Contact: +91 99725 24322 |
Menu
Menu
Quick summary: Explore the intricacies of the Plastic Value Chain in our latest blog. Uncover the journey from raw material extraction to manufacturing, consumption, and waste management. Delve into the environmental impact, sustainability challenges, and innovative solutions within this complex network. Join us as we unravel the complexities and discover opportunities for positive change in the plastic industry.

In the intricate web of modern industry, understanding the plastic value chain is paramount. From raw material extraction to manufacturing, distribution, consumption, and eventual waste management, each link plays a crucial role. Understanding the plastic value chain is crucial for informed decision-making, as it enables stakeholders to identify environmental impacts, optimize resource use, and implement sustainable practices. It aids in developing circular economy strategies, mitigating pollution, and fostering innovation for a more environmentally responsible plastic industry.
Starting as a groundbreaking material known for its affordability, lightweight nature, versatility, and effective preservation capabilities, plastic production has now surged to an astonishing 8.3 billion metric tons since the 1950s.
This blog explores the nuances of the plastic value chain, shedding light on the environmental impact, sustainability challenges, and innovative solutions within this intricate network. Join us on a journey to unravel the complexities and discover opportunities for positive change in the plastic industry.
In this initial phase, the industry identifies and assesses potential sources of raw materials, primarily fossil fuels like crude oil and natural gas. Companies explore regions with rich petroleum reservoirs, conducting geological surveys to determine extraction feasibility. Sourcing strategies aim to secure a stable supply chain for the petrochemicals essential for plastic production.
Following sourcing, the extraction process begins. Petrochemicals, such as ethylene and propylene, are derived through refining crude oil or cracking natural gas. These building blocks are pivotal for subsequent plastic production stages.
The extracted petrochemicals undergo polymerization, a chemical process where monomers link to form polymer chains. Catalysts facilitate this transformation, resulting in the creation of plastic resin, the raw material for various plastic products. Polymerization methods vary, including techniques like injection molding and extrusion.
Once polymerization is complete, manufacturers employ diverse processes to shape plastic into final products. Injection molding forms intricate shapes, while extrusion creates continuous profiles. Thermoforming molds heated plastic into desired forms, and rotational molding produces hollow items. Understanding these processes is integral to optimizing efficiency and minimizing waste in the plastic value chain.
Plastic products move through extensive distribution networks. Transportation methods include shipping, trucking, and rail. Efficient logistics play a crucial role in minimizing environmental impact and costs. Sustainable practices, such as optimizing routes and utilizing eco-friendly transportation options, are increasingly prioritized.
Storage facilities and warehouses serve as key nodes in the distribution network, ensuring timely delivery to manufacturers and retailers. Proper inventory management reduces the risk of overproduction and waste. Implementing sustainable warehousing practices, like energy-efficient facilities and waste reduction measures, contributes to the overall environmental responsibility of the plastic value chain.
Packaging represents a significant segment of the plastic value chain, providing containment, protection, and marketing for various products. From food packaging to industrial materials, plastics offer versatility, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Balancing functionality with sustainability is crucial in this sector, driving innovations like eco-friendly materials and minimalist designs to reduce environmental impact
In the realm of consumer goods, plastics play a pivotal role in the manufacturing of a diverse range of products, including electronics, appliances, and everyday items. The durability, lightweight nature, and design flexibility of plastics contribute to the creation of efficient and aesthetically pleasing consumer goods. Sustainable practices in this sector involve responsible material
selection, recycling initiatives, and product lifecycle considerations.
Plastic materials are increasingly utilized in construction and infrastructure projects. From pipes and insulation to architectural elements, plastics offer durability, insulation, and cost-effectiveness. Integrating recycled plastics into construction practices contributes to sustainability, addressing environmental concerns and fostering innovation in the construction industry.
The first step in recycling involves gathering used plastics through various collection methods, including curbside pickups, recycling bins, and specialized collection centers. Efficient collection systems are vital for maximizing the amount of plastic diverted from landfills.
Collected plastics undergo sorting based on material type and color. Advanced technologies, such as automated sorting systems and optical scanners, enhance precision. After sorting, the plastics are processed through methods like shredding or melting to create raw materials for the production of new plastic products. Effective sorting and processing contribute to the economic viability of recycling initiatives.
Traditional waste management involves disposing of non-recyclable plastics in landfills. While landfills are still widely used, there is a growing awareness of their environmental impact. Modern landfill practices incorporate liners and containment measures to mitigate soil and water contamination. However, reducing reliance on landfills remains a key sustainability goal.
Incineration involves burning plastic waste to generate energy. While it can reduce the volume of waste and produce energy, concerns about air pollution and the release of harmful emissions persist. Advanced incineration technologies with pollution control measures aim to minimize environmental impact. However, the emphasis is increasingly shifting toward recycling and waste reduction to address long-term sustainability challenges.
Approximately 60% of produced plastics have found their way into landfills or the natural environment. If current trends persist, there is a looming possibility that, by 2050, the ocean could contain more plastic than fish, measured by weight.
The improper disposal of plastic waste contributes significantly to pollution. Plastic takes hundreds of years to decompose, leading to persistent environmental issues. Plastic pollution adversely affects ecosystems, contaminating oceans, soil, and water sources. Microplastics, resulting from the breakdown of larger plastic items, pose threats to marine life and enter the food chain, impacting human health.
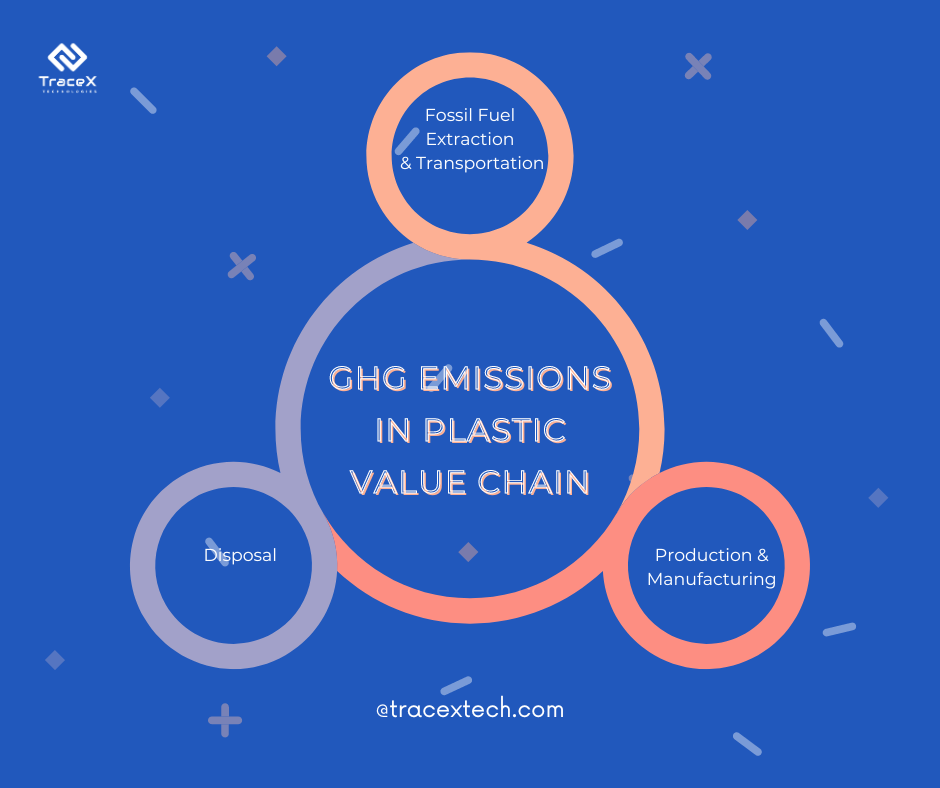
The plastic value chain, from extraction to production and disposal, contributes to carbon emissions. Petrochemical extraction, manufacturing processes, and transportation in the plastic industry all generate greenhouse gases. Addressing the carbon footprint of plastics involves adopting sustainable practices, reducing reliance on fossil fuels, and promoting circular economy approaches.
Plastics disrupt ecosystems, endangering wildlife and biodiversity. Marine environments suffer as animals mistake plastic for food or get entangled in debris. On land, plastic waste disrupts habitats and can lead to soil degradation. The cumulative impact on ecosystems highlights the urgent need for responsible plastic management, recycling, and the development of eco-friendly alternatives to mitigate environmental harm.
Greenwashing involves the deceptive practice of presenting misleading or unsupported assertions regarding the environmental advantages of a product, service, or organization. Some businesses adopt this tactic to give the false impression of being more environmentally friendly than they actually are, potentially confusing consumers striving to make eco-conscious choices. This hinders genuine sustainability efforts, discouraging authentic green initiatives and impeding progress toward truly sustainable practices.
Blockchain technology emerges as a groundbreaking solution to tackle greenwashing. Renowned for its transparency, immutability, and decentralized nature, blockchain ensures a verifiable and auditable record of every transaction within the recycling process. Each step, from plastic waste collection to recycling and reprocessing, is securely documented on the blockchain. This establishes an unchangeable history, eliminating the possibility for companies to make inaccurate claims about their recycling practices.
Shifting towards a circular economy stands as a fundamental pillar in combating the climate crisis. With the rising integration of plastics into daily products, the efficient reuse and recycling of these materials has become more crucial than ever. Additionally, the production of plastic, derived from fossil fuels, exerts unparalleled impacts on the planet, exacerbating the challenges posed by climate change.
Seeking sustainable alternatives involves exploring materials that are environmentally friendly and biodegradable. Innovations in materials like plant-based plastics, mushroom-based packaging, and other renewable resources offer eco-conscious choices, reducing reliance on traditional plastics and minimizing environmental impact.
Embracing a circular economy involves designing products with a focus on reuse, recycling, and minimizing waste. Closed-loop systems aim to keep materials in use for as long as possible. This approach encourages responsible consumption, efficient recycling practices, and the creation of durable products, ultimately reducing the demand for new raw materials and lessening the environmental footprint of the plastic value chain.
Technological advancements play a pivotal role in addressing plastic-related challenges. Innovations include advanced recycling technologies that improve the efficiency of plastic recycling processes, the development of bio-based plastics, and the use of artificial intelligence for waste management optimization. Investing in and adopting these technologies contribute to more sustainable practices in the plastic industry, fostering environmental responsibility and resource efficiency.
Proactive industry initiatives involve businesses adopting sustainable practices, investing in research and development for eco-friendly alternatives, and participating in circular economy models. Collaboration within the industry is crucial to drive collective efforts towards reducing the environmental impact of plastic production and consumption.
Do you know what a Plastic Net Zero Product is?
A Plastic Net Zero product is designed to eliminate any plastic it releases into the environment. This means the product does not contribute to the existing plastic pollution; it essentially creates a net addition of zero.
Governments play a pivotal role in shaping sustainable practices through regulations. Implementing policies that restrict single-use plastics, promote recycling, and encourage the use of environmentally friendly materials drive positive change. Well-crafted regulations create a framework for responsible industry behavior, aligning economic activities with environmental preservation goals.
Informed consumer choices contribute to sustainable practices. Raising awareness about the environmental impact of plastic consumption empowers individuals to make eco-conscious decisions. Educated consumers drive market demand for sustainable products, influencing businesses to adopt greener practices and fostering a collective commitment to reducing plastic-related environmental harm.
In conclusion, addressing the challenges posed by the plastic value chain requires a multifaceted approach. From industry initiatives promoting sustainable practices and technological innovations driving eco-friendly alternatives to government regulations shaping responsible policies, collaborative efforts are essential. Concurrently, cultivating consumer awareness empowers individuals to make informed choices, influencing market demands towards more sustainable solutions. To achieve a meaningful reduction in the environmental impact of plastic production and waste, a concerted effort is necessary across all stakeholders. Embracing circular economy approaches, investing in recycling infrastructure, and exploring sustainable alternatives collectively form a promising pathway towards a more responsible and environmentally conscious future in the realm of plastics.
