Contact: +91 99725 24322 |
Menu
Menu
Quick summary: Farmers need to have access to high quality seeds to enhance crop production and parameters like seed purity, germination percentage and moisture content are critical. The inadequate information in seed production and processing, the malicious mixing of quality seeds with spurious ones and the manual-based record keeping has triggered the need for digital traceability solutions in the seed sector
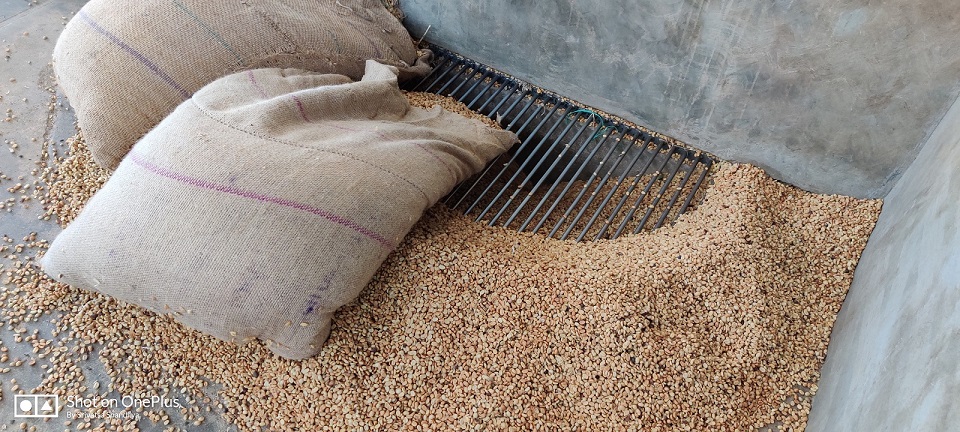

Seed is the fundamental and critical input for agriculture and the seed sector has grown parallelly with the agriculture sector. Availability of quality seeds is highly essential for a productive harvest in agriculture. This has been enabled with the advance in technology and modern agriculture techniques.
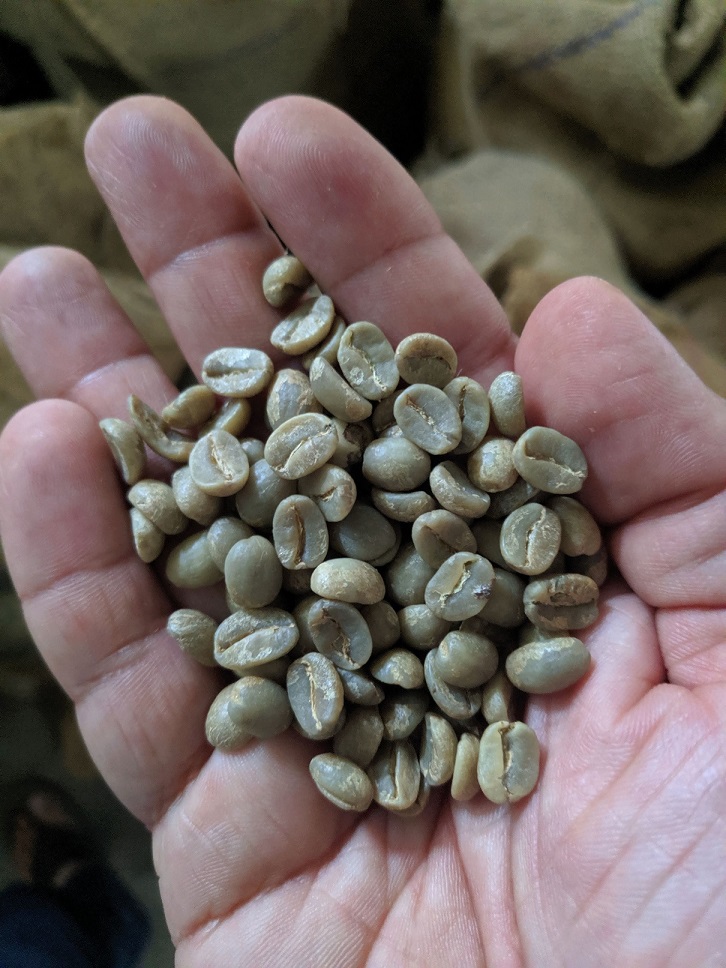

1The global seed market is estimated to account for a value of USD 63 billion in 2021, growing at a CAGR of 6.6% during the period 2021-26 to grow to a value of USD86.8 billion. The demand for food, animal feed, biofuels has triggered the growth of the seed market. The Indian seed industry is the fifth largest seed market in the world, accounting for 4.4% of seed production globally. India is self-sufficient in fruits, vegetables and field crop seeds and is seeing a potential growth in paddy and maize. The active participation of both the public and private sectors has played a crucial role in laying a foundation for this seed industry.
The increasing need for food to feed the growing population, the requirement from the farmers to produce quality and productive yields with profitability and the sustainable agriculture practices are driving the global seed market. There has also been an increase in R&D activity for innovating new products especially in GM crops and responding to climatic and biofuel challenges, while protecting genetic diversity. The globalization of the seed industry and the strengthening of IPR has brought positive changes in the seed R&D sector.
Advancement in technology has increased agriculture productivity but the challenges due to climate changes, pests and diseases and the supply chain disruptions continue to unsettle this sector.
Seed industry plays an important role in providing quality seeds to farmers to increase productivity and conserve the environment. In order to ensure food and nutritional security and environmental resiliency and support the farmer fraternity, it is necessary that there are innovations and research done on seeds. Seed companies work with farmers, distributors, retailers and consumers to deliver a range of seeds as a solution to meet sustainability goals.
Seed industries help to
Normally the Government sets certain protocols for seed development. The certified foundations cultivates varieties of seeds under a controlled environment before sending it to the aggregators.
Certification validates the high quality and propagation varieties of the seed to the public. It fetches a higher premium and facilitates crop insurance. A certified seed validates the provenance, and it helps the farmers to capitalize on traceability.
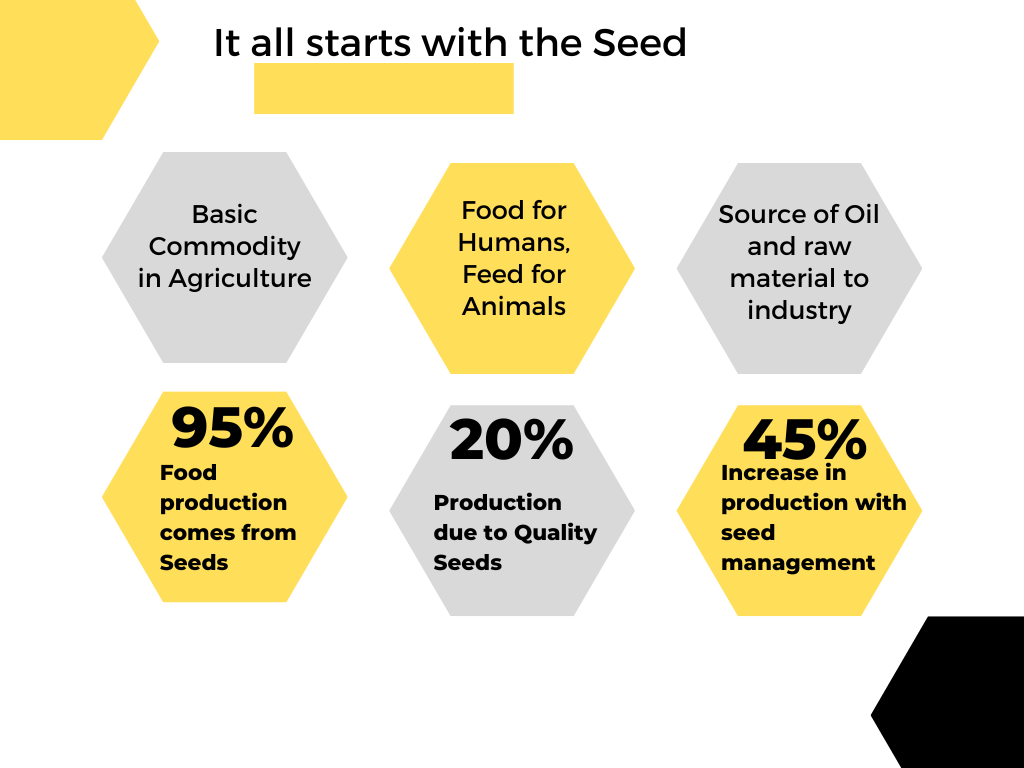
Farmers need to have access to high quality seeds to enhance crop production and parameters like seed purity, germination percentage and moisture content are critical. The inadequate information in seed production and processing, the malicious mixing of quality seeds with spurious ones and the manual-based record keeping has triggered the need for digital traceability solutions in the seed sector. The origin of seed, breeding and selection data, phytosanitary treatments during processing, the handling procedures and tracking shipping and logistics can be captured and shared among the various stakeholders in the seed supply chain. The transparency in operational activities like seed treatment, sorting and grading and packaging ensures a safe and an authentic seed.
The seed industry is disorganized with a dark ecosystem running in parallel. Traders sell GMO or low quality non-certified seeds to farmers who end up with crop losses. Lot of scams have surfaced with farmer complaints on non- germination of seeds leading to heavy losses and pressure on the food sector. Digital interventions help in achieving a streamlined flow across the seed value chain leveraging on collection and sharing of data among the stakeholders. This will strengthen seed exports by conforming to seed quality and enhanced productivity. The end to end transparency will ensure a clean system, eliminating frauds, malpractices and adulteration.
Blockchain powered traceability solutions guarantee an authentic product thereby building trust into the food ecosystem. The digital ledgers capture real-time data thereby assuring a single source of truth and exchange of information on the decentralized platform helps to build trust and transparency in the seed supply chain. The QR codes recreate the product journey from the seed to shelf assuring customers of a trustworthy and a safe brand.
TraceX has provided Blockchain traceability solutions to the Telangana Government to counter the rampant, spurious and counterfeit seed market. The pilot project with PJTSAU in Telangana triggered an opportunity for TraceX to implement seed traceability in the state of Telangana. The Farm management solutions help in realizing a digitized supply chain assuring enhanced productivity and profitability and reduction in time to reach export compliance. The tracking of package of practice deviations assures high quality compliance and food security. Check how TraceX helps farmers manage their farms with the digital traceability solutions.
Post-harvest management features also help to build a robust seed supply chain. Tracking the various processes of sorting, grading, packaging and labelling ensures tamper-proof products. Inventory management helps to build visibility in the system with reduction of wastage and losses. Batch management helps to handle SKUs and aid in situations of recalls. The QR digital identity to the seed packets assure an authentic and a safe product.
Organizations need to align to their business models to realize smallholder farmer success with the adoption of good practices. The transparency, visibility and accountability in the seed supply chains should increase the farmer productivity and ensure him a fair livelihood. With seed being the starting point in the food value chain, industries need to focus on providing food and nutritional security to meet the needs of the global population. Focusing on optimal usage of inputs with sustainable practices, prioritizing R&D efforts, increasing collaboration and embracing blockchain technologies should see a way forward to stay ahead of competition and the demand.
