainability.
Tobacco farming can lead to deforestation, excessive pesticide use, and soil degradation. Sustainable farming practices and traceability systems are essential to minimizing these environmental impacts and ensuring responsible sourcing.
Sustainable procurement helps tobacco companies ensure that they are sourcing tobacco responsibly, avoiding practices like child labor, and meeting environmental standards. It fosters consumer trust and aligns with global sustainability goals, leading to long-term industry growth.
